Article contents
Resistive tearing-mode instability in a magnetic-field-reversing current sheet with coplanar viscous stagnation-point flow
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 13 March 2009
Abstract
The tearing-mode instability of a magnetic-field-reversing current sheet in the presence of coplanar incompressible stagnation-point flow is examined. The unperturbed equilibrium state is an exact solution of the steady-state, dissipative, incompressible magnetohydrodynamic equations; thus the analysis is valid even for small viscous and resistive Lundquist numbers Sν and Sη. The instability problem has no known analytical solution; for this reason, it is studied numerically by use of a finite-element method. Simulation results indicate stability for sufficiently small values of Sν or Sη and instability for large values. The boundary separating stable and unstable regions in the (Sν, Sη) plane is located. In the unstable regime, the simulation results show formation and subsequent convection of magnetic islands along the current sheet at about 80% of the unperturbed outflow flow speed, on average. Stretching and pinching of convecting magnetic islands are also observed. The results show the occurrence of multiple X-line reconnection at the centre of the current sheet (x = 0). Small-scale structures of vorticity and current density near the X-point reconnection sites are found to be qualitatively consistent with results obtained by Matthaeus. Normalized global linear growth rates are found to obey the approximate power law, 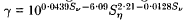 within the ranges 20 ≦ Sν ≦ 70 and 200 ≦ Sη 1000. At least for Sν ≦ 1000, the number of magnetic islands is found to be nearly independent of Sν indicating the existence of a narrow band of dominant wavelengths in this range. The stretching of magnetic islands, which is present in this coplanar flow and field configuration, but not in the perpendicular flow and field configuration examined by Phan and Sonnerup, causes a substantial decrease in linear growth rate relative to that obtained by those authors. The stability curves obtained are qualitatively similar in both analyses, but the stable region is much larger for coplanar flow and field. Unlike most simulations of the tearing mode, no symmetry conditions are imposed on the perturbations; nevertheless, they develop in a symmetric manner.
within the ranges 20 ≦ Sν ≦ 70 and 200 ≦ Sη 1000. At least for Sν ≦ 1000, the number of magnetic islands is found to be nearly independent of Sν indicating the existence of a narrow band of dominant wavelengths in this range. The stretching of magnetic islands, which is present in this coplanar flow and field configuration, but not in the perpendicular flow and field configuration examined by Phan and Sonnerup, causes a substantial decrease in linear growth rate relative to that obtained by those authors. The stability curves obtained are qualitatively similar in both analyses, but the stable region is much larger for coplanar flow and field. Unlike most simulations of the tearing mode, no symmetry conditions are imposed on the perturbations; nevertheless, they develop in a symmetric manner.
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Cambridge University Press 1996
References
REFERENCES
- 19
- Cited by




