Article contents
Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene):sulfonated poly(diphenylacetylene) complex as a hole injection material in organic light-emitting diodes
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 07 August 2017
Abstract
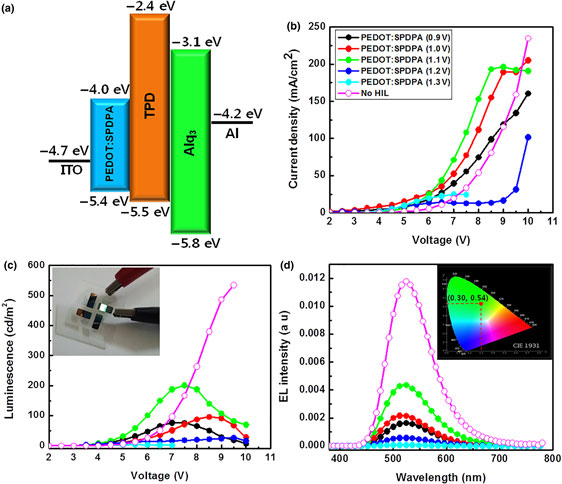
New ionic conjugated polyelectrolyte complex films based on poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene):sulfonated poly(diphenylacetylene) (PEDOT:SPDPA) are electrochemically formed on indium thin oxide substrates using a potentiostatic method, and their physical properties are evaluated using various analytical tools. Depending on a constant applied voltage, the surface morphological features and electrochemically doped states are different due to the conformational structure related to the oxidation state in the PEDOT growth process and concomitant SPDPA doping state in the films. For the purpose of use as a hole injection layer in organic light-emitting diodes, a well-known configuration (ITP/PEDOT:SPDPA/TPD/Alq3/LiF/Al) is adopted to investigate the optoelectronic properties.
- Type
- Research Letters
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 2017
Footnotes
These authors contributed equally to this work.
References
- 5
- Cited by




