Article contents
THE  $q$-SCHUR ALGEBRAS AND
$q$-SCHUR ALGEBRAS AND  $q$-SCHUR DUALITIES OF FINITE TYPE
$q$-SCHUR DUALITIES OF FINITE TYPE
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 19 February 2020
Abstract
We formulate a  $q$-Schur algebra associated with an arbitrary
$q$-Schur algebra associated with an arbitrary 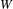 $W$-invariant finite set
$W$-invariant finite set 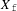 $X_{\text{f}}$ of integral weights for a complex simple Lie algebra with Weyl group
$X_{\text{f}}$ of integral weights for a complex simple Lie algebra with Weyl group 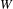 $W$. We establish a
$W$. We establish a  $q$-Schur duality between the
$q$-Schur duality between the  $q$-Schur algebra and Hecke algebra associated with
$q$-Schur algebra and Hecke algebra associated with 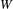 $W$. We then realize geometrically the
$W$. We then realize geometrically the  $q$-Schur algebra and duality and construct a canonical basis for the
$q$-Schur algebra and duality and construct a canonical basis for the  $q$-Schur algebra with positivity. With suitable choices of
$q$-Schur algebra with positivity. With suitable choices of 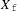 $X_{\text{f}}$ in classical types, we recover the
$X_{\text{f}}$ in classical types, we recover the  $q$-Schur algebras in the literature. Our
$q$-Schur algebras in the literature. Our  $q$-Schur algebras are closely related to the category
$q$-Schur algebras are closely related to the category 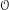 ${\mathcal{O}}$, where the type
${\mathcal{O}}$, where the type 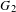 $G_{2}$ is studied in detail.
$G_{2}$ is studied in detail.
MSC classification
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Journal of the Institute of Mathematics of Jussieu , Volume 21 , Issue 1 , January 2022 , pp. 129 - 160
- Copyright
- © The Author(s) 2020. Published by Cambridge University Press
References
- 6
- Cited by




