162 results
76 Lessons learned during implementation of OMOP common data model across multiple health systems
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 8 / Issue s1 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 April 2024, p. 20
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Emergency Medical Services Protocols for Assessment and Treatment of Patients with Ventricular Assist Devices
-
- Journal:
- Prehospital and Disaster Medicine , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 March 2024, pp. 1-6
-
- Article
- Export citation
Research agenda for antibiotic stewardship within the Veterans’ Health Administration, 2024–2028
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 February 2024, pp. 1-7
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
46 Cognitive Reserve and Gait Speed are Associated with Cognitive Performance in Black/African American Older Adults
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 29 / Issue s1 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 December 2023, pp. 354-355
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
In vitro activity of clindamycin, doxycycline, and trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole against clinical isolates of β-hemolytic Streptococcus spp. via BD Phoenix and broth microdilution
-
- Journal:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship & Healthcare Epidemiology / Volume 3 / Issue 1 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 December 2023, e238
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Radiofrequency ice dielectric measurements at Summit Station, Greenland
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Glaciology , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 October 2023, pp. 1-12
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
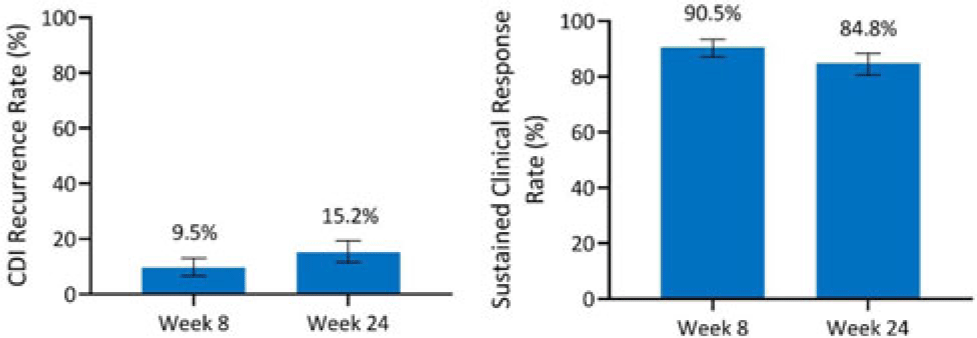
Integrated efficacy analysis from phase 3 studies of investigational microbiome therapeutic, SER-109, in recurrent Clostridioides difficile infection
-
- Journal:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship & Healthcare Epidemiology / Volume 3 / Issue S2 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 September 2023, p. s5
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Integrated safety analysis of phase 3 studies for investigational microbiome therapeutic, SER-109, in recurrent CDI
-
- Journal:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship & Healthcare Epidemiology / Volume 3 / Issue S2 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 September 2023, pp. s44-s45
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
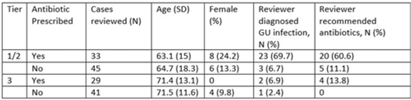
Validation of antibiotic stewardship metrics for genitourinary infection management in Veterans Affairs outpatient settings
-
- Journal:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship & Healthcare Epidemiology / Volume 3 / Issue S2 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 September 2023, p. s35
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
A qualitative evaluation of frontline clinician perspectives toward antibiotic stewardship programs
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 44 / Issue 12 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 March 2023, pp. 1995-2001
- Print publication:
- December 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Reconstructing Middle Horizon Camelid Diets and Foddering Practices: Microbotanical and Isotope Analyses of Dental Remains from Quilcapampa, Peru
-
- Journal:
- Latin American Antiquity / Volume 34 / Issue 4 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 January 2023, pp. 783-803
- Print publication:
- December 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
13 - The Role of Academic Libraries in Developing Social Capital by Promoting Quality Reading in Local Communities
-
-
- Book:
- The Social Future of Academic Libraries
- Published by:
- Facet
- Published online:
- 11 February 2023
- Print publication:
- 22 December 2022, pp 257-272
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Lack of correlation between standardized antimicrobial administration ratios (SAARs) and healthcare-facility–onset Clostridioides difficile infection rates in Veterans Affairs medical facilities
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 44 / Issue 6 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 December 2022, pp. 945-947
- Print publication:
- June 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Approaches to Monitoring Structural Modification Using In Situ Electron Microscopy
-
- Journal:
- Microscopy and Microanalysis / Volume 28 / Issue S1 / August 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 July 2022, pp. 144-145
- Print publication:
- August 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Interpretability of Low-Dose HRTEM Images of Supported Metal Nanoparticles
-
- Journal:
- Microscopy and Microanalysis / Volume 28 / Issue S1 / August 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 July 2022, pp. 2152-2154
- Print publication:
- August 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Formation of Defects in MoS2 during Data Acquisition of High-resolution Transmission Electron Microscopy
-
- Journal:
- Microscopy and Microanalysis / Volume 28 / Issue S1 / August 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 July 2022, pp. 2192-2193
- Print publication:
- August 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Large-scale Automated Analysis of High-Resolution Transmission Electron Microscopy Data Assisted by Deep Learning Neural Networks
-
- Journal:
- Microscopy and Microanalysis / Volume 28 / Issue S1 / August 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 July 2022, pp. 2984-2986
- Print publication:
- August 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
1 - Climate justice, social policy and the transition to net zero in the UK
-
-
- Book:
- Social Policy Review 34
- Published by:
- Bristol University Press
- Published online:
- 13 October 2022
- Print publication:
- 27 June 2022, pp 5-23
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Regulation of baby food marketing in Thailand: a NetCode analysis
-
- Journal:
- Public Health Nutrition / Volume 25 / Issue 10 / October 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 June 2022, pp. 2680-2692
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Characteristics of nursing home residents and healthcare personnel with repeated severe acute respiratory coronavirus virus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) tests positive ≥90 days after initial infection: Four US jurisdictions, July 2020–March 2021
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 44 / Issue 5 / May 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 May 2022, pp. 809-812
- Print publication:
- May 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation