92 results
Highly pathogenic avian influenza causes mass mortality in Sandwich Tern Thalasseus sandvicensis breeding colonies across north-western Europe
-
- Journal:
- Bird Conservation International / Volume 34 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 February 2024, e6
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
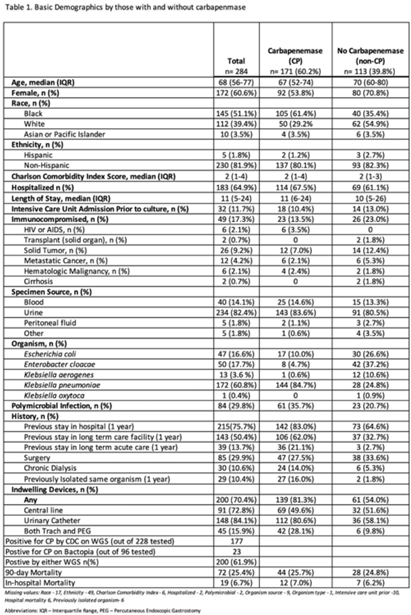
Evaluating indwelling devices and other risk factors for mortality in invasive Carbapenem-resistant Enterobacterales infections in Georgia, 2012–2019
-
- Journal:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship & Healthcare Epidemiology / Volume 3 / Issue 1 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 January 2024, e254
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
3 - The Mosaic of International Dispute Settlement
- from Part I - Recent Trends and Cross-Cutting Issues in International Dispute Settlement
-
-
- Book:
- The Changing Character of International Dispute Settlement
- Published online:
- 14 December 2023
- Print publication:
- 21 December 2023, pp 76-105
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Clearing the Bench: The Perils of Appointing Politicians to the Cabinet
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Policy History / Volume 36 / Issue 1 / January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 December 2023, pp. 67-94
-
- Article
- Export citation
Severe and common mental disorders and risk of emergency hospital admissions for ambulatory care sensitive conditions among the UK Biobank cohort
-
- Journal:
- BJPsych Open / Volume 9 / Issue 6 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 November 2023, e211
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
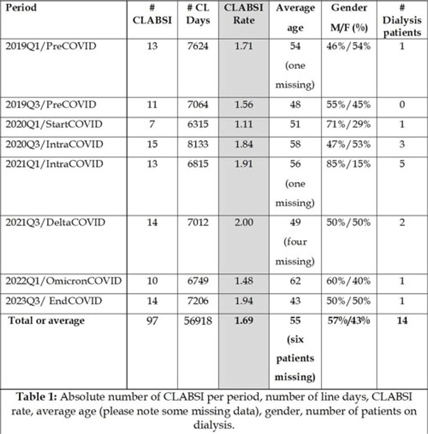
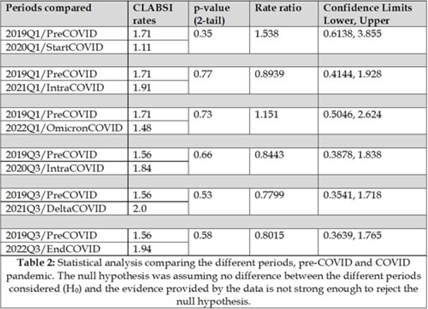
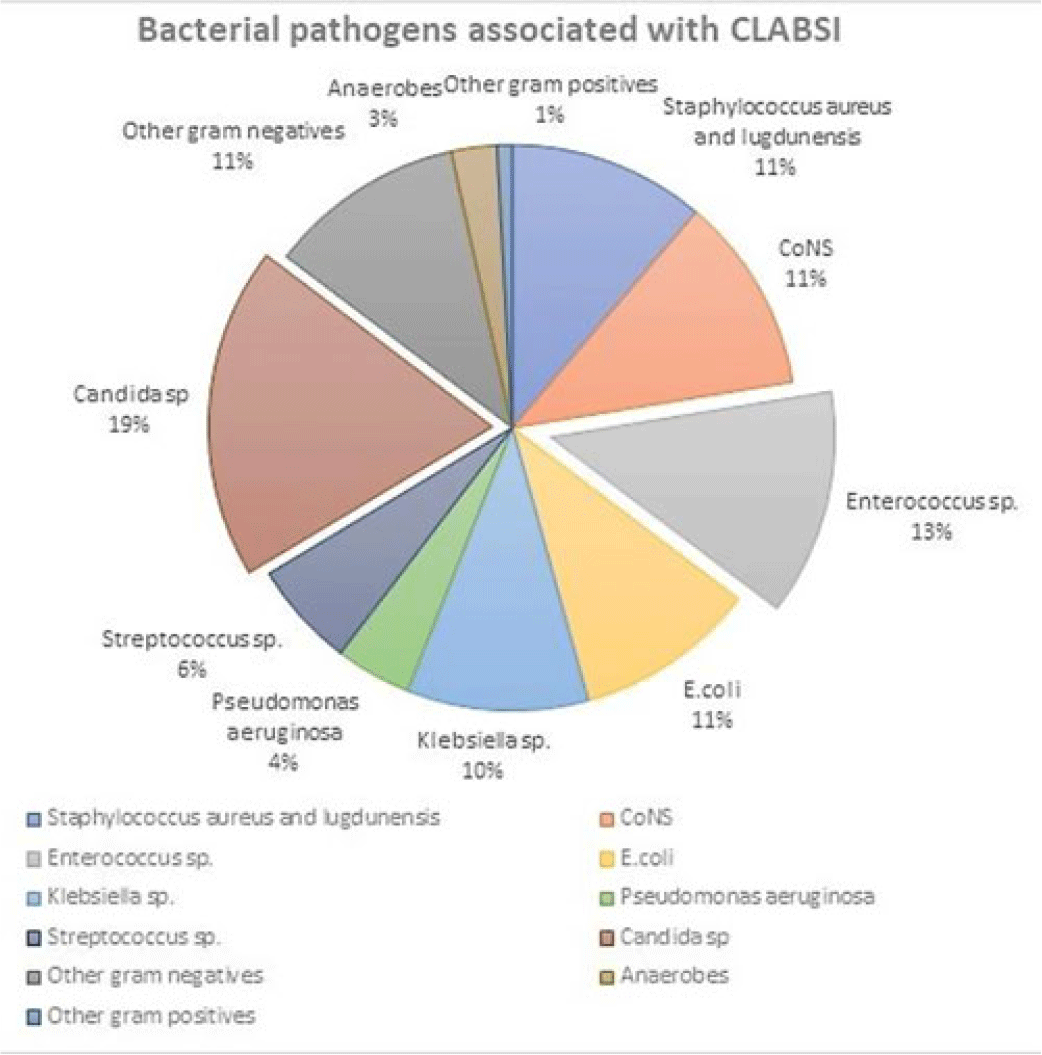
Retrospective data analysis of CLABSI rates at Baystate Medical Center during the COVID-19 pandemic
-
- Journal:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship & Healthcare Epidemiology / Volume 3 / Issue S2 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 September 2023, pp. s47-s48
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Carbapenemase genes and mortality in patients with carbapenem-resistant Enterobacterales, Atlanta, Georgia, 2011–2020
-
- Journal:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship & Healthcare Epidemiology / Volume 3 / Issue S2 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 September 2023, pp. s12-s13
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Epidemiology of carbapenem-resistant and extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing Enterobacterales in US children, 2016–2020
-
- Journal:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship & Healthcare Epidemiology / Volume 3 / Issue S2 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 September 2023, p. s16
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Advocacy at the Eighth World Congress of Pediatric Cardiology and Cardiac Surgery
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 33 / Issue 8 / August 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 August 2023, pp. 1277-1287
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Reflective liberals and intuitive conservatives: A look at the Cognitive Reflection Test and ideology – ADDENDUM
-
- Journal:
