Article contents
A MODIFIED IMMERSED FINITE VOLUME ELEMENT METHOD FOR ELLIPTIC INTERFACE PROBLEMS
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 13 May 2020
Abstract
This paper presents a new immersed finite volume element method for solving second-order elliptic problems with discontinuous diffusion coefficient on a Cartesian mesh. The new method possesses the local conservation property of classic finite volume element method, and it can overcome the oscillating behaviour of the classic immersed finite volume element method. The idea of this method is to reconstruct the control volume according to the interface, which makes it easy to implement. Optimal error estimates can be derived with respect to an energy norm under piecewise 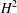 $H^{2}$ regularity. Numerical results show that the new method significantly outperforms the classic immersed finite volume element method, and has second-order convergence in
$H^{2}$ regularity. Numerical results show that the new method significantly outperforms the classic immersed finite volume element method, and has second-order convergence in 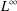 $L^{\infty }$ norm.
$L^{\infty }$ norm.
MSC classification
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- © 2020 Australian Mathematical Society
References
- 1
- Cited by




