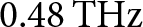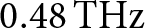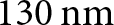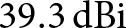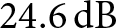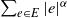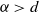176 results
Amygdala-related electrical fingerprint is modulated with neurofeedback training and correlates with deep-brain activation: proof-of-concept in borderline personality disorder
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 December 2023, pp. 1-10
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
PP140 Burden of Illness And Health Care Costs In People with Alzheimer’s Disease
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Technology Assessment in Health Care / Volume 39 / Issue S1 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 December 2023, p. S90
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Prevalence of reported penicillin allergy and associations with perioperative complications, length of stay, and cost in patients undergoing elective cancer surgery
-
- Journal:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship & Healthcare Epidemiology / Volume 3 / Issue 1 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 December 2023, e234
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A compact and fully integrated
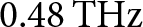 $\text{0.48}\,\text{THz}$ FMCW radar transceiver combined with a dielectric lens
$\text{0.48}\,\text{THz}$ FMCW radar transceiver combined with a dielectric lens
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Microwave and Wireless Technologies , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 December 2023, pp. 1-12
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Preterm birth, birthweight, and subsequent risk for depression
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Developmental Origins of Health and Disease / Volume 14 / Issue 5 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 October 2023, pp. 623-630
-
- Article
- Export citation
Radiofrequency ice dielectric measurements at Summit Station, Greenland
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Glaciology , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 October 2023, pp. 1-12
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
TIME SERIES OF SURFACE WATER DISSOLVED INORGANIC CARBON ISOTOPES FROM THE SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA BIGHT
-
- Journal:
- Radiocarbon , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 September 2023, pp. 1-16
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
REQUIREMENTS FOR A SMART PRODUCT-SERVICE SYSTEM DEVELOPMENT FRAMEWORK
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Design Society / Volume 3 / July 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 June 2023, pp. 3085-3094
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Upper large deviations for power-weighted edge lengths in spatial random networks
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Advances in Applied Probability / Volume 56 / Issue 1 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 June 2023, pp. 34-70
- Print publication:
- March 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
The Effect of Weather and Heat-Related Variation on Patient Presentation and Transport Rates
-
- Journal:
- Prehospital and Disaster Medicine / Volume 38 / Issue S1 / May 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 July 2023, p. s172
- Print publication:
- May 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Momentum maps and the Kähler property for base spaces of reductive principal bundles
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society / Volume 66 / Issue 1 / February 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 April 2023, pp. 218-230
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Millijoule ultrafast optical parametric amplification as replacement for high-gain regenerative amplifiers
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 11 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 March 2023, e48
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Effectiveness and long-term stability of outpatient cognitive behavioural therapy (CBT) for children and adolescents with anxiety and depressive disorders under routine care conditions
-
- Journal:
- Behavioural and Cognitive Psychotherapy / Volume 51 / Issue 4 / July 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 March 2023, pp. 320-334
- Print publication:
- July 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Processing of social and monetary rewards in autism spectrum disorders
-
- Journal:
- The British Journal of Psychiatry / Volume 222 / Issue 3 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 January 2023, pp. 100-111
- Print publication:
- March 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Governments commit to forest restoration, but what does it take to restore forests?
-
- Journal:
- Environmental Conservation / Volume 49 / Issue 4 / December 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 September 2022, pp. 206-214
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Sex and age differences in the proportion of experienced symptoms by SARS-CoV-2 serostatus in a community-based cross-sectional study
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 150 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 August 2022, e157
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Automation of Supported Nanoparticle Recognition in Low Contrast STEM Images
-
- Journal:
- Microscopy and Microanalysis / Volume 28 / Issue S1 / August 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 July 2022, pp. 3032-3034
- Print publication:
- August 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Diffraction of shock waves through a non-quiescent medium
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 944 / 10 August 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 July 2022, A39
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Age-related brain deviations and aggression
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 53 / Issue 9 / July 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 April 2022, pp. 4012-4021
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Antimicrobial use in Canadian acute-care hospitals: Findings from three national point-prevalence surveys between 2002 and 2017
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 43 / Issue 11 / November 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 March 2022, pp. 1558-1564
- Print publication:
- November 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation