Article contents
Ion angular distribution simulation of the Highly Efficient Multistage Plasma Thruster
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 22 February 2017
Abstract
Ion angular current and energy distributions are important parameters for ion thrusters, which are typically measured at a few tens of centimetres to a few metres distance from the thruster exit. However, fully kinetic particle-in-cell (PIC) simulations are not able to simulate such domain sizes due to high computational costs. Therefore, a parallelisation strategy of the code is presented to reduce computational time. The calculated ion beam angular distributions in the plume region are quite sensitive to boundary conditions of the potential, possible additional source contributions (e.g. from secondary electron emission at vessel walls) and charge exchange collisions. Within this work a model for secondary electrons emitted from the vessel wall is included. In order to account for limits of the model due to its limited domain size, a correction of the simulated angular ion energy distribution by the potential boundary is presented to represent the conditions at the location of the experimental measurement in 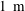 $1~\text{m}$ distance. In addition, a post-processing procedure is suggested to include charge exchange collisions in the plume region not covered by the original PIC simulation domain for the simulation of ion angular distributions measured at
$1~\text{m}$ distance. In addition, a post-processing procedure is suggested to include charge exchange collisions in the plume region not covered by the original PIC simulation domain for the simulation of ion angular distributions measured at 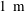 $1~\text{m}$ distance.
$1~\text{m}$ distance.
Keywords
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- © Cambridge University Press 2017
References
- 7
- Cited by




