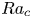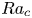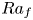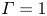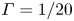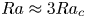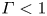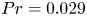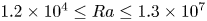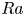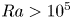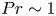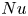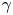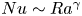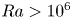33 results
Transition to fully developed turbulence in liquid-metal convection facilitated by spatial confinement
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 981 / 25 February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 February 2024, R2
-
- Article
- Export citation
Design-oriented dynamic model of deployable fin under time-varying elevated temperature environment
-
- Journal:
- The Aeronautical Journal / Volume 128 / Issue 1322 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 August 2023, pp. 631-654
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
A novel multi-shot target platform for laser-driven laboratory astrophysics experiments
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 11 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 February 2023, e17
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Flow states and heat transport in liquid metal convection
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 951 / 25 November 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 October 2022, R1
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Prosthetic and robotic wrists comparing with the intelligently evolved human wrist: A review
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A prospective epidemiological analysis of controlling nutritional status score with the poor functional outcomes in Chinese patients with haemorrhagic stroke
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 128 / Issue 2 / 28 July 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 August 2021, pp. 192-199
- Print publication:
- 28 July 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Provenance and tectonic setting of the Triassic clastic deposits in the Napo basin, South China: evidence from petrography, whole-rock geochemistry and detrital zircon U–Pb geochronology
-
- Journal:
- Geological Magazine / Volume 158 / Issue 12 / December 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 July 2021, pp. 2095-2114
-
- Article
- Export citation
First radiative shock experiments on the SG-II laser
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 9 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 June 2021, e27
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Projectile energy dependence of L X-ray emission in collisions of Xe23+ with In target: role of Coulomb ionization and quasi-molecular effects
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 38 / Issue 2 / June 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 March 2020, pp. 148-151
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Magnetic field–dependent microstructure evolution and magnetic property of Fe–6.5 Si–0.05 B alloy during solidification
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 34 / Issue 24 / 30 December 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 December 2019, pp. 4076-4084
- Print publication:
- 30 December 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
Association between gestational weight gain and exclusive breast-feeding for the first 6 months postpartum in Chinese women
-
- Journal:
- Public Health Nutrition / Volume 22 / Issue 11 / August 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 March 2019, pp. 2092-2098
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Genes in immune pathways associated with abnormal white matter integrity in first-episode and treatment-naïve patients with schizophrenia
-
- Journal:
- The British Journal of Psychiatry / Volume 214 / Issue 5 / May 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 February 2019, pp. 281-287
- Print publication:
- May 2019
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Status and development of high-power laser facilities at the NLHPLP
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 6 / 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 November 2018, e55
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Seed traits and germination of native grasses and invasive forbs are largely insensitive to parental temperature and CO2 concentration
-
- Journal:
- Seed Science Research / Volume 28 / Issue 4 / December 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 August 2018, pp. 303-311
-
- Article
- Export citation
Design and performance of final optics assembly in SG-II Upgrade laser facility
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 6 / 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 April 2018, e14
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Target alignment in the Shen-Guang II Upgrade laser facility
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 6 / 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 March 2018, e10
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Energy loss of protons in hydrogen plasma
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 36 / Issue 1 / March 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 February 2018, pp. 98-104
-
- Article
- Export citation
Evidence of different compounds in smoke derived from legumes and grasses acting on seed germination and seedling emergence
-
- Journal:
- Seed Science Research / Volume 27 / Issue 2 / June 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 April 2017, pp. 154-164
-
- Article
- Export citation
Beam guiding system geometric arrangement in the target area of high-power laser drivers
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 3 / 2015
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 March 2015, e12
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Synergistic effects of high dietary calcium and exogenous parathyroid hormone in promoting osteoblastic bone formation in mice
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 113 / Issue 6 / 28 March 2015
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 March 2015, pp. 909-922
- Print publication:
- 28 March 2015
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation