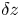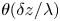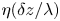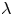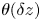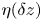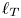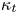135 results
Airfoil response to periodic vertical and longitudinal gusts
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 979 / 25 January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 January 2024, A35
-
- Article
- Export citation
Preparation and Properties of Sepiolite-Based 3D Flame-Retardant Aerogel
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 70 / Issue 6 / December 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 865-881
-
- Article
- Export citation
Preparation of Organo-Montmorillonites and the Relationship Between Microstructure and Swellability
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 65 / Issue 6 / December 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 417-430
-
- Article
- Export citation
Origin and Mineralogy of Sepiolite and Palygorskite From the Tuluanshan Formation, Eastern Taiwan
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 57 / Issue 5 / October 2009
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 521-530
-
- Article
- Export citation
RNA Sequencing Reveals the Differentially Expressed circRNAs between Stable and Unstable Carotid Atherosclerotic Plaques
-
- Journal:
- Genetics Research / Volume 2023 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e13
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Evaluation of phase-adjusted interventions for COVID-19 using an improved SEIR model
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 152 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 November 2023, e9
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The therapeutic effect of Mongolian medicine based on Qiwei Guangzao pill on depression
-
- Journal:
- CNS Spectrums / Volume 28 / Issue S2 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 October 2023, pp. S1-S2
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Cognitive-behavioral group teaching on social anxiety disorder of tourism management majors
-
- Journal:
- CNS Spectrums / Volume 28 / Issue S2 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 October 2023, p. S129
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Lift generation mechanism of the leading-edge vortex for an unsteady plate
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 972 / 10 October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 October 2023, A30
-
- Article
- Export citation
Ethnic differences in eating patterns and their associations with obesity among adults in West China
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 131 / Issue 2 / 28 January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 August 2023, pp. 321-332
- Print publication:
- 28 January 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Association Among Negative Life Events, Sense of Security, and Depressive Symptoms in Chinese Adolescents After the 2013 Ya’an Earthquake
-
- Journal:
- Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness / Volume 17 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 March 2023, e352
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Farmer perceived challenges toward conservation practice usage in the margins of the Corn Belt, USA
-
- Journal:
- Renewable Agriculture and Food Systems / Volume 38 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 February 2023, e14
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Number preferences in lotteries
-
- Journal:
- Judgment and Decision Making / Volume 11 / Issue 3 / May 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2023, pp. 243-259
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Fluctuation-induced slip of thermal boundary layers at a stable liquid–liquid interface
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 951 / 25 November 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 November 2022, A10
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A comparison between three-dimensional, transient, thermomechanically coupled first-order and Stokes ice flow models
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Glaciology / Volume 69 / Issue 275 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 October 2022, pp. 513-524
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Long-term psychological profile of general population following COVID-19 outbreak: symptom trajectories and evolution of psychopathological network
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology and Psychiatric Sciences / Volume 31 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 September 2022, e69
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Designing a toroidal crystal for monochromatic X-ray imaging of a laser-produced He-like plasma
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 10 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 September 2022, e37
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Dual-channel LIDAR searching, positioning, tracking and landing system for rotorcraft from ships at sea
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Navigation / Volume 75 / Issue 4 / July 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 July 2022, pp. 901-927
- Print publication:
- July 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
Exploring the association of dietary patterns with the risk of hypertension using principal balances analysis and principal component analysis
-
- Journal:
- Public Health Nutrition / Volume 26 / Issue 1 / January 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 April 2022, pp. 160-170
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation