No CrossRef data available.
Article contents
Pulsar Spin-Down by 3P2 Superfluid Neutrons
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 26 May 2016
Abstract
To describe pulsar spin-down, a simple combined torque model, that takes into account both the standard magnetic dipole radiation and the electromagnetic radiation from the 3P2 superfluid vortex neutrons inside neutron star, is presented. Using an ordinary exponential model for the magnetic field decay, we investigate pulsar evolution tracks on the 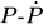 diagram, which is quite different from that of the standard magnetic dipole radiation model, especially when the superfluid torque or field decay become dominate.
diagram, which is quite different from that of the standard magnetic dipole radiation model, especially when the superfluid torque or field decay become dominate.
- Type
- Part 5 Pulsars and Other Neutron Stars
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Astronomical Society of the Pacific 2003




