Article contents
Triclinic titanite from the Heftetjern granitic pegmatite, Tørdal, southern Norway
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 05 July 2018
Abstract
Two crystals from a sample of titanite from the Heftetjern granitic pegmatite, Tørdal, southern Norway, were extracted for structure analysis and shown to have triclinic symmetry. Unit-cell parameters are as follows: a = 7.0696(4) Å, b = 8.7167(5) Å, c = 6.5695(3) Å, α = 89.7372(11)°, β = 113.7607(10)°, γ = 90.2929(13)°, V = 370.52(6) Å3 for one crystal and a = 7.0612(5) Å, b = 8.7102(6) Å, c = 6.5628(4) Å, α = 89.7804(16)°, β = 113.7713(13)°, γ = 90.2502(16)°, V = 369.39(7) Å3 for the other. The interaxial angles α and γ deviate from the value of 90° required for monoclinic symmetry by ~200–250 standard deviations. The single-crystal X-ray intensities were averaged in both monoclinic and triclinic Laue symmetries, giving R(merge) values of ~14% and ~1.3% respectively. For both crystals, more than 50 reflections with I > 3σI violated the criterion for the presence of the a-glide required for monoclinic A2/a symmetry. Both crystals were refined in the space group A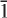 with Z = 4, and final R1 indices are 4.4% and 4.7% (wR2 = 8.4 and 8.9%) respectively. The composition of one crystal was determined by electron microprobe analysis: Ca[Ti0.623Ta0.105Nb0.018Al0.137Fe0.0463+Sn0.0834+]Σ=1.012(SiO4)O. The characteristic corner-sharing [MO5] chains of identical octahedra observed in monoclinic titanite become chains of alternating M(1) and M(2) octahedra of different size, with the stronger X-ray scattering constituents concentrated at the M(2) site. Short-range bond-valence considerations suggest that the M cations will order as Al—O—Ta in adjacent octahedra, and when present in sufficient amounts, will couple along the chain to break long-range monoclinic symmetry.
with Z = 4, and final R1 indices are 4.4% and 4.7% (wR2 = 8.4 and 8.9%) respectively. The composition of one crystal was determined by electron microprobe analysis: Ca[Ti0.623Ta0.105Nb0.018Al0.137Fe0.0463+Sn0.0834+]Σ=1.012(SiO4)O. The characteristic corner-sharing [MO5] chains of identical octahedra observed in monoclinic titanite become chains of alternating M(1) and M(2) octahedra of different size, with the stronger X-ray scattering constituents concentrated at the M(2) site. Short-range bond-valence considerations suggest that the M cations will order as Al—O—Ta in adjacent octahedra, and when present in sufficient amounts, will couple along the chain to break long-range monoclinic symmetry.
Keywords
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © The Mineralogical Society of Great Britain and Ireland 2009
References
- 9
- Cited by




