No CrossRef data available.
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 20 September 2019
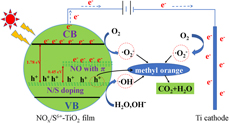
Anatase phase NOx/S6+–TiO2 (x= 0, 1) film with high solar-driven activity has been successfully prepared via electro-assisted oxidation processes. The morphological and structural properties of the film were characterized by scanning electron microscopy, transmission electron microscopy, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, and X-ray diffraction, while the optical property was detected by UV-vis-NIR absorption spectroscopy. The results showed that the NOx/S6+–TiO2 film was composed of “flower-like” microvoids structure and displayed broad and strong optical absorption at around 544 and 1500 nm. Transient photocurrent response, photoluminescence spectroscopy, and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy indicated that the generation and separation of photogenerated charges were significantly enhanced under simulated solar irradiation. The NOx/S6+–TiO2 film exhibited excellent photoelectrocatalytic activity for the degradation of methyl orange (MO), and the decoloration rate and TOC removal respectively reached 98.97 and 59.44% at 20 min under solar irradiation. The film still had good stability after reusing ten times. Furthermore, a possible mechanism of photoelectrocatalysis was suggested in MO degradation by using NOx/S6+–TiO2 film.