No CrossRef data available.
Article contents
Migration of confined micro-swimmers subject to anisotropic diffusion
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 29 April 2024
Abstract
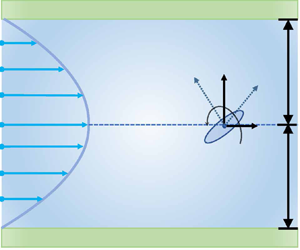
Shear-induced migration of elongated micro-swimmers exhibiting anisotropic Brownian diffusion at a population scale is investigated analytically in this work. We analyse the steady motion of confined ellipsoidal micro-swimmers subject to coupled diffusion in a general setting within a continuum homogenisation framework, as an extension of existing studies on macro-transport processes, by allowing for the direct coupling of convection and diffusion in local and global spaces. The analytical solutions are validated successfully by comparison with numerical results from Monte Carlo simulations. Subsequently, we demonstrate from the probability perspective that symmetric actuation does not yield net vertical polarisation in a horizontal flow, unless non-spherical shapes, external fields or direct coupling effects are harnessed to generate steady locomotion. Coupled diffusivities modify remarkably the drift velocity and vertical migration of motile micro-swimmers exposed to fluid shear. The interplay between stochastic swimming and preferential alignment could explain the diverse concentration and orientation distributions, including rheological formations of depletion layers, centreline focusing and surface accumulation. Results of the analytical study shed light on unravelling peculiar self-propulsion strategies and dispersion dynamics in active-matter systems, with implications for various transport problems arising from the fluctuating shape, size and other external or inter-particle interactions of swimmers in confined environments.
JFM classification
- Type
- JFM Papers
- Information
- Copyright
- © The Author(s), 2024. Published by Cambridge University Press





