Article contents
On The Asymptotic Values of Length Functions In Krull And Finitely Generated commutative Monoids
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 09 April 2009
Abstract
Let M be a commutative cancellative atomic monoid. We consider the behaviour of the asymptotic length functions 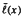 and
and 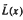 on M. If M is finitely generated and reduced, then we present an algorithm for the computation of both
on M. If M is finitely generated and reduced, then we present an algorithm for the computation of both 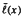 and
and 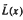 where x is a nonidentity element of M. We also explore the values that the functions
where x is a nonidentity element of M. We also explore the values that the functions 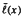 and
and 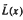 can attain when M is a Krull monoid with torsion divisor class group, and extend a well-known result of Zaks and Skula by showing how these values can be used to characterize when M is half-factorial.
can attain when M is a Krull monoid with torsion divisor class group, and extend a well-known result of Zaks and Skula by showing how these values can be used to characterize when M is half-factorial.
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Australian Mathematical Society 2003
References
- 2
- Cited by




