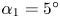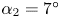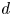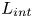240 results
Macrolide-Resistance of Mycoplasma pneumoniae in Several Regions of China from 2013 to 2019
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 April 2024, pp. 1-18
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Efficacy of catheter ablation in ganglionated plexus for malignant vasovagal syncope children
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 April 2024, pp. 1-6
-
- Article
- Export citation
November 2023 international forum on species in Haikou, China
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Cross-Section Measurements of the 11B(p,α)2α Reaction near the First Resonant Energy
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 2023 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e12
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Enhancement of Magnetic Vortex Acceleration by Laser Interaction with Near-Critical Density Plasma inside a Hollow Conical Target
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 2022 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e24
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Compact Thomson Scattering Source Based on a Mixed Injection Assisted Laser Wakefield Accelerator
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 2022 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e9
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The origins of saddles and riding technology in East Asia: discoveries from the Mongolian Altai
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Reevaluation of the protein requirement in Chinese elderly adults without sarcopenia with the indicator amino acid oxidation technique
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 131 / Issue 8 / 28 April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 December 2023, pp. 1377-1383
- Print publication:
- 28 April 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Zoonotic pathogens identified in rodents and shrews from four provinces, China, 2015–2022
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology & Infection / Volume 151 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 September 2023, e174
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A 115 ps, 100 Hz high-beam-quality laser based on transient stimulated Brillouin scattering pulse compression
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 11 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 August 2023, e70
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
High-energy, alignment-insensitive, injection-seeded Q-switched Ho:yttrium aluminum garnet single-frequency laser
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 11 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 July 2023, e66
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The Application of Information Technology in Preventing and Controlling COVID-19 Pandemic: A Bibliometric Study
-
- Journal:
- Prehospital and Disaster Medicine / Volume 38 / Issue S1 / May 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 July 2023, pp. s61-s62
- Print publication:
- May 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Separation length scaling for dual-incident shock wave–turbulent boundary layer interactions with different shock wave distances
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 960 / 10 April 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 March 2023, A9
-
- Article
- Export citation
Relationship between local-scale topography and vegetation on the invasive C4 perennial bunchgrass buffelgrass (Pennisetum ciliare) size and reproduction
-
- Journal:
- Invasive Plant Science and Management / Volume 16 / Issue 1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 March 2023, pp. 38-46
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Enhanced proton acceleration from laser interaction with curved surface nanowire targets
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Plasma Physics / Volume 89 / Issue 1 / February 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 March 2023, 905890113
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Effectiveness of a decade of treatments to reduce invasive buffelgrass (Pennisetum ciliare)
-
- Journal:
- Invasive Plant Science and Management / Volume 16 / Issue 1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 January 2023, pp. 27-37
-
- Article
- Export citation
Waiting is painful: The impact of anticipated dread on negative discounting in the loss domain
-
- Journal:
- Judgment and Decision Making / Volume 17 / Issue 6 / November 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2023, pp. 1353-1378
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Comparing mixed intertemporal tradeoffs with pure gains or pure losses
-
- Journal:
- Judgment and Decision Making / Volume 16 / Issue 3 / May 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2023, pp. 709-728
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation