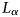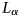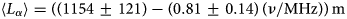230 results
Vitamin K1 intake and incident diabetes in the Danish Diet Cancer and Health study
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Nutrition Society / Volume 82 / Issue OCE2 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 March 2023, E177
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Thunder Go North: The Hunt for Sir Francis Drake's Fair and Good Bay. MELISSA DARBY. 2019. University of Utah Press, Salt Lake City. xiv + 315 pp. $24.95 (hardcover), ISBN 978-1-60781-725-3. $24.95 (paperback), ISBN 978-1-60781-744-4. $20.00 (e-book), ISBN 978-1-60781-726-0.
-
- Journal:
- American Antiquity / Volume 87 / Issue 4 / October 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 June 2022, pp. 853-855
- Print publication:
- October 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
In situ, broadband measurement of the radio frequency attenuation length at Summit Station, Greenland
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Glaciology / Volume 68 / Issue 272 / December 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 May 2022, pp. 1234-1242
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
P.120 Case series: Clinical and genetic spectrum of SCN8A-related disorders in British Columbia
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 48 / Issue s3 / November 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 January 2022, p. S53
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
An observational study of the association of vitamin D status and other patient characteristics with COVID-19 severity and mortality
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Nutrition Society / Volume 80 / Issue OCE3 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 August 2021, E125
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
The role of demographic and clinical characteristics on risk of COVID-19 related infection and mortality
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Nutrition Society / Volume 80 / Issue OCE3 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 August 2021, E116
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Irish Jesuits in penal times, 1695–1811. Thomas Betagh and his companions. By Thomas J. Morrissey sj. Pp. 166 incl. frontispiece and 23 ills. Dublin: Messenger Publications, 2020. €19.95 (paper). 978 1 78812 115 6
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Ecclesiastical History / Volume 72 / Issue 1 / January 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 December 2020, p. 201
- Print publication:
- January 2021
-
- Article
- Export citation
Pathways to a more peaceful and sustainable world: The transformative power of children in families
-
- Journal:
- Development and Psychopathology / Volume 33 / Issue 2 / May 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 September 2020, pp. 409-420
-
- Article
- Export citation
Overactivation of the middle cingulate cortex and the caudate nucleus as neural correlates of the familial liability to major depressiive disorder
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 26 / Issue S2 / March 2011
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 April 2020, p. 648
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Lonely in a crowd: loneliness in New Zealand retirement village residents
-
- Journal:
- International Psychogeriatrics / Volume 33 / Issue 5 / May 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 April 2020, pp. 481-493
-
- Article
- Export citation
Health screening, cardiometabolic disease and adverse health outcomes in individuals with severe mental illness
-
- Journal:
- BJPsych Open / Volume 5 / Issue 6 / November 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 November 2019, e97
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
B.01 AVXS-101 gene-replacement therapy (GRT) for spinal muscular atrophy type 1 (SMA1): pivotal phase 3 study (STR1VE) update
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 46 / Issue s1 / June 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 June 2019, p. S10
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Interactive impact of childhood maltreatment, depression, and age on cortical brain structure: mega-analytic findings from a large multi-site cohort
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 50 / Issue 6 / April 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 May 2019, pp. 1020-1031
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Reinvestigating Cougar Mountain Cave: New Perspectives on Stratigraphy, Chronology, and a Younger Dryas Occupation in the Northern Great Basin
-
- Journal:
- American Antiquity / Volume 84 / Issue 3 / July 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 April 2019, pp. 559-573
- Print publication:
- July 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
PAPER CITIES - Julia Guarneri. Newsprint Metropolis: City Papers and the Making of Modern Americans. Chicago: University of Chicago Press, 2017. 330 pp. $45.00 (cloth), ISBN 0-226-34133-x.
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of the Gilded Age and Progressive Era / Volume 18 / Issue 1 / January 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 January 2019, pp. 142-144
- Print publication:
- January 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
The Boulter letters. By Kenneth Milne and Paddy McNally . Pp. 467. Portland, Or–Dublin: Four Courts Press, 2016. £50. 978 1 84682 290 2
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Ecclesiastical History / Volume 69 / Issue 1 / January 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 January 2018, pp. 190-191
- Print publication:
- January 2018
-
- Article
- Export citation
COST ANALYSIS OF PERIPHERALLY INSERTED CENTRAL CATHETER IN PEDIATRIC PATIENTS
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Technology Assessment in Health Care / Volume 34 / Issue 1 / 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 December 2017, pp. 38-45
-
- Article
- Export citation
Violence, politics and Catholicism in Ireland. By Oliver P. Rafferty sj . Pp. 247. Dublin–Portland, Or: Four Courts Press, 2016. £40. 978 1 84682 583 5
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Ecclesiastical History / Volume 68 / Issue 4 / October 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 September 2017, pp. 894-896
- Print publication:
- October 2017
-
- Article
- Export citation
Factors associated with delay in trauma team activation and impact on patient outcomes
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Emergency Medicine / Volume 20 / Issue 4 / July 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 September 2017, pp. 606-613
- Print publication:
- July 2018
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation