Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by
Crossref.
Wu, Meng
Wang, Yicao
Mourrain, Bernard
Nkonga, Boniface
and
Cheng, Changzheng
2017.
Convergence rates for solving elliptic boundary value problems with singular parameterizations in isogeometric analysis.
Computer Aided Geometric Design,
Vol. 52-53,
Issue. ,
p.
170.
Wu, Meng
Mourrain, Bernard
Galligo, André
and
Nkonga, Boniface
2017.
H1-parametrizations of complex planar physical domains in isogeometric analysis.
Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering,
Vol. 318,
Issue. ,
p.
296.
Toshniwal, Deepesh
Speleers, Hendrik
and
Hughes, Thomas J.R.
2017.
Smooth cubic spline spaces on unstructured quadrilateral meshes with particular emphasis on extraordinary points: Geometric design and isogeometric analysis considerations.
Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering,
Vol. 327,
Issue. ,
p.
411.
Wei, Xiaodong
Zhang, Yongjie Jessica
Toshniwal, Deepesh
Speleers, Hendrik
Li, Xin
Manni, Carla
Evans, John A.
and
Hughes, Thomas J.R.
2018.
Blended B-spline construction on unstructured quadrilateral and hexahedral meshes with optimal convergence rates in isogeometric analysis.
Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering,
Vol. 341,
Issue. ,
p.
609.
Wu, Meng
and
Wang, Xuhui
2018.
AH1-integrability condition of surfaces with singular parametrizations in isogeometric analysis.
Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering,
Vol. 332,
Issue. ,
p.
136.
Pan, Qing
Rabczuk, Timon
Chen, Chong
Xu, Guoliang
and
Pan, Kejia
2018.
Isogeometric analysis of minimal surfaces on the basis of extended Catmull–Clark subdivision.
Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering,
Vol. 337,
Issue. ,
p.
128.
Chan, C.L.
Anitescu, C.
and
Rabczuk, T.
2018.
Isogeometric analysis with strong multipatch C1-coupling.
Computer Aided Geometric Design,
Vol. 62,
Issue. ,
p.
294.
Kapl, Mario
Sangalli, Giancarlo
and
Takacs, Thomas
2018.
Construction of analysis-suitableG1planar multi-patch parameterizations.
Computer-Aided Design,
Vol. 97,
Issue. ,
p.
41.
Urick, Benjamin
Marussig, Benjamin
Cohen, Elaine
Crawford, Richard H.
Hughes, Thomas J.R.
and
Riesenfeld, Richard F.
2019.
Watertight Boolean operations: A framework for creating CAD-compatible gap-free editable solid models.
Computer-Aided Design,
Vol. 115,
Issue. ,
p.
147.
Pan, Qing
Rabczuk, Timon
Xu, Gang
and
Chen, Chong
2019.
Isogeometric analysis for surface PDEs with extended Loop subdivision.
Journal of Computational Physics,
Vol. 398,
Issue. ,
p.
108892.
Kapl, Mario
Sangalli, Giancarlo
and
Takacs, Thomas
2019.
An isogeometric C1 subspace on unstructured multi-patch planar domains.
Computer Aided Geometric Design,
Vol. 69,
Issue. ,
p.
55.
Chan, Chiu Ling
Anitescu, Cosmin
and
Rabczuk, Timon
2019.
Strong multipatch C1-coupling for isogeometric analysis on 2D and 3D domains.
Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering,
Vol. 357,
Issue. ,
p.
112599.
Cao, Juan
Chen, Zhonggui
Wei, Xiaodong
and
Zhang, Yongjie Jessica
2019.
A finite element framework based on bivariate simplex splines on triangle configurations.
Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering,
Vol. 357,
Issue. ,
p.
112598.
Chen, Leilei
Lu, Chuang
Lian, Haojie
Liu, Zhaowei
Zhao, Wenchang
Li, Shengze
Chen, Haibo
and
Bordas, Stéphane P.A.
2020.
Acoustic topology optimization of sound absorbing materials directly from subdivision surfaces with isogeometric boundary element methods.
Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering,
Vol. 362,
Issue. ,
p.
112806.
Hughes, Thomas J.R.
Sangalli, Giancarlo
Takacs, Thomas
and
Toshniwal, Deepesh
2021.
Geometric Partial Differential Equations - Part II.
Vol. 22,
Issue. ,
p.
467.
Azman, Anis Nur’ain
Hadi, Normi Abdul
and
Nasir, Mohd Agos Salim
2021.
A systematic review of Bezier-like Triangular in surface reconstruction.
Journal of Physics: Conference Series,
Vol. 1988,
Issue. 1,
p.
012032.
Wu, Meng
Wang, Xuhui
Ni, Qian
and
Wei, Mingqiang
2021.
Solve Laplace-Beltrami Equation on Geometrically Continuous Curves in Isogeometric Analysis.
Journal of Computer-Aided Design & Computer Graphics,
Vol. 33,
Issue. 12,
p.
1916.
Mishra, Bhaskar
and
Peters, Jörg
2023.
Polyhedral control-net splines for analysis.
Computers & Mathematics with Applications,
Vol. 151,
Issue. ,
p.
215.
Peters, Jörg
Lo, Kyle
and
Karčiauskas, Kȩstutis
2023.
Algorithm 1032: Bi-cubic Splines for Polyhedral Control Nets.
ACM Transactions on Mathematical Software,
Vol. 49,
Issue. 1,
p.
1.
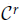 parameter continuity. And we compute their dimension and exhibit basis functions called Hermite bases for bicubic spline spaces. We investigate their potential applications for solving partial differential equations (PDEs) over a physical domain in the framework of Isogeometric analysis. For instance, we analyze the property of approximation of these spline spaces for the L
2-norm; we show that the optimal approximation order and numerical convergence rates are reached by setting a proper parameterization, although the fact that the basis functions are singular at extraordinary vertices.
parameter continuity. And we compute their dimension and exhibit basis functions called Hermite bases for bicubic spline spaces. We investigate their potential applications for solving partial differential equations (PDEs) over a physical domain in the framework of Isogeometric analysis. For instance, we analyze the property of approximation of these spline spaces for the L
2-norm; we show that the optimal approximation order and numerical convergence rates are reached by setting a proper parameterization, although the fact that the basis functions are singular at extraordinary vertices.



