1. Introduction
Obesity is a common multifactorial disorder that may cause or exacerbate several major public health problems such as type 2 diabetes, hypertension and coronary heart disease (Frayn & Coppack, Reference Frayn and Coppack1992; Carroll, Reference Carroll1998; Kopelman, Reference Kopelman2000; Shibata et al., Reference Shibata, Sato, Pimentel, Takemura, Kihara, Ohashi, Funahashi, Ouchi and Walsh2005).
Human obesity is the result of complex interactions between genetic and environmental factors (Arya et al., Reference Arya, Duggirala, Jenkinson, Almasy, Blangero, O'Connell and Stern2004). Numerous studies have convincingly established that obesity is under strong genetic control (Price et al., Reference Price, Cadoret, Stunkard and Troughton1987; Barsh et al., Reference Barsh, Farooqi and O'Rahilly2000), with the heritability (h 2) ranging from 0·25 to 0·65 (Price, Reference Price and Wadden2002; Platte et al., Reference Platte, Papanicolaou, Johnston, Klein, Doheny, Pugh, Roy-Gagnon, Stunkard, Francomano and Wilson2003). Total body fat mass (TBFM) and total body lean mass (TBLM) are phenotypic traits, with a strong genetic determination, that have been used to characterize obesity. Previous studies showed that the heritability was 0·2–0·65 for TBFM and 0·52–0·77 for TBLM (Nguyen et al., Reference Nguyen, Sambrook and Eisman1998; Hanisch et al., Reference Hanisch, Dittmar, Hohler and Alt2004; Hsu et al., Reference Hsu, Lenchik, Nicklas, Lohman, Register, Mychaleckyj, Langefeld, Freedman, Bowden and Carr2005; Fischer & Van der Werf, Reference Fischer and Van der Werf2006). Interestingly, TBFM and TBLM are highly correlated, phenotypically and genetically (Gray & Bauer, Reference Gray and Bauer1991; Zhao et al., Reference Zhao, Guo, Xiong, Xiao, Recker and Deng2006), suggesting that they may share common genetic factors.
Recent data demonstrate that adipose tissue acts as an active organ, secreting factors that regulate the metabolism of skeletal muscle (Shimabukuro et al., Reference Shimabukuro, Koyama, Chen, Wang, Trieu, Lee, Newgard and Unger1997). Conversely, it has also been demonstrated that skeletal muscle (largely represented by TBLM (Burr, Reference Burr1997; Van der Meulen et al., Reference Van der Meulen, Moro, Kiratli, Marcus and Bachrach2000; Petit et al., Reference Petit, Beck, Shults, Zemel, Foster and Leonard2005)) can oxidize fat under appropriate physiological conditions (Kelley, Reference Kelley2005) and that inactivation of the melanocortin 3 receptor (MC3R) gene may result in increased body fat at the expense of body lean mass (Chen et al., Reference Chen, Marsh, Trumbauer, Frazier, Guan, Yu, Rosenblum, Vongs, Feng, Cao, Metzger, Strack, Camacho, Mellin, Nunes, Min, Fisher, Gopal-Truter, MacIntyre, Chen and Van der Ploeg2000). In addition, a clinical statistical study (Gray & Bauer, Reference Gray and Bauer1991) reported a linear positive relationship between TBFM and TBLM. Collectively, this biochemical and statistical evidence demonstrated that TBFM and TBLM are highly correlated. Few studies, however, have been performed to unveil the genetic mechanisms underlying this correlation between TBFM and TBLM.
The major purpose of the present study was to identify the specific genetic determinants shared by TBFM and TBLM. In order to accomplish this with a large sample of 3255 Caucasians from 420 pedigrees, we performed bivariate linkage analysis in both the entire sample and a gender-specific subsample, to search for quantitative trait loci (QTLs) that may have pleiotropic effects on TBFM and TBLM.
2. Material and methods
2.1. Subjects
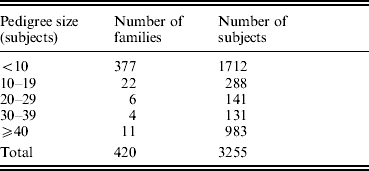
The study was approved by the Creighton University Institutional Review Board. All the study subjects were Caucasians of European origin, and all the subjects signed informed-consent documents before entering the project. The sampling scheme and exclusion criteria have been detailed in previous publications (Deng et al., Reference Deng, Deng, Liu, Liu, Xu, Shen, Conway, Li, Huang, Davies and Recker2002, Reference Deng, Deng, Liu, Liu, Xu, Shen, Conway, Li, Huang, Davies and Recker2003). Briefly, patients with chronic diseases and conditions that might potentially affect bone mass, bone structure or metabolism were excluded. These diseases/conditions included chronic disorders involving vital organs (heart, lung, liver, kidney and brain), serious metabolic diseases (diabetes, hypo- and hyper-parathyroidism, hyperthyroidism, etc.), other skeletal diseases (Paget's disease, osteogenesis imperfecta, rheumatoid arthritis, etc.), chronic use of drugs affecting bone metabolism (hormone replacement therapy, corticosteroid therapy and anticonvulsant drugs), malnutrition conditions (such as chronic diarrhoea and chronic ulcerative colitis) and so forth. The sample contained a total of 3255 subjects from 420 families, and the pedigree size varied from 3 to 384 individuals. The distribution of pedigree size is summarized in Table 1.
Table 1. Distribution of pedigree sizes
2.2. Measurement
The phenotypes of TBFM and TBLM were both measured in grams by a Hologic 1000, 2000t or 4500 dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry scanner (Hologic Corp., Waltham, MA, USA). All the machines were calibrated daily and long-term precision was monitored with external phantoms. Significant efforts were made to measure members of the same pedigree with the same type of machine. The coefficients of variation (CVs; for measurement of reproducibility) for TBFM and TBLM were 1·2 and 1·0%, respectively, with the Hologic 4500 scanner. Similar CVs were observed on Hologic 1000 and 2000t scanners. Weight (kg) and height (m) were measured by using standard methods at the same visit for the TBFM and TBLM measurements.
2.3. Genotyping
For each subject, DNA was extracted from peripheral blood by using a Puregene DNA isolation kit (Gentra Systems, Inc., Minneapolis, MN, USA). All the subjects were genotyped for 410 microsatellite markers (including 392 markers for 22 autosomes and 18 markers for chromosome X) from the Marshfield screening set 14 by Marshfield Center for Medical Genetics. These markers had an average population heterozygosity of 0·75±0·06 and were spaced on the average 8·9 cM apart. The detailed genotyping protocol is available at http://research.marshfieldclinic.org/genetics/Lab_Methods/methods.html. A genetic database management system (GenoDB) (Li et al., Reference Li, Deng, Lai, Xu, Chen, Gao, Recker and Deng2001) was used to manage the phenotype and genotype data for linkage analyses. PedCheck (O'Connell & Weeks, Reference O'Connell and Weeks1998) was employed to check the Mendelian inheritance pattern at all the marker loci and to confirm the alleged relationships of family members within pedigrees. Moreover, we used MERLIN (Abecasis et al., Reference Abecasis, Cherny, Cookson and Cardon2002) to detect genotyping errors of unlikely recombination (e.g. double recombination) in our sample. The overall genotyping error rate was ~0·03%.
2.4. Statistical analyses
The basic characteristics of the study sample were calculated using SAS (SAS Institute, Cary, NC, USA). We also examined phenotypic, genetic and environmental correlations between TBFM and TBLM. Bivariate linkage analysis was performed for TBFM and TBLM using SOLAR v3.0.4 (Sequential Oligogenic Linkage Analysis Routines, available at http://www.sfbr.org/solar/) (Almasy et al., Reference Almasy, Dyer and Blangero1997; Almasy & Blangero, Reference Almasy and Blangero1998; Williams et al., Reference Williams, Van Eerdewegh, Almasy and Blangero1999). The normality of distribution of TBFM and TBLM was indexed by kurtosis, which was 0·28 and 0·64, respectively, within the range that SOLAR requires for robust variance component analysis (kurtosis<2·0) (Amos, Reference Amos1994). Heritability and covariate contributions to each trait variance were estimated by SOLAR. Bivariate linkage analyses were performed for TBFM and TBLM on the 22 autosomes. We performed a two-point linkage analysis on chromosome X, because the current version of SOLAR can only handle two-point analysis on chromosome X. As the currently available version of SOLAR cannot handle multipoint linkage analysis for the X chromosome, we only calculated two-point LOD scores for X-specific markers. Other software, such as GENEHUNTER (Kruglyak et al., Reference Kruglyak, Daly, Reeve-Daly and Lander1996) that is capable of multipoint linkage analysis for the X chromosome, however, cannot handle large pedigrees that made up the major part of our sample. Breaking down the large pedigrees into smaller ones might be an option, but this procedure would result in a considerable loss of statistical power.
Bivariate quantitative genetic analysis is a powerful method to directly evaluate the degree of genetic and environmental correlations between pairs of traits. We estimate the genetic correlations ρG and environmental correlations ρE between the studied pairs of phenotypes, based on the maximum likelihood ratio and variance component decomposition. The phenotypic correlations ρP between the studied pairs of phenotypes were divided into the portions due to genes shared in common and that due to the shared environment, as shown in the formula below:
where h 12 and h 22 are the respective heritabilities of traits 1 and 2. The significance of ρG, ρE and ρP was determined by the likelihood ratio test, which compares the likelihood of a full model with that of a constrained one in which the particular component is constrained to zero. Genetic correlations are 0·91 (±0·01) between weight and TBFM, 0·21(±0·046) between height and TBFM, 0·87 (±0·013) between weight and TBLM, 0·53 (±0·03) between height and TBLM, respectively. Thus, weight and height are highly genetically correlated with the two studied traits and not suitable for covariates in the bivariate linkage model. Herein, only age and gender were incorporated as covariates in the analyses.
The bivariate linkage analysis extended the univariate variance components approach to the multivariate framework. Briefly, the phenotype covariance is further decomposed into a genetic part and an environmental part. The information from the genetic correlation between two traits caused by additive genetic effects and the shared effects of the QTLs could be incorporated into the analysis. The covariation between two individuals for two traits can be given by:
where Δ is a covariance matrix of 2×2 covariance matrices, where the elements are defined by
where σqaσqb is the additive genetic variance caused by the major locus, σgaσgb is the genetic variance caused by residual additive genetic factors, σeaσeb is the variance caused by individual-specific environmental effects, and ρg and ρe are the additive genetic and environmental correlations between the two traits. More detailed descriptions for ![]() , Φ and I were provided elsewhere (Almasy et al., Reference Almasy, Dyer and Blangero1997; Almasy & Blangero, Reference Almasy and Blangero1998). Briefly,
, Φ and I were provided elsewhere (Almasy et al., Reference Almasy, Dyer and Blangero1997; Almasy & Blangero, Reference Almasy and Blangero1998). Briefly, ![]() estimates the probability that individuals are identity by descent (IBD) at a QTL linked to a genetic marker locus, Φ is the kinship matrix and I is an identity matrix. If a=b, it is a univariate genetic linkage analysis model. In the univariate linkage analysis, twice the difference between the log10 likelihoods of these models yields a test statistic that is asymptotically distributed as a
estimates the probability that individuals are identity by descent (IBD) at a QTL linked to a genetic marker locus, Φ is the kinship matrix and I is an identity matrix. If a=b, it is a univariate genetic linkage analysis model. In the univariate linkage analysis, twice the difference between the log10 likelihoods of these models yields a test statistic that is asymptotically distributed as a ![]() mixture of a χ2 variable and a point mass at zero (Self & Liang, Reference Self and Liang1987).
mixture of a χ2 variable and a point mass at zero (Self & Liang, Reference Self and Liang1987).
In the bivariate linkage analysis model, we compared the likelihood of a restricted model in which σq12 and σq22 are constrained to 0 (no-linkage) for both traits with that of a model in which they are estimated for the traits. Twice the difference in ln likelihoods of these models yields a test statistic that is asymptotically distributed as a mixture distribution of ![]() (Almasy et al., Reference Almasy, Dyer and Blangero1997; Almasy & Blangero, Reference Almasy and Blangero1998). Noticeably, by default, the current version of SOLAR provides easily interpreted ‘one degree of freedom effective’ LOD scores equivalent to those in classical univariate models automatically in a bivariate linkage analysis.
(Almasy et al., Reference Almasy, Dyer and Blangero1997; Almasy & Blangero, Reference Almasy and Blangero1998). Noticeably, by default, the current version of SOLAR provides easily interpreted ‘one degree of freedom effective’ LOD scores equivalent to those in classical univariate models automatically in a bivariate linkage analysis.
To identify gender-specific QTLs, we also conducted the bivariate linkage analyses in females and males, separately. In gender-specific linkage analyses, phenotypic values for individuals of the opposite sex were recorded as missing. IBD estimation was obtained by the total samples.
We also performed further analyses to differentiate the pleiotropic effect of a specific locus and co-incident linkage of tightly linked loci within the disclosed genomic regions. Briefly, likelihoods of the linkage model in which ρm was estimated (ρm, namely rhoq, a measure of the shared major gene effect near the region for which linkage is being assessed) were compared with that of the model in which ρm was constrained to 0 (i.e. co-incident linkage), or compared with that of the model in which ρm was constrained to 1 (complete pleiotropy) (Self & Liang, Reference Self and Liang1987; Almasy et al., Reference Almasy, Dyer and Blangero1997). The possibility of co-incident linkage and complete pleiotropy was denoted by p 1 and p 2 in the results, respectively.
3. Results
3.1. Basic characteristics
The basic characteristics of all the subjects in the study sample, which contained a total of 3255 subjects from 420 pedigrees, are presented in Table 2. Generally, TBFM in female subjects was higher than TBFM in age-matched males. Accordingly, TBLM in females was lower than TBLM in age-matched males. As shown in Table 3, our sample contained a large number of relative pairs informative for linkage analyses. The correlations between TBFM and TBLM, shown in Table 4, indicate significant phenotypic and genetic correlations (ρG=0·606, ρP=0·593) between the two traits.
Table 2. The basic characteristics (mean±SD) of the study sample (n=3255)

Note: Only subjects with both genotypes and phenotypes of TBFM and TBLM were included.
Table 3. The informative relationships in our sample
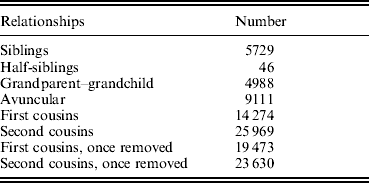
Table 4. Correlations (±SE) between TBFM and TBLM

Note: ρE, ρG and ρP denote environmental, genetic and phenotype correlations, respectively. All P<0·0001.
3.2. Bivariate linkage analysis
Figure 1 displays bivariate linkage signals (multipoint LOD scores) on the 22 autosomes for both the whole sample and for gender-specific groups. Utilizing the widely adopted threshold for ‘suggestive’ linkage (LOD⩾1·90) (Lander & Kruglyak, Reference Lander and Kruglyak1995), we summarize the main results of bivariate linkage analysis in Table 5 and Fig. 2. Suggestive linkage was found on chromosome 20p12-11 (LOD=2·04, P=0·0011) in the total sample. Male-specific QTLs were found on chromosomes 20p12 (LOD=2·08, P=0·0010) and 3p26-25 (LOD=1·92, P=0·0015). However, we did not find any suggestive linkage for females.

Fig. 1. Bivariate linkage results of multipoint WGLS (whole genome linkage scan) for autosomes in the entire sample, female sample and male sample. Note: Maximum LOD scores across the autosomes.

Fig. 2. Bivariate linkage analysis results for TBFM and TBLM. (A) Results of chromosome 20 for the entire sample. (B) Results of chromosome 20 for males. (C) Results of chromosome 3 for males.
Table 5. Results of bivariate linkage analyses
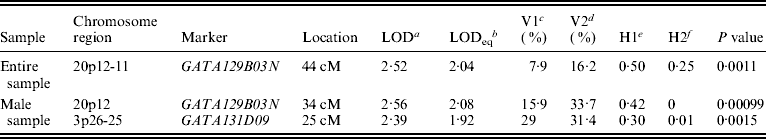
a Bivariate LOD scores.
b Univariate LOD equivalent to bivariate LOD.
c V1 denotes body lean mass variance.
d V2 denotes body fat mass variance.
e H1 denotes body lean mass heritability.
f H2 denotes body fat mass heritability.
3.3. Two-point linkage analyses on chromosome X
Since SOLAR cannot handle multipoint linkage analysis for chromosome X, we only conducted two-point linkage analyses on chromosome X. Table 6 lists the suggestive linkage results from bivariate linkage analysis on chromosome X for both the entire sample and for sex-specific subgroups. For the entire sample, the highest LOD score was detected at GATA175D03 (Xp22) with LOD=2·14. With the female-specific sample, significant linkage (LOD=3·05) was found at Xp22 near the marker GATA175D03. No evidence of linkage was found in the male group.
