Article contents
Effect of temperature on the growth of a-axis ZnO films: a reactive force field-based molecular dynamics study
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 05 January 2017
Abstract
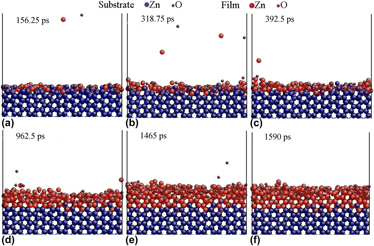
Understanding film initiation and growth mechanisms at the atomic level is crucial to obtain high-quality nonpolar ZnO films. Using the advanced reactive force field-based molecular dynamics method, we theoretically studied the effect of substrate temperature (350–950 K) on the quality, layer develop mechanism and defect formation of ZnO films. Investigation of the energy, radial distribution function, layer coverage, sputtering and injecting phenomena indicated that the present films grown at 500–600 K possessed the optimal quality. Further investigation of the growth condition, instant film profiles, interfacial microstructure evolutions and layered snapshots revealed that, addition of atoms on newly formed localized films can induce some partially bonded or extruded atoms out of the film plane. Further adherence of depositing atoms to these unstable or extruded atoms induces the initiation and growth of a new layer.
- Type
- Articles
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 2017
Footnotes
References
REFERENCES
- 1
- Cited by





