Article contents
Flexible solution-processed high-voltage organic thin film transistor
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 23 November 2017
Abstract
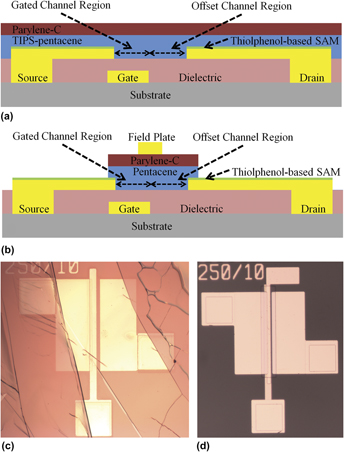
6,13-Bis(triisopropylsilylethynyl)pentacene (TIPS-pentacene) and pentacene-based high-voltage organic thin film transistors (HVOTFTs) have been fabricated on solid and flexible substrates via a low-temperature (<100 °C) solution-processed and vacuum-deposited fabrication method. A high-k dielectric Bi1.5Zn1Nb1.5O7 and an organic dielectric parylene-C have been incorporated into the transistor design. The reliability of the HVOTFTs was analyzed under flexure, where a nonsaturating I–V characteristic behavior was observed. Here, the HVOTFT exhibited a mobility μ of 0.018 cm2/(V s) and a large breakdown voltage of |VDS| > 120 V and >550 V for TIPS-pentacene and pentacene devices, respectively. The large breakdown voltages are attributed to an organic semiconductor channel region which is partially gated, allowing for a large potential drop. Thiolphenol-based SAMs were used to help improve charge injection. Electrical measurements were also performed with samples designed with a top metal field plate to improve control of the charge carrier within the channel.
Keywords
- Type
- Invited Paper
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 2017
Footnotes
Contributing Editor: Sam Zhang
References
REFERENCES
- 6
- Cited by