Table 6. Results of two-point bivariate linkage analysis on chromosome X

a Bivariate LOD scores.
b Univariate LOD equivalent to bivariate LOD.
c V1 denotes body lean mass variance.
d V2 denotes body fat mass variance.
e H1 denotes body lean mass heritability.
f H2 denotes body fat mass heritability.
3.4. Pleiotropy vs. co-incident linkage
Using a P value of 0·01 as a cutoff point for the rejection of either complete pleiotropy or co-incident linkage (Almasy et al., Reference Almasy, Dyer and Blangero1997), the discrimination analysis suggested that 20p12 (34 cM, p 1<0·001, p 2=0·7363) and 3p26-25 (25 cM, p 1<0·001, p 2=0·8288) have complete pleiotropic effects on TBFM and TBLM in the male. Incomplete or partial pleiotropy was suggested for the other regions.
4. Discussion
During the past decade, a number of investigators have attempted to identify specific chromosomal regions and/or genes that contribute to the development of obesity. Though many of these studies have successfully identified genes or chromosomal regions that putatively contribute to the development of obesity, there have been many inconsistencies between the findings of these studies. It is highly plausible that a lack of methodological stringency may be one potential explanation for the inconsistent results between studies. Consequently, we considered it important to apply a more robust bivariate linkage analysis, compared with a univariate linkage analysis, to more effectively identify QTLs underlying obesity (Marlow et al., Reference Marlow, Fisher, Francks, MacPhie, Cherny, Richardson, Talcott, Stein, Monaco and Cardon2003). Our current study utilizes a novel method and serves as an example of the bivariate linkage approach to genetic studies of complex diseases, such as obesity.
To our knowledge, our study is the first to search for QTLs having pleiotropic effects on two highly correlated obesity traits, TBFM and TBLM. Evidence for linkage between the two traits was found at 20p12-11, 20p12, 3p26-25, Xp22 and Xq24, among which 20p12 and 3p26-25 are male-specific and showed complete pleiotropy.
For convenience, we list previously reported obesity-related genes that map to any of the regions we have discovered in the current study (Table 7); these genes can be regarded as candidate genes for both TBFM and TBLM, and will be the focus of our future investigations. Obviously, we cannot exclude the possibility that the chromosomal regions we have identified contain additional genes that have not been previously associated with obesity.
Table 7. Candidate genes around the disclosed genomic regions showing evidence of suggestive linkage

Generally, the bivariate linkage analysis in which the correlations between the phenotypes are explicitly modelled can provide greater statistical power for identifying QTLs whose effects are too small to be detected by univariate analysis of individual traits. In our earlier study (Zhao et al., Reference Zhao, Xiao, Liu, Xiong, Shen, Recker and Deng2007), using the same sample as this study, a univariate whole genome linkage scan was conducted for four obesity-related phenotypes, including TBFM and TBLB. In that study, for TBFM, linkage evidence was found on 20p11-12 (LOD=3·31), 8q13 (LOD=2·06), 10p12 (LOD=1·90) and 17q11 (LOD=1·97) in the entire sample, and 20p12 (LOD=3·24), 18p11 (LOD=2·22) and 4q21 (LOD=2·70) were linked in males (Zhao et al., Reference Zhao, Xiao, Liu, Xiong, Shen, Recker and Deng2007). For TBLM, linkages were found on 5q35 for both the entire sample (LOD=2·54) and for males (LOD=3·50), whereas 7q32 (LOD=2·79) and 15q13 (LOD=2·72) were found to be linked in females (Zhao et al., Reference Zhao, Xiao, Liu, Xiong, Shen, Recker and Deng2007). Our current study showed consistency with our earlier study (Zhao et al., Reference Zhao, Xiao, Liu, Xiong, Shen, Recker and Deng2007), but expanded the findings by revealing the pleiotropic effects on 20p12 and 3p26-25. Our current bivariate linkage study highlighted the importance and the necessity to explore the pleiotropic QTLs responsible for the highly correlated obesity phenotypes. Our data showed that body fat mass and lean mass are significantly correlated. In this study, environmental, genetic and phenotypic correlations between body fat mass and body lean mass were positive and strong, which is consistent with our previous univariate study (Zhao et al., Reference Zhao, Guo, Xiong, Xiao, Recker and Deng2006). This study represented our effort to investigate the potential mechanisms underlying the genetic correlation between body fat mass and body lean mass.
In general, univariate analysis has some potential limitations in dealing with multiple correlated traits