Article contents
PROPRIÉTÉS LOCALES DES CHIFFRES DES NOMBRES PREMIERS
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 04 April 2017
Abstract
Let 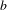 $b$ be an integer larger than 1. We give an asymptotic formula for the exponential sum
$b$ be an integer larger than 1. We give an asymptotic formula for the exponential sum 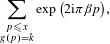 $$\begin{eqnarray}\mathop{\sum }_{\substack{ p\leqslant x \\ g(p)=k}}\exp \big(2\text{i}\unicode[STIX]{x1D70B}\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FD}p\big),\end{eqnarray}$$
$$\begin{eqnarray}\mathop{\sum }_{\substack{ p\leqslant x \\ g(p)=k}}\exp \big(2\text{i}\unicode[STIX]{x1D70B}\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FD}p\big),\end{eqnarray}$$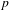 $p$ and where
$p$ and where 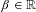 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FD}\in \mathbb{R}$,
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FD}\in \mathbb{R}$, 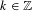 $k\in \mathbb{Z}$, and
$k\in \mathbb{Z}$, and 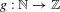 $g:\mathbb{N}\rightarrow \mathbb{Z}$ is a strongly
$g:\mathbb{N}\rightarrow \mathbb{Z}$ is a strongly 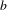 $b$-additive function such that
$b$-additive function such that 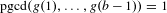 $\operatorname{pgcd}(g(1),\ldots ,g(b-1))=1$.
$\operatorname{pgcd}(g(1),\ldots ,g(b-1))=1$.
Soit 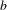 $b$ un nombre entier supérieur ou égal à 2. Nous donnons une formule asymptotique pour la somme d’exponentielles
$b$ un nombre entier supérieur ou égal à 2. Nous donnons une formule asymptotique pour la somme d’exponentielles 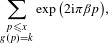 $$\begin{eqnarray}\mathop{\sum }_{\substack{ p\leqslant x \\ g(p)=k}}\exp \big(2\text{i}\unicode[STIX]{x1D70B}\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FD}p\big),\end{eqnarray}$$
$$\begin{eqnarray}\mathop{\sum }_{\substack{ p\leqslant x \\ g(p)=k}}\exp \big(2\text{i}\unicode[STIX]{x1D70B}\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FD}p\big),\end{eqnarray}$$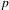 $p$, et où
$p$, et où 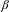 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FD}$ est un nombre réel,
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FD}$ est un nombre réel, 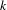 $k$ un nombre entier et
$k$ un nombre entier et 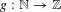 $g:\mathbb{N}\rightarrow \mathbb{Z}$ une fonction fortement
$g:\mathbb{N}\rightarrow \mathbb{Z}$ une fonction fortement 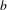 $b$-additive telle que
$b$-additive telle que 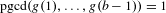 $\operatorname{pgcd}(g(1),\ldots ,g(b-1))=1$.
$\operatorname{pgcd}(g(1),\ldots ,g(b-1))=1$.
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Journal of the Institute of Mathematics of Jussieu , Volume 18 , Issue 1 , January 2019 , pp. 189 - 224
- Copyright
- © Cambridge University Press 2017
Footnotes
Ce travail a bénéficié des aides de l’Agence nationale de la recherche portant les références « ANR-14-CE34-0009 » MUDERA, de Ciência sem Fronteiras, projet PVE 407308/2013-0, et du projet d’échange DynEurBraz (FP7 Irses 230844).
References
Références
- 4
- Cited by




