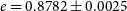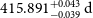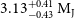330 results
Attitude maneuver planning and robust tracking control for flexible satellite
-
- Journal:
- The Aeronautical Journal , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 March 2024, pp. 1-19
-
- Article
- Export citation
Validation of the Passive Surveillance Stroke Severity Score in Three Canadian Provinces
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 March 2024, pp. 1-6
-
- Article
- Export citation
Ground collision avoidance system with multi-trajectory risk assessment and decision function
-
- Journal:
- The Aeronautical Journal , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 February 2024, pp. 1-16
-
- Article
- Export citation
94 Associations Between African Neuropsychological Tests of Memory and Medial Temporal Lobe Structures in Older Congolese Adults with Suspected Dementia
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 29 / Issue s1 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 December 2023, pp. 293-294
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Pro-inflammatory markers are associated with response to sequential pharmacotherapy in major depressive disorder: a CAN-BIND-1 report
-
- Journal:
- CNS Spectrums / Volume 28 / Issue 6 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 May 2023, pp. 739-746
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Effects of environment and breed on growth performance and meat quality of fattening pigs
-
- Journal:
- Animal Welfare / Volume 29 / Issue 2 / May 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2023, pp. 177-184
-
- Article
- Export citation
Inertial torque on a squirmer
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 953 / 25 December 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 December 2022, R1
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Ten new insights in climate science 2022
-
- Journal:
- Global Sustainability / Volume 5 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 November 2022, e20
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Volume Imaging By Tracking Sparse Topological Features In Electron Micrograph Tilt Series
-
- Journal:
- Microscopy and Microanalysis / Volume 28 / Issue S1 / August 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 July 2022, pp. 242-244
- Print publication:
- August 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Nanoscale Imaging of Biomolecules Using Molecule Anchorable Gel-enabled Nanoscale In-situ Fluorescence Microscopy
-
- Journal:
- Microscopy and Microanalysis / Volume 28 / Issue S1 / August 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 July 2022, pp. 1568-1569
- Print publication:
- August 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Forecasting the monthly incidence of scarlet fever in Chongqing, China using the SARIMA model
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 150 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 April 2022, e90
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Simultaneous bilateral transcutaneous bone conduction device implantation: sound localisation and speech perception in children with bilateral conductive hearing loss
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Laryngology & Otology / Volume 136 / Issue 10 / October 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 October 2021, pp. 939-946
- Print publication:
- October 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
HD 76920 b pinned down: A detailed analysis of the most eccentric planetary system around an evolved star
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 38 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 April 2021, e019
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Variation in PLIN2 and its association with milk traits and milk fat composition in dairy cows
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Agricultural Science / Volume 158 / Issue 8-9 / November 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 March 2021, pp. 774-780
-
- Article
- Export citation
Self-Affirmation and Identity-Driven Political Behavior
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Experimental Political Science / Volume 9 / Issue 2 / Summer 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 February 2021, pp. 225-240
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Characterization of a hospital-based gastroenteritis outbreak caused by GII.6 norovirus in Jinshan, China
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 148 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 December 2020, e289
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Neutron Star Extreme Matter Observatory: A kilohertz-band gravitational-wave detector in the global network
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 37 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 November 2020, e047
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Parity and the risk of incident dementia: a COSMIC study
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology and Psychiatric Sciences / Volume 29 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 October 2020, e176
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Alignment statistics of rods with the Lagrangian stretching direction in a channel flow
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 901 / 25 October 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 August 2020, A16
-
- Article
- Export citation
4346 Potential Sudden Unexpected Death in Epilepsy (SUDEP) Biomarkers in Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Cardiomyocytes with DEPDC5 Loss-of-Function
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 4 / Issue s1 / June 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 July 2020, p. 100
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation