Vitamin D deficiency has recently been described as being pandemic( Reference Holick 1 ), affecting 50 % of the population worldwide( Reference Caccamo, Ricca and Curro 2 ). Undeniable public health implications may arise as vitamin D insufficiency/deficiency has been associated with various conditions of development and ageing, such as rickets, fractures and osteoporosis, as well as an overall higher risk of all-cause mortality( Reference Gaksch, Jorde and Grimnes 3 , Reference Pilz, Grübler and Gaksch 4 ). Increasingly, the epidemiological evidence is growing to support the role of vitamin D in the aetiology of chronic diseases like cancer, CHD, diabetes, neurological disorders and so on(2).
The main source of vitamin D is cutaneous exposure to UVB radiation from the sun, which catalyses the conversion of 7-dehydrocholesterol in the skin to vitamin D( Reference Hollis 5 ). However, in Northern areas such as Canada, UVB irradiation during winter is insufficient for cutaneous production( Reference Schwartz and Hanchette 6 ). Thus, dietary vitamin D from natural sources (e.g. fish, eggs) and fortified foods (e.g. milk, cereals) and supplements( Reference de Lourdes Samaniego-Vaesken, Alonso-Aperte and Varela-Moreiras 7 ) represents an important source. Vitamin D that is endogenously produced or derived from diet is then converted in the liver to 25-hydroxycholecalciferol (25-hydroxyvitamin D (25(OH)D)) and finally to 1,25(OH)2D primarily in the kidney( Reference Giovannucci 8 ).
The best available biomarker for total vitamin D exposure is serum concentration of 25(OH)D( Reference Johnson and Trump 9 ). However, the cost of its measurement can be prohibitive in an epidemiological study. A suggested cost-efficient alternative is to use models that predict serum 25(OH)D from self-reported values of lifestyle and personal attributes associated with 25(OH)D( Reference Bertrand, Giovannucci and Liu 10 ). Such models have been previously developed( Reference Bertrand, Giovannucci and Liu 10 – Reference Wang, Ingles and Torres-Mejia 24 ) and may have predictive ability for other similar populations. However, models developed within a sub-population of a study, which can then be applied to full study populations, can allow for the consideration of the full range of information that was collected with flexibility on how to best represent the data, which may result in improved prediction ability. We developed and validated multivariable regression models that quantified the relationships between vitamin D determinants measured through an in-person interview and the concentration of serum 25(OH)D in a Montreal, Canada, population.
Methods
Study population and data collection
This study was conducted within the PRevention of OVArian Cancer in Quebec (PROVAQ) study, a population-based case–control study conducted by our team in Montreal, Canada, from 2011 to 2016( Reference Koushik, Grundy and Abrahamowicz 25 ). Cases were women aged 18–79 years with incident epithelial cancer of the ovary, fallopian tube or peritoneum. Population controls, randomly sampled from the Quebec electoral list throughout the recruitment period, were frequency-matched to cases according to 5-year age group and Montreal region. The population for the current study included the first 200 controls that agreed to participate in the PROVAQ study and to provide a blood sample within 2 weeks of participating. This study was conducted according to the guidelines laid down in the Declaration of Helsinki, and all procedures involving human subjects were approved by the Research Ethics Committee of the Centre de recherche du CHUM. Written informed consent was obtained from all participants.
An in-person interview was carried out among all participants to collect information on socio-demographic, reproductive, medical and lifestyle characteristics. Questionnaire items on vitamin D sources included sun exposure during school, work, commuting and leisure activities, as well as sun protection behaviours (e.g. sunscreens, covering body). Dietary vitamin D from natural and fortified foods, supplement use, use of tanning salons and sun vacations was also assessed. Although the questionnaire assessed these exposures over the life course, specific questions also targeted recent exposure (past 2–3 months). The questionnaire also assessed factors related to sun sensitivity, including eye colour, natural hair colour as a teenager, tendency to burn at first summer sun exposure without protection, tanning ability after repeated summer sun exposure and skin tone.
Potential predictors
We considered the following potential predictors based on the most recent exposures occurring in the past 2–3 months (Table 1): age, season of blood draw, self-reported ethnicity, highest education level, menopausal status, BMI, recent sun vacation and sun protection, outdoor time with total sun protection (i.e. arms/legs all covered using clothing or sunscreen), outdoor time with partial sun protection (i.e. arms/legs partially covered using clothing or sunscreen), outdoor time with no sun protection (i.e. no protection from the sun using clothing or sunscreen), vitamin D supplement dose, dietary vitamin D intake, alcohol intake and smoking. Only one woman had recently used tanning salons, and thus this variable could not be considered. Sun vacation was defined as having taken a vacation to a location with a summer climate. Season of blood draw was classified according to summer (April to September) v. winter (October to March), based on the months in Canada that have sufficient v. insufficient UVB irradiation for cutaneous vitamin D synthesis, respectively( Reference Hollis 5 , Reference Webb, Kline and Holick 26 ). Outdoor time was based on the accumulated reported time outside for school, work, commuting and leisure activities. Dietary vitamin D was based on intake of milk, margarine, tuna, salmon (canned, fresh or frozen, smoked), canned sardines and eggs, which are the major natural and fortified dietary sources of vitamin D in Canada( Reference Munasinghe, Willows and Yuan 27 ). The vitamin D content in each food/beverage, obtained from the Canadian Nutrient File( 28 ), was multiplied by the frequency of intake of a standard serving of that food/beverage and then summed to give total dietary vitamin D intake. We also defined a sun sensitivity score variable based on responses to eye colour, hair colour, skin tone, tendency to burn at first exposure to sun and tanning ability( Reference Tacke, Dietrich and Steinebrunner 29 ). For each of these items, responses were assigned a value between 1 and 4, with low values indicating high sun sensitivity and high values indicating low sensitivity, based on the literature when available( Reference Tacke, Dietrich and Steinebrunner 29 , Reference Veierod, Weiderpass and Thorn 30 ). The sum of the values determined the sun sensitivity score, ranging from 5 (highest sun sensitivity) to 19 (lowest sun sensitivity).
Table 1 Distributions of potential vitamin D predictors and their bivariate relationships with total serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25(OH)D) in users and non-users of vitamin D supplements(Mean values and standard deviations and β-coefficients; numbers and percentages)
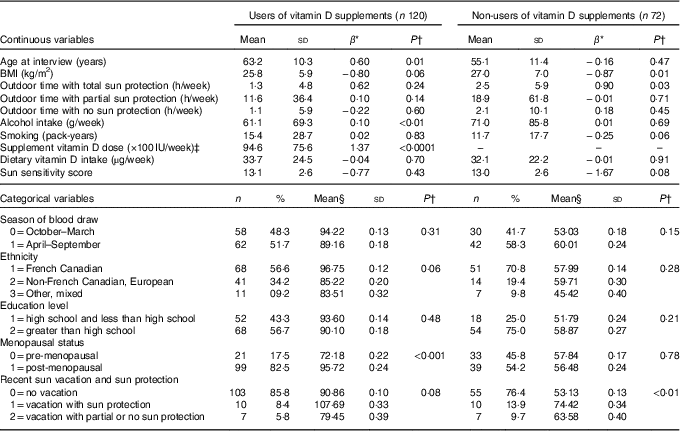
* Regression coefficient (slope) from a simple, bivariate linear regression model between variable and 25(OH)D.
† P-value for the t test of H0: β=0 for continuous variables and µ=µ 0 for categorical variables.
‡ Mean supplement vitamin D dose is equivalent to 236·5 (SD 199·9) μg/week.
§ Mean of the 25(OH)D level in the category of interest.
Laboratory analysis
Serum 25(OH)D3, 25(OH)D2 and 3-epi-25(OH)D3 concentrations were measured by a liquid chromatography–tandem MS method (Department of Clinical Biochemistry, CHU Ste-Justine)( Reference Jensen, Ducharme and Theoret 31 , Reference Jensen, Ducharme and Theoret 32 ). Within each batch, two quality control samples, independent of our study population, were included in duplicate. In addition, 10 % of the study population was measured in duplicate in different batches.
Average intra-batch and inter-batch correlations of variation were below 3 and 5 %, respectively. Quantification of serum 25(OH)D2, 25(OH)D3 and 3-epi-25(OH)D3 concentrations above the limit of detection of our assay was successful for 14, 199 and 131 participants, respectively. For one participant, ion suppression caused a reduced detector response for 25(OH)D3, 25(OH)D2 and 3-epi-25(OH)D3, as well as the internal standards, resulting in uninterpretable values for all three vitamin D metabolites. Concentrations below the limit of detection were assigned a value of 0. Total serum 25(OH)D was calculated as the sum of 25(OH)D2, 25(OH)D3 and 3-epi-25(OH)D3 concentrations (in nmol/l).
Statistical analysis
We developed a series of model-building steps that are outlined below and described in more detail in the online Supplementary material (Section 1). Seven women were missing values for menopausal status (n 5) or smoking (n 2); thus, the final sample size was 192. Modelling was conducted using multivariable least squares regression, using both the forward and backward selection procedures in SAS 9.3. We also used the lasso method in a sensitivity analysis( Reference Tibshirani 33 ). Whenever the forward and backward procedures yielded different predictors, all predictors selected by at least one of the two procedures were included at the next modelling step. As our initial examination of variable distributions showed that the prevalence of vitamin D supplement use was higher than expected based on past studies( Reference Kuhn, Kaaks and Teucher 23 , Reference van der Meer, Boeke and Lips 34 ), we conducted a set of preliminary analyses to examine the interaction between each predictor variable and supplement use. We observed several statistically significant interactions (results not shown), and thus we performed all our multivariable model building separately for users (n 120) and non-users (n 72) of vitamin D supplements.
Step 1: assessing potential non-linearity
We first assessed whether continuous variables would be better represented with the inclusion of a quadratic term to account for non-linearity. At this step, all categorical variables and the linear terms for continuous variables were forced into the model. Selection of quadratic terms was conducted in one model and limited to the quadratic terms that were statistically significant at an α-level of 0·15, which corresponds approximately to the cut-off for improving the model’s Akaike information criterion( Reference Steyerberg, Eijkemans and Harrell 35 ).
Step 2: assessing interactions with season
As season is a strong predictor of 25(OH)D concentrations( Reference Sahota, Barnett and Lesosky 11 ), we hypothesised that season of blood draw may modify relationships between other predictors and 25(OH)D. To ensure that any important interactions with season would be accounted for, we considered the two-way interactions between each of the other predictors and season; all the main effect categorical and linear continuous variables were forced into the model. An α-level of 0·15 was used to determine statistical significance of the interaction term.
Step 3: building alternative multivariable ‘candidate models’
After identifying higher-order terms for inclusion in Steps 1 and 2, four alternative multivariable models of different complexity were built.
Model 3·1: main effects only
The model in Step 3·1 was limited to the main effects variables only. Selection was conducted including all categorical variables and linear terms, with no variables forced. An α-level of 0·15 was used to select the final model variables.
Model 3·2: main effects, plus quadratic and interaction terms
In Step 3·2, the higher-order terms identified in Steps 1 and 2 were now considered, along with all main effects variables. No variables were forced into the models, and an α-level of 0·10 was used to select the final model variables.
Model 3·3: final complex model
In this step, all variables that were selected in Steps 3·1 or 3·2 were considered for selection. No variables were forced into the models, and an α-level of 0·05 was used to select the final model variables.
Model 3·4: final simplified model
In this step, we assessed whether the final model in Step 3·3 could be simplified. Thus, the variables considered for selection were those that were selected in Step 3·3 but excluded any higher-order terms. An α-level of 0·15 was used to select the final model variables.
Lasso model
In a sensitivity analysis, we estimated prediction models for users and non-users of vitamin D supplements using the lasso method through the ‘glmnet’ R package (Section 2, online Supplementary material). All categorical and linear main effects, as well as the higher-order quadratic and interaction terms, were considered simultaneously.
Step 4: validation of model performance
To evaluate the performance of the prediction models generated in Steps 3·1 to 3·4 and the lasso method for users and non-users of vitamin D supplements, we used cross-validation, which approximates the expected performance of the models to predict 25(OH)D in a future independent data set( Reference Harrell 36 ). The performance indicators that we estimated were the R 2 (percentage of the total variation in observed 25(OH)D values explained by the model), the Pearson linear correlation coefficient between the predicted and observed 25(OH)D values and the root mean square prediction error (RMSPE: square root of the mean of the squared differences between the predicted and observed 25(OH)D values). We used the leave-one-out 5-fold procedure( Reference Stone 37 ), where the original data set (for users and non-users separately) was first randomly partitioned into five equal-size sub-samples (or folds). Subsequently, a random sample of four of the sub-samples was used as a ‘training’ sample to re-estimate the parameters of a given model, which was then applied to the remaining ‘testing’ sub-sample to calculate their predicted 25(OH)D concentrations. The predicted and observed 25(OH)D values were then compared, with the users and non-users pooled, to calculate the aforementioned performance indicators. This was repeated five times such that each of the five sub-samples was used exactly once as a ‘testing’ sample while each combination of four sub-samples was used as a ‘training’ sample. To obtain stable and unbiased estimates of the performance indicators, we repeated this leave-one-out 5-fold procedure ten times, with different random partitioning of the original data set each time. The performance statistics were then averaged across the fifty iterations (i.e. ten replications of the five folds). To further assess the performance of all final prediction models, we categorised the observed and the predicted 25(OH)D levels into quartiles and quantified the concordance of the two classifications using the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC)( Reference Hand and Till 38 ).
Application of previously published prediction models
We also evaluated the application of three previously published prediction models( Reference Bertrand, Giovannucci and Liu 10 , Reference Sahota, Barnett and Lesosky 11 ) to our population, one also based on a Canadian population of women in Ontario( Reference Sahota, Barnett and Lesosky 11 ) and the other two based on the Nurses’ Health Studies (NHS and NHSII), which represents the largest and most comprehensive modelling endeavour for 25(OH)D( Reference Bertrand, Giovannucci and Liu 10 ). We calculated the predicted 25(OH)D in our study population using the published regression coefficients for their model variables defined in our population (Section 3, online Supplementary materials), and calculated the Pearson correlation coefficient comparing the predicted to observed 25(OH)D values.
Justification of sample size
Our sample size was determined by the feasibility and budget limits associated with blood collection and the 25(OH)D assay. Thus, we can only provide a post hoc assessment of the statistical power ensured by our fixed sample size of 192 (120 users and seventy-two non-users of vitamin D supplements). Power estimation was carried out using the PASS software program (NCSS Statistical Software)( 39 ) for multivariable linear regression. Because candidate predictors included both categorical and continuous variables, and our focus was not on estimating associations with specific exposure variables, we calculated the minimum R 2 value for an individual predictor variable that can be detected with 80 % power, given the sample size and an α-level of 0·05. In these calculations, we assumed that covariates included in the same multivariable model together explained 20 % of the total variance in 25(OH)D. Under these assumptions, with 120 users of vitamin D supplements, we had 80 % power to detect as significant an individual variable with an R 2 of 5 %, corresponding to a partial correlation of approximately 0·22. For the seventy-two non-users of supplements, we had 80 % power to detect as significant an individual variable with an R 2 of 8 %, corresponding to a partial correlation of about 0·28. If we assumed that covariates included in the same multivariable model together explained more than 20 % of the total variance in 25(OH)D, the minimum detectable R 2 decreased negligibly. Under the most conservative assumption that covariates do not explain any variance, the detectable R 2 increased slightly to 6 and 10 % for supplement users and non-users, respectively. Thus, for both models, we had adequate power to identify and, thus, include in the final multivariable model predictors that explained between 5 and 10 % of the total variance in 25(OH)D concentration.
Results
Bivariate relationships
Table 1 summarises the means and distributions of all continuous and categorical potential predictors, respectively, as well as their bivariate associations with 25(OH)D, separately for vitamin D supplement users and non-users. Mean serum 25(OH)D concentrations were higher for vitamin D supplement users (mean=91·60, sd=27·20) compared with non-users (mean=57·10, sd=20·44). Among vitamin D supplement users, 25(OH)D concentrations increased with increasing age (P=0·01), alcohol intake (P<0·01) and dose of vitamin D supplement intake (P<0·0001), and decreased with increasing BMI (P=0·06). 25(OH)D concentration was higher for French Canadians than for other ethnicities, as well as for post-menopausal v. pre-menopausal women (P<0·0001) and people who had recently taken a sun vacation (P=0·08) (Table 1). Similar to vitamin D supplement users, BMI (P=0·01) was inversely associated with 25(OH)D concentration among non-users. In addition, 25(OH)D concentration was positively associated with longer outdoor time with total sun protection (P=0·03), higher in those who had taken a recent sun vacation (P<0·01), inversely associated with pack-years of smoking (P=0·06) and inversely associated with sun sensitivity score (P=0·08).
Prediction modelling among vitamin D supplement users
In Step 1, quadratic terms suggesting non-linearity were retained for BMI and vitamin D supplement dose (P=0·12 and P=0·07, respectively). In Step 2, the interaction between season and menopausal status was retained (P=0·04).
Table 2 presents the regression coefficients for the variables retained in each of Steps 3·1–3·4 of model building among vitamin D supplement users. In Step 3·1 that considered all linear and categorical main effects terms only, alcohol, outdoor time with partial sun protection and vitamin D supplement dose were positively associated with 25(OH)D. Ethnicity and menopausal status were also associated with 25(OH)D, with French Canadian and post-menopausal women having higher concentrations. 25(OH)D was higher among those who had recently been on a sun vacation with sun protection as compared with those who did not take a sun vacation.
Table 2 Associations from prediction models of lifestyle factors and personal attributes identified in Steps 3·1 to 3·4 and from the lasso procedure with total serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25(OH)D) for vitamin D supplement users
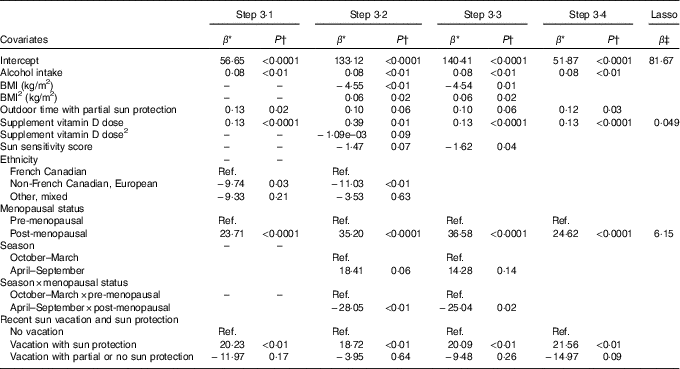
Ref., referent values.
* Regression coefficient from the multivariable linear regression model: it corresponds to the slope for continuous covariates and to the average variation in 25(OH)D level compared with the reference category for categorical variables.
† P-value for the t test of H0: β=0.
‡ Shrinked lasso coefficients.
In Step 3·2, which included the same starting variables as in Step 3·1 along with the higher-order terms identified in Steps 1 and 2, the quadratic terms for BMI and vitamin D supplement dose were retained, as well as the interaction between season and menopausal status. Post-menopausal women had higher 25(OH)D concentrations than pre-menopausal women, but the difference was stronger in winter v. summer months (Table 2). In addition, the sun sensitivity score was retained in this model and showed that those with a lower sun sensitivity (i.e. high score) had lower 25(OH)D. Associations with alcohol, ethnicity and being on a recent sun vacation were similar to those observed in Step 3·1.
In Step 3·3 where the starting variables included all variables retained in Steps 3·1 and 3·2, all of the same variables as in Step 3·2 were retained in the model, except for ethnicity and the quadratic term for supplement vitamin D dose (Table 2). In Step 3·4, which started with the final model from Step 3·3 but removed any higher-order terms (i.e. the quadratic term for BMI and the interaction between menopausal status and season), the main BMI effect, the sun sensitivity score and the main season effect were no longer retained.
Prediction modelling among vitamin D supplements non-users
In Step 1, quadratic terms suggesting non-linearity were retained for BMI, the sun sensitivity score and time spent outdoors without sun protection (P=0·10, P=0·13 and P=0·14, respectively). In Step 2, the interaction with season was retained for education level and dietary vitamin D intake (P=0·04 and P=0·14, respectively).
Table 3 presents the regression coefficients for the variables identified in model building among non-users of vitamin D supplements. In Step 3·1 that considered only linear and categorical main effects terms, age, BMI and the sun sensitivity score were retained and inversely associated with 25(OH)D, whereas higher 25(OH)D concentrations were observed among post-menopausal v. pre-menopausal women, women with a blood draw during the summer v. winter season and those having had a recent vacation v. not having taken a vacation (Table 3).
Table 3 Associations from prediction models of lifestyle factors and personal attributes identified in Steps 3·1 to 3·4 and from the Lasso procedure with total serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25(OH)D) for non-users of vitamin D supplements
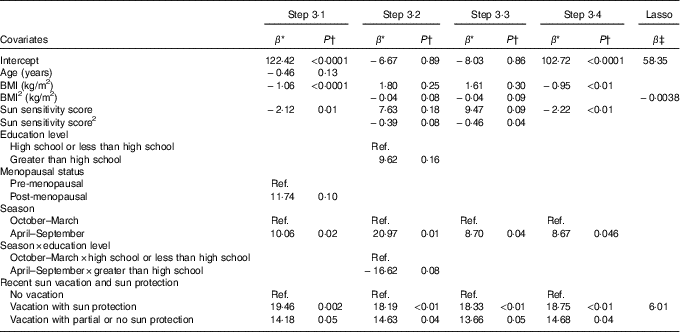
Ref., referent values.
* Regression coefficient from the multivariable linear regression model: it corresponds to the slope for continuous covariates and to the average variation in 25(OH)D level compared with the reference category for categorical variables.
† P-value for the t test of H0: β=0.
‡ Shrinked lasso coefficients.
In Step 3·2 that added the higher-order terms, additional variables that were retained included the quadratic terms for BMI and the sun sensitivity score, as well as the interaction between education level and season. Step 3·3 that considered all retained terms from Steps 3·1 and 3·2 confirmed the associations with BMI, sun sensitivity score, season, vacation with sun protection and 25(OH)D (Table 3). The interaction term between educational level and season was not retained. In Step 3·4, which differed from Step 3·3 only by the exclusion of the quadratic terms for BMI and the sun sensitivity score, all retained variables from Step 3·3 were similarly retained (i.e. BMI, sun sensitivity score, season, sun protection on vacation).
Sensitivity analyses using lasso
The predictors of 25(OH)D identified by the lasso procedure for users of vitamin D supplements were vitamin D supplement dose and menopausal status, both positively associated with 25(OH)D (Table 2). For non-users of vitamin D supplements, the predictors identified were BMI, for which a non-linear effect was observed, and recent vacation with sun protection (Table 3).
Performance of the prediction models
Table 4 presents the cross-validation results for each of the final models identified in Steps 3·1–3·4 and the lasso method. Each predictive model explained a very similar percentage of the total variation in 25(OH)D concentration, with R 2 values ranging from 46 to 47 %. Accordingly, the Pearson correlation coefficients were also very similar across models, and all close to 0·7, indicating a strong correlation between the predicted and observed vitamin D values. Finally, the RMSPE ranged from 21·43 to 21·75, suggesting that in future applications to similar populations the predicted vitamin D concentrations based on our models may diverge on average by about 21–22 nmol/l from the corresponding true values. The model selected by the lasso procedure performed slightly worse, explaining 38 % of the variation of the outcome (R 2), with a Pearson correlation of 0·61 and RMSPE of 24·50.
Table 4 Comparison of performance for different models using cross-validation and AUC statistics
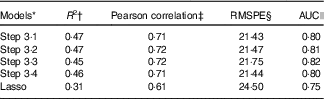
RMSPE, root mean square prediction error; 25(OH)D, 25-hydroxyvitamin D.
† The mean percentage of the total variation of the 25(OH)D values, over ten iterations of the 5-fold cross-validation, explained in the independent ‘testing’ sub-samples by the respective model, with coefficients estimated from the ‘training sub-sample’.
‡ The mean measure of the linear dependence between values predicted by the respective model and the observed values over ten iterations of the 5-fold cross-validation.
§ The mean root mean squared prediction error, i.e. average absolute difference between the 25(OH)D values predicted by the respective model and actually observed over ten iterations of the 5-fold cross-validation.
|| Performance of models when 25(OH)D is categorised into quartiles.
The AUC values indicated satisfactory concordance between quartiles of predicted 25(OH)D, based on each of the four models, and quartiles of actual (measured) 25(OH)D, with the model developed in Step 3·3 having the highest AUC (0·82) and the lasso-based model the lowest AUC (0·75) (Table 4).
Comparison with published prediction models
When previously published prediction models( Reference Bertrand, Giovannucci and Liu 10 , Reference Sahota, Barnett and Lesosky 11 ) were applied to our population, we found that the models from the NHS by Bertrand et al. ( Reference Bertrand, Giovannucci and Liu 10 ) and the Ontario study by Sahota et al. ( Reference Sahota, Barnett and Lesosky 11 ), respectively, systematically under- and over-estimated the concentrations of 25(OH)D of our participants. The mean difference between the predicted v. observed 25(OH)D values was −50·5 and −54·7 nmol/l for the NHS and NHSII models, respectively, by Bertrand et al. ( Reference Bertrand, Giovannucci and Liu 10 ), and 32 nmol/l for the models in Sahota et al. ( Reference Sahota, Barnett and Lesosky 11 ). The Pearson correlation coefficients between the predicted and observed 25(OH)D values (which do not depend on the absolute 25(OH)D values) were 0·37 for the Sahota et al.( Reference Sahota, Barnett and Lesosky 11 ) model and 0·39 and 0·14 for the NHS and NHSII models, respectively.
Discussion
In this study, we developed and validated multivariable models that predict serum concentrations of 25(OH)D, considered the gold-standard measure of current vitamin D status( Reference Horst, Reinhardt and Reddy 40 – Reference Webb 45 ), from vitamin D-related variables derived from interview responses, as a cost-efficient alternative to biomarkers for measuring vitamin D in epidemiological studies. We assessed potentially relevant higher-order effects, not usually considered in traditional prediction modelling. In cross-validation analyses, we contrasted more complex models, which incorporated these higher-order terms with simpler models and found that performance was comparable across all the estimated models with an expected 46–47 % of the total variation in 25(OH)D concentrations explained in an independent sample of women drawn from a population similar to our study participants.
As the performance was so similar across models, our discussion is limited to the simplest model, identified in Step 3·4. Among vitamin D supplement users, predictors of higher 25(OH)D were increasing alcohol intake, hours spent outside with partial sun protection, dose of vitamin D supplement, being post-menopausal and having taken a recent sun vacation. Among non-users of vitamin D supplements, a lower BMI, higher sun sensitivity, having had their blood drawn in the summer months and having taken a recent sun vacation were associated with higher concentrations of 25(OH)D.
Many previous studies have investigated associations between vitamin D-related variables and serum 25(OH)D concentrations, among which we considered eighteen to be comparable to ours as they considered similar vitamin D predictors in populations residing in regions with similar latitudes( Reference Bertrand, Giovannucci and Liu 10 – Reference Wang, Ingles and Torres-Mejia 24 , Reference van der Meer, Boeke and Lips 34 , Reference Looker, Pfeiffer and Lacher 46 , Reference Knight, Wong and Cole 47 ). The predictors most frequently considered among previous studies were season of blood draw( Reference Bertrand, Giovannucci and Liu 10 – Reference Kuhn, Kaaks and Teucher 23 , Reference van der Meer, Boeke and Lips 34 , Reference Looker, Pfeiffer and Lacher 46 , Reference Knight, Wong and Cole 47 ), BMI( Reference Bertrand, Giovannucci and Liu 10 – Reference Touvier, Deschasaux and Montourcy 20 , Reference Hansen, Tang and Hootman 22 – Reference Wang, Ingles and Torres-Mejia 24 , Reference van der Meer, Boeke and Lips 34 , Reference Looker, Pfeiffer and Lacher 46 , Reference Knight, Wong and Cole 47 ), supplemental vitamin D use( Reference Bertrand, Giovannucci and Liu 10 , Reference Sahota, Barnett and Lesosky 11 , Reference Chan, Jaceldo-Siegl and Fraser 13 – Reference Shirazi, Almquist and Malm 18 , Reference Hypponen and Power 21 – Reference Wang, Ingles and Torres-Mejia 24 , Reference Looker, Pfeiffer and Lacher 46 , Reference Knight, Wong and Cole 47 ) and age( Reference Bertrand, Giovannucci and Liu 10 – Reference Greene-Finestone, Berger and de Groh 15 , Reference Richter, Breitner and Webb 17 , Reference Shirazi, Almquist and Malm 18 , Reference Touvier, Deschasaux and Montourcy 20 , Reference Hansen, Tang and Hootman 22 – Reference Wang, Ingles and Torres-Mejia 24 , Reference van der Meer, Boeke and Lips 34 , Reference Looker, Pfeiffer and Lacher 46 , Reference Knight, Wong and Cole 47 ). As we observed among non-users of vitamin D supplements, a higher BMI has consistently been associated with lower 25(OH)D concentrations in all but one study( Reference Hedlund, Brembeck and Olausson 16 ), whereas a summer v. winter blood draw has been associated with a higher 25(OH)D in all studies. Age, however, has been associated with 25(OH)D levels in only eleven of the fourteen studies in which it was considered, and in inconsistent directions( Reference Bertrand, Giovannucci and Liu 10 – Reference Greene-Finestone, Berger and de Groh 15 , Reference Richter, Breitner and Webb 17 , Reference Shirazi, Almquist and Malm 18 , Reference Touvier, Deschasaux and Montourcy 20 , Reference van der Meer, Boeke and Lips 34 , Reference Looker, Pfeiffer and Lacher 46 ). Our findings for age were also inconsistent as it was a predictor only among non-users of vitamin D supplements in model 3·1, and not in other models, nor among vitamin D supplement users. Although cutaneous vitamin D synthesis deteriorates with age, our participants were exposed to vitamin D additionally through dietary and supplemental sources, which may explain the lack of association with age, particularly in supplement users. Regarding vitamin D supplement use, which has been consistently associated with higher 25(OH)D concentrations in past studies( Reference Bertrand, Giovannucci and Liu 10 – Reference Shirazi, Almquist and Malm 18 , Reference Hypponen and Power 21 – Reference Wang, Ingles and Torres-Mejia 24 , Reference Looker, Pfeiffer and Lacher 46 , Reference Knight, Wong and Cole 47 ), we did not examine use v. non-use as a potential predictor of 25(OH)D concentrations; rather, we built our models separately for users and non-users given the high prevalence of use in our study population. However, vitamin D supplement dose was considered among users and a positive association with 25(OH)D concentrations was observed, similar to that seen in eight previous studies that also considered dose( Reference Bertrand, Giovannucci and Liu 10 , Reference Chan, Jaceldo-Siegl and Fraser 13 , Reference Greene-Finestone, Berger and de Groh 15 , Reference Hedlund, Brembeck and Olausson 16 , Reference Shirazi, Almquist and Malm 18 , Reference Kuhn, Kaaks and Teucher 23 , Reference Wang, Ingles and Torres-Mejia 24 , Reference Knight, Wong and Cole 47 ).
Several studies have also considered outdoor time( Reference Sahota, Barnett and Lesosky 11 – Reference Greene-Finestone, Berger and de Groh 15 , Reference Richter, Breitner and Webb 17 , Reference Thuesen, Husemoen and Fenger 19 – Reference Wang, Ingles and Torres-Mejia 24 , Reference van der Meer, Boeke and Lips 34 , Reference Knight, Wong and Cole 47 ) and alcohol intake( Reference Bertrand, Giovannucci and Liu 10 , Reference Cheng, Millen and Wactawski-Wende 14 , Reference Greene-Finestone, Berger and de Groh 15 , Reference Shirazi, Almquist and Malm 18 – Reference Touvier, Deschasaux and Montourcy 20 , Reference Kuhn, Kaaks and Teucher 23 , Reference Knight, Wong and Cole 47 ), and increases in each of these variables have been associated with higher 25(OH)D in the majority of studies, consistent with our results. Aspects of diet have been considered as predictors of 25(OH)D in seventeen studies( Reference Bertrand, Giovannucci and Liu 10 – Reference Hedlund, Brembeck and Olausson 16 , Reference Shirazi, Almquist and Malm 18 – Reference Wang, Ingles and Torres-Mejia 24 , Reference van der Meer, Boeke and Lips 34 , Reference Looker, Pfeiffer and Lacher 46 , Reference Knight, Wong and Cole 47 ), but the majority focused on individual foods or food groups. Only seven studies examined a measure of dietary vitamin D intake from all foods, excluding supplements, as we did( Reference Bertrand, Giovannucci and Liu 10 , Reference Chan, Jaceldo-Siegl and Fraser 13 , Reference Hedlund, Brembeck and Olausson 16 , Reference Shirazi, Almquist and Malm 18 – Reference Touvier, Deschasaux and Montourcy 20 ). Results similar to ours, indicating that dietary vitamin D was not a predictor of 25(OH)D levels, were observed in most of these studies( Reference Chan, Jaceldo-Siegl and Fraser 13 , Reference Hedlund, Brembeck and Olausson 16 , Reference Thuesen, Husemoen and Fenger 19 , Reference Touvier, Deschasaux and Montourcy 20 ). An absence of a relation between dietary vitamin D intake and 25(OH)D level in multivariable models may reflect a greater importance of other determinants. The intake of dietary vitamin D in our study population was very similar to the general Canadian population( 48 ).
Interestingly, our finding of a positive association with outdoor time was among people who used partial sun protection. In all, eight studies( Reference Sahota, Barnett and Lesosky 11 , Reference Chan, Jaceldo-Siegl and Fraser 13 , Reference Greene-Finestone, Berger and de Groh 15 – Reference Richter, Breitner and Webb 17 , Reference van der Meer, Boeke and Lips 34 , Reference Looker, Pfeiffer and Lacher 46 , Reference Knight, Wong and Cole 47 ) have reported on sun protection use, all of which reported an association with 25(OH)D. Our measure of sun protection was combined with outdoor time, which we believe better represents the intensity of sun exposure with outdoor time, as sun protection use reduces cutaneous vitamin D production( Reference Libon, Courtois and Le Goff 49 ). In addition, our estimate of outdoor time was not based on a self-reported global estimate by participants, but rather on distinct questions asking participants to report on their patterns of outdoor time occurring during commuting, work and recreation, which would reduce the error in the overall measure of outdoor time. We also observed an association with recent sun vacation, which has only been considered as a predictor in four previous studies( Reference Sahota, Barnett and Lesosky 11 , Reference Burnand, Sloutskis and Gianoli 12 , Reference Hedlund, Brembeck and Olausson 16 , Reference Richter, Breitner and Webb 17 ).
Among vitamin D supplement users, we observed that post-menopausal women had higher 25(OH)D levels compared with pre-menopausal women in multivariable models. Only four previous studies( Reference Bertrand, Giovannucci and Liu 10 , Reference Sahota, Barnett and Lesosky 11 , Reference Shirazi, Almquist and Malm 18 , Reference Touvier, Deschasaux and Montourcy 20 ) have considered the role of menopausal status on 25(OH)D concentrations, none of which found menopausal status to be a significant predictor of 25(OH)D in multivariable models. It is not clear why menopausal status would be associated with 25(OH)D levels, particularly in multivariable models including other vitamin D predictors. Although vitamin D supplement dose was in our multivariable model, our results pertaining to menopausal status may reflect the fact that all women in this analysis were taking supplements. No other study on predictors of 25(OH)D has stratified on vitamin D supplement use, as we did.
Our study is the first to consider a sun sensitivity score based on eye colour, hair colour, skin colour, tendency to burn and tanning ability. Among non-users of vitamin D supplements, a lower sun sensitivity was associated with lower 25(OH)D. Other studies have considered elements of sun sensitivity such as skin colour, tendency to burn, tanning ability and constitutive skin pigmentation measures( Reference Sahota, Barnett and Lesosky 11 , Reference Chan, Jaceldo-Siegl and Fraser 13 , Reference Cheng, Millen and Wactawski-Wende 14 , Reference Hedlund, Brembeck and Olausson 16 , Reference Richter, Breitner and Webb 17 , Reference Touvier, Deschasaux and Montourcy 20 , Reference Wang, Ingles and Torres-Mejia 24 , Reference Knight, Wong and Cole 47 ), among which two studies reported similar findings to ours where a lower sun sensitivity was associated with lower levels of 25(OH)D( Reference Sahota, Barnett and Lesosky 11 , Reference Wang, Ingles and Torres-Mejia 24 ). In general, the variables selected in our models were associated with 25(OH)D in a manner consistent with what has been previously observed.
In the application of two previously published prediction models( Reference Bertrand, Giovannucci and Liu 10 , Reference Sahota, Barnett and Lesosky 11 ) to our study population, we had all the relevant variables from their models, except UVB flux in the models by Bertrand et al. ( Reference Bertrand, Giovannucci and Liu 10 ). However, our Montreal population did not have meaningful variability in latitude and altitude. We observed that, based on the correlation coefficient, the published models did not perform as well as our own models performed in our study population, which may suggest that population-specific models may be needed for attaining the best predictive ability. However, it is also possible that our parametrisation of certain variables (e.g. outdoor time combined with sun protection in one variable, separate modelling by vitamin D supplement use) may have better captured predictors of 25(OH)D.
Limitations of this study include the small sample size, which combined with a skewed distribution for some variables may have limited our evaluation of their influence on 25(OH)D concentrations. Nonetheless, our cross-validation results indicated that our model explained about 45–47 % of the total variation of 25(OH)D concentrations in an independent sample drawn from our study population. Although the RMSPE of 21–22 nmol/l is too high to precisely predict 25(OH)D values for a given individual, as may be needed in a clinical context, we believe that predictions based on our models could be useful in an epidemiological research setting, where the estimation of a relative risk for the association between vitamin D and a particular disease would be of interest. Indeed, in large population-based epidemiological studies, it may be much easier to collect data on the predictors included in our models than to obtain direct 25(OH)D measurements. However, the measurement error due to discrepancies between predicted and unknown true 25(OH)D levels will result in reduced statistical power, necessitating larger sample sizes, and relative risk estimates will be attenuated. From this perspective, the fact that we estimated the cross-validated RMSPE is of practical importance for future epidemiological studies that use our prediction model, as this estimate will allow the use of the simulation extrapolation (SIMEX) methodology for measurement error correction( Reference Cook and Stefanski 50 ).
In summary, our study found that interview responses to lifestyle and personal attributes were highly predictive of circulating 25(OH)D in a population of middle-aged women. In the absence of available biomarker measures of vitamin D, results from our study support that predicted 25(OH)D scores derived from interview items may be used to assign exposure in epidemiological studies that aim to examine the relation between vitamin D and disease risk.
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to France Dumas for carrying out the blood collection, processing and storage. The authors also thank our interviewers Claire Walker, Françoise Pineault and Martine Le Comte.
This work was supported by the Canadian Cancer Society (grant no. 700485). V. H. received a postdoctoral fellowship from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research and Lung Cancer Canada to conduct this work and is currently supported by the Cancer Research Society, Fonds de recherche du Québec – Santé and Ministère de l'Économie, de la Science et de l’Innovation du Québec. M. A. is a James McGill Professor. A. K. was supported by the Cancer Research Society-Cancer Guzzo Université de Montréal Award, the Fonds de recherche du Québec – Santé Research Scholar Program and the Canadian Institutes of Health Research New Investigator programme.
Each coauthor has directly participated in the planning, execution or analysis of the study. M. A. and A. K. designed the sub-study within the PROVAQ study; J. L. coordinated recruitment and data collection; A.-S. B. and E. D. carried out the 25(OH)D assays; V. H., C. D., M. A. and A. K. designed the analytic strategy and drafted the manuscript; V. H. and C. D. carried out the data analysis; and V. B. assisted in carrying out the literature review.
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Supplementary material
For supplementary material/s referred to in this article, please visit https://doi.org/10.1017/S000711451800199X







