Article contents
New insights on ion track morphology in pyrochlores by aberration corrected scanning transmission electron microscopy
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 13 December 2016
Abstract
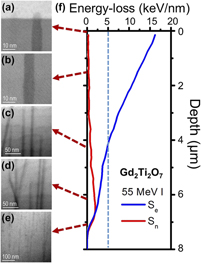
Here, we demonstrate the enhanced imaging capabilities of an aberration corrected scanning transmission electron microscope to advance the understanding of ion track structure in pyrochlore structured materials (i.e., Gd2Ti2O7 and Gd2TiZrO7). Track formation occurs due to the inelastic transfer of energy from incident ions to electrons, and atomic-level details of track morphology as a function of energy-loss are revealed in the present work. A comparison of imaging details obtained by varying collection angles of detectors is discussed in the present work. A quantitative analysis of phase identification using high-angle annular dark field imaging is performed on the ion tracks. Finally, a novel 3-dimensional track reconstruction method is provided that is based on depth-dependent imaging of the ion tracks. The technique is used in extracting the atomic-level details of nanoscale features, such as the disordered ion tracks, which are embedded in relatively thicker matrix. Another relevance of the method is shown by measuring the tilt of the ion tracks relative to the electron beam incidence that helps in knowing the structure and geometry of ion tracks quantitatively.
- Type
- Review
- Information
- Journal of Materials Research , Volume 32 , Issue 5: Focus Issue: Aberration Corrected Transmission Electron Microscopy , 14 March 2017 , pp. 928 - 935
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 2016
Footnotes
Contributing Editor: Thomas Walther
This section of Journal of Materials Research is reserved for papers that are reviews of literature in a given area.
This author was an editor of this journal during the review and decision stage. For the JMR policy on review and publication of manuscripts authored by editors, please refer to http://www.mrs.org/jmr-editor-manuscripts/.
References
REFERENCES
- 13
- Cited by





