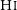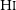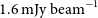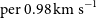45 results
2 Neurocognition and Functional Status Among Ethnoculturally Diverse Older Adults: Support for the External Validity of the ADAS-Cog
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 29 / Issue s1 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 December 2023, pp. 86-87
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
RE: Proposed Assisted Dying Bill: implications for mental healthcare and psychiatrists
-
- Journal:
- The British Journal of Psychiatry / Volume 222 / Issue 2 / February 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 January 2023, p. 88
- Print publication:
- February 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Depression, anxiety and PTSD symptoms before and during the COVID-19 pandemic in the UK
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 53 / Issue 12 / September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 July 2022, pp. 5428-5441
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
GASKAP-HI pilot survey science I: ASKAP zoom observations of Hi emission in the Small Magellanic Cloud
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 39 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 February 2022, e005
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Evidence for distinct genetic and environmental influences on fear acquisition and extinction
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 53 / Issue 3 / February 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 September 2021, pp. 1106-1114
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Federal and Political Party Reforms in Asia: Is There a New Model of Federal Democracy Emerging in Ethnically Diverse Countries in Asia?
-
- Journal:
- Government and Opposition / Volume 57 / Issue 2 / April 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 December 2020, pp. 296-317
- Print publication:
- April 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
How Can Pharmacogenomics Biomarkers Be Translated into Patient Benefit
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 30 / Issue S1 / March 2015
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 April 2020, p. 1
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Genetic Relationship Between Depression and Body Mass Index
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 30 / Issue S1 / March 2015
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 April 2020, p. 1
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
O-56 - Response to Acetyl Cholinesterase Inhibitor Agents in Dementia: Longitudinal Analysis of Cognitive Trajectories Before and After Treatment Initiation in a Large Mental Health Case Register
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 27 / Issue S1 / 2012
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 April 2020, p. 1
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Linear stability of stellar rotating spheres
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the International Astronomical Union / Volume 14 / Issue S353 / June 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 May 2020, pp. 246-247
- Print publication:
- June 2019
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Phase space complexity of star clusters: Fresh observables for old and new questions
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the International Astronomical Union / Volume 14 / Issue S351 / May 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 March 2020, pp. 389-394
- Print publication:
- May 2019
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
A linear stability study of stellar rotating spheres
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the International Astronomical Union / Volume 14 / Issue S351 / May 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 March 2020, pp. 494-497
- Print publication:
- May 2019
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Capacity is only one aspect of decision-making at life's end
-
- Journal:
- The British Journal of Psychiatry / Volume 214 / Issue 3 / March 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 February 2019, pp. 171-172
- Print publication:
- March 2019
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Thinking Fast and Slow By Daniel Kahneman. Penguin. 2012. £10.99 (pb). 512 pp. ISBN 9780141033570.
-
- Journal:
- The British Journal of Psychiatry / Volume 213 / Issue 3 / September 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 August 2018, pp. 563-564
- Print publication:
- September 2018
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Thermogravimetric, infrared and mass-spectroscopic analysis of the desorption of methanol, propan-1-ol, propan-2-ol and 2-methylpropan-2-ol from montmorillonite
-
- Journal:
- Clay Minerals / Volume 28 / Issue 1 / March 1993
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 July 2018, pp. 123-137
-
- Article
- Export citation
Clozapine withdrawal syndrome
-
- Journal:
- BJPsych Bulletin / Volume 41 / Issue 6 / December 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 January 2018, p. 366
- Print publication:
- December 2017
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Contents
-
- Book:
- Studies in Medievalism XXV
- Published by:
- Boydell & Brewer
- Published online:
- 05 July 2016
- Print publication:
- 21 June 2016, pp vii-viii
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
II - Medievalist Visions
-
- Book:
- Studies in Medievalism XXV
- Published by:
- Boydell & Brewer
- Published online:
- 05 July 2016
- Print publication:
- 21 June 2016, pp 45-46
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Volume XXV 2016
-
- Book:
- Studies in Medievalism XXV
- Published by:
- Boydell & Brewer
- Published online:
- 05 July 2016
- Print publication:
- 21 June 2016, pp x-x
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Frontmatter
-
- Book:
- Studies in Medievalism XXV
- Published by:
- Boydell & Brewer
- Published online:
- 05 July 2016
- Print publication:
- 21 June 2016, pp i-iv
-
- Chapter
- Export citation