Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by
Crossref.
Kumar, P. Arun
Kumar, S. M. Aravindh
Mitra, A. Surya
and
Rathakrishnan, E.
2018.
Fluidic injectors for supersonic jet control.
Physics of Fluids,
Vol. 30,
Issue. 12,
p.
126101.
Arun Kumar, P.
Aileni, Manideep
and
Rathakrishnan, E.
2019.
Impact of tab location relative to the nozzle exit on the shock structure of a supersonic jet.
Physics of Fluids,
Vol. 31,
Issue. 7,
Perumal, Arun Kumar
S M, Aravindh Kumar
and
E, Rathakrishnan
2019.
Empirical analysis of supersonic jet control using steady minijet injection.
Arun Kumar, P.
Aravindh Kumar, S. M.
Surya Mitra, A.
and
Rathakrishnan, E.
2019.
Empirical scaling analysis of supersonic jet control using steady fluidic injection.
Physics of Fluids,
Vol. 31,
Issue. 5,
Fan, D. W.
Zhou, Y.
and
Noack, B. R.
2020.
Fast triple-parameter extremum seeking exemplified for jet control.
Experiments in Fluids,
Vol. 61,
Issue. 7,
Zhou, Yu
Fan, Dewei
Zhang, Bingfu
Li, Ruiying
and
Noack, Bernd R.
2020.
Artificial intelligence control of a turbulent jet.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 897,
Issue. ,
Fan, Dewei
Zhou, Yu
and
Noack, Bernd R.
2021.
Fluid-Structure-Sound Interactions and Control.
p.
365.
Blanchard, Antoine B.
Cornejo Maceda, Guy Y.
Fan, Dewei
Li, Yiqing
Zhou, Yu
Noack, Bernd R.
and
Sapsis, Themistoklis P.
2021.
Bayesian optimization for active flow control.
Acta Mechanica Sinica,
Vol. 37,
Issue. 12,
p.
1786.
Perumal, Arun Kumar
and
Zhou, Yu
2021.
Axisymmetric jet manipulation using multiple unsteady minijets.
Physics of Fluids,
Vol. 33,
Issue. 6,
Shahsavari, Mohammad
Wang, Bing
Zhang, Bo
Jiang, Guanyu
and
Zhao, Dan
2021.
Response of supercritical round jets to various excitation modes.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 915,
Issue. ,
Perumal, Arun Kumar
and
Rathakrishnan, Ethirajan
2021.
Scaling law for shock-cell length and its correlation with shock-associated noise of circular and elliptic supersonic free jets.
Physics of Fluids,
Vol. 33,
Issue. 9,
Perumal, Arun Kumar
and
Rathakrishnan, Ethirajan
2022.
Design of Fluidic Injector for Supersonic Jet Manipulation.
AIAA Journal,
Vol. 60,
Issue. 8,
p.
4639.
Perumal, A.K.
Wu, Z.
Fan, D.W.
and
Zhou, Y.
2022.
A hybrid artificial intelligence control of a turbulent jet: Reynolds number effect and scaling.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 942,
Issue. ,
Eri, Qitai
Ding, Wenhao
and
Kong, Bo
2022.
Numerical Investigation of Jet Control Using Two Pulsed Jets under Different Amplitudes.
Energies,
Vol. 15,
Issue. 2,
p.
640.
Fan, Dewei
and
Zhou, Yu
2022.
Scaling and classification of a minijet-manipulated turbulent jet.
Physical Review Fluids,
Vol. 7,
Issue. 7,
R, Arun Prasad
S, Thanigaiarasu
M, Sembaruthi
and
E, Rathakrishnan
2022.
Study of Correctly Expanded Sonic Jet with Air Tabs
.
International Journal of Turbo & Jet-Engines,
Vol. 39,
Issue. 4,
p.
565.
Eri, Qitai
Lin, Chunyu
and
Kong, Bo
2022.
Numerical Investigation of Fluidic Injection for Supersonic Jet Control and its Infrared Radiation Characteristics.
SSRN Electronic Journal,
Khan, Aqib
Nageswara Rao, A.
Baghel, Trishank
Perumal, Arun Kumar
and
Kumar, Rakesh
2022.
Parametric study and scaling of Mach 1.5 jet manipulation using steady fluidic injection.
Physics of Fluids,
Vol. 34,
Issue. 3,
Kong, Bo
Duan, Ran
and
Eri, Qitai
2022.
Investigation of jet control using pulsed jets with three azimuthal modes.
International Journal of Heat and Fluid Flow,
Vol. 93,
Issue. ,
p.
108900.
Suseela Moorthi, Aravindh Kumar
Perumal, Arun Kumar
and
Rathakrishnan, Ethirajan
2023.
Jet mixing manipulation with asymmetric orientation of tabs.
Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part G: Journal of Aerospace Engineering,
Vol. 237,
Issue. 7,
p.
1571.
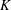 $K$ of the jet centreline mean velocity are investigated, including the mass flow rate ratio
$K$ of the jet centreline mean velocity are investigated, including the mass flow rate ratio 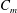 $C_{m}$ , excitation frequency ratio
$C_{m}$ , excitation frequency ratio 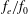 $f_{e}/f_{0}$ and exit diameter ratio
$f_{e}/f_{0}$ and exit diameter ratio 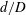 $d/D$ of the minijet to main jet, along with the duty cycle (
$d/D$ of the minijet to main jet, along with the duty cycle ( $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FC}$ ) of the minijet injection. Extensive hot-wire, particle image velocimetry and flow visualization measurements were performed in the manipulated jet. Various flow structures have been identified, such as the flapping flow, non-flapping flow and that showing a manipulable thrust vector, depending on
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FC}$ ) of the minijet injection. Extensive hot-wire, particle image velocimetry and flow visualization measurements were performed in the manipulated jet. Various flow structures have been identified, such as the flapping flow, non-flapping flow and that showing a manipulable thrust vector, depending on 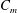 $C_{m}$ ,
$C_{m}$ , 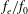 $f_{e}/f_{0}$ and
$f_{e}/f_{0}$ and  $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FC}$ . Empirical scaling analysis unveils that, prior to the minijet impingement upon the wall of the nozzle and the generation of turbulence, the relationship
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FC}$ . Empirical scaling analysis unveils that, prior to the minijet impingement upon the wall of the nozzle and the generation of turbulence, the relationship 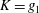 $K=g_{1}$ (
$K=g_{1}$ (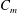 $C_{m}$ ,
$C_{m}$ , 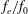 $f_{e}/f_{0}$ ,
$f_{e}/f_{0}$ , 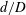 $d/D$ ,
$d/D$ ,  $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FC}$ ) may be reduced to
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FC}$ ) may be reduced to 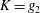 $K=g_{2}$ (
$K=g_{2}$ (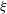 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D709}$ ), where
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D709}$ ), where 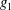 $g_{1}$ and
$g_{1}$ and 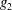 $g_{2}$ are different functions and the scaling factor
$g_{2}$ are different functions and the scaling factor 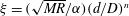 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D709}=(\sqrt{MR}/\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FC})(d/D)^{n}$ (
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D709}=(\sqrt{MR}/\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FC})(d/D)^{n}$ (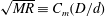 $\sqrt{MR}\equiv C_{m}(D/d)$ is the momentum ratio and
$\sqrt{MR}\equiv C_{m}(D/d)$ is the momentum ratio and  $n$ is a constant that depends on
$n$ is a constant that depends on  $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FC}$ ) is physically the effective momentum ratio per pulse or effective penetration depth. Discussion is conducted based on
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FC}$ ) is physically the effective momentum ratio per pulse or effective penetration depth. Discussion is conducted based on 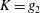 $K=g_{2}$ (
$K=g_{2}$ (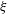 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D709}$ ), which provides important insight into the jet control physics.
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D709}$ ), which provides important insight into the jet control physics.

