Article contents
On the effect of adverse pressure gradients on wall-pressure statistics in a controlled-diffusion aerofoil turbulent boundary layer
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 31 March 2023
Abstract
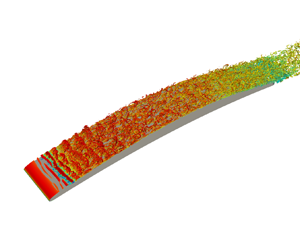
Wall-pressure and velocity statistics in the turbulent boundary layer (TBL) on a cambered controlled-diffusion aerofoil at  $8^{\circ }$ incidence, a Mach number of 0.25 and a chord-based Reynolds number
$8^{\circ }$ incidence, a Mach number of 0.25 and a chord-based Reynolds number  ${Re}_c=1.5\times 10^{5}$ are analysed at four locations on the suction side with zero and adverse pressure gradients (ZPG and APG), characterised by increasing Reynolds numbers based on momentum thickness,
${Re}_c=1.5\times 10^{5}$ are analysed at four locations on the suction side with zero and adverse pressure gradients (ZPG and APG), characterised by increasing Reynolds numbers based on momentum thickness,  ${Re}_{\theta }=319$, 390, 877 and
${Re}_{\theta }=319$, 390, 877 and  $1036$. The strong APG yields a highly non-equilibrium TBL at the trailing edge that significantly affects the turbulent flow statistics. Different normalisations of the full wall-pressure statistics involved in trailing-edge noise are analysed for the first time in such strong APG with convex curvature, and compared with available experimental and numerical data. Good overall agreement is found in the ZPG region, and most results obtained in previous APG TBL can be extended to the present highly non-equilibrium case. The presence of strong APG augments the intensity of wall-pressure fluctuations noticeably at low frequencies, shortens the streamwise and broadens the spanwise coherence of wall-pressure fluctuations in both time and space, and significantly reduces the convection velocity. The wall-pressure power spectral density are found to scale with the displacement thickness, the Zaragola–Smits velocity and the root-mean-squared pressure, the latter possibly being replaced by the local maximum Reynolds shear stress. The other two key parameters to trailing-edge noise modelling, the spanwise coherence length and the convection velocity, rather scale with displacement thickness and friction velocity, respectively.
$1036$. The strong APG yields a highly non-equilibrium TBL at the trailing edge that significantly affects the turbulent flow statistics. Different normalisations of the full wall-pressure statistics involved in trailing-edge noise are analysed for the first time in such strong APG with convex curvature, and compared with available experimental and numerical data. Good overall agreement is found in the ZPG region, and most results obtained in previous APG TBL can be extended to the present highly non-equilibrium case. The presence of strong APG augments the intensity of wall-pressure fluctuations noticeably at low frequencies, shortens the streamwise and broadens the spanwise coherence of wall-pressure fluctuations in both time and space, and significantly reduces the convection velocity. The wall-pressure power spectral density are found to scale with the displacement thickness, the Zaragola–Smits velocity and the root-mean-squared pressure, the latter possibly being replaced by the local maximum Reynolds shear stress. The other two key parameters to trailing-edge noise modelling, the spanwise coherence length and the convection velocity, rather scale with displacement thickness and friction velocity, respectively.
JFM classification
- Type
- JFM Papers
- Information
- Copyright
- © The Author(s), 2023. Published by Cambridge University Press
References
- 6
- Cited by