- Judgment and Decision Making / Volume 18 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 March 2023, e9
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Zebra Finch Behaviour and Effect of Modest Enrichment of Standard Cages
-
- Journal:
- Animal Welfare / Volume 4 / Issue 1 / February 1995
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 January 2023, pp. 3-9
-
- Article
- Export citation
Reflective liberals and intuitive conservatives: A look at the Cognitive Reflection Test and ideology
-
- Journal:
- Judgment and Decision Making / Volume 10 / Issue 4 / July 2015
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2023, pp. 314-331
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Work-up and Management of Asymptomatic Extracranial Traumatic Vertebral Artery Injury
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 50 / Issue 5 / September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 August 2022, pp. 662-672
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Atomistic Reaction Kinetics and Chemistry Revealed using In Situ STEM
-
- Journal:
- Microscopy and Microanalysis / Volume 28 / Issue S1 / August 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 July 2022, pp. 1838-1839
- Print publication:
- August 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Correcting Scan Distortions in Cryogenic 4DSTEM Acquisitions using Affine Transformations
-
- Journal:
- Microscopy and Microanalysis / Volume 28 / Issue S1 / August 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 July 2022, pp. 490-491
- Print publication:
- August 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Canadian Stroke Best Practice Recommendations: Secondary Prevention of Stroke Update 2020 – ADDENDUM
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 50 / Issue 3 / May 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 June 2022, p. 481
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Using 3D Models to Understand the Changing Role of Fluting in Paleoindian Point Technology from Clovis to Dalton
-
- Journal:
- American Antiquity / Volume 87 / Issue 3 / July 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 April 2022, pp. 544-566
- Print publication:
- July 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
Infection control and the prevalence, management and outcomes of SARS-CoV-2 infections in mental health wards in London, UK: lessons learned from wave 1 to wave 2
-
- Journal:
- BJPsych Open / Volume 8 / Issue 2 / March 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 March 2022, e63
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Occupational risk factors for severe acute respiratory coronavirus virus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection among healthcare personnel: A 6-month prospective analysis of the COVID-19 Prevention in Emory Healthcare Personnel (COPE) Study
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 43 / Issue 11 / November 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 February 2022, pp. 1664-1671
- Print publication:
- November 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Impact of data extraction errors in meta-analyses on the association between depression and peripheral inflammatory biomarkers: an umbrella review
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 53 / Issue 5 / April 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 November 2021, pp. 2017-2030
-
- Article
- Export citation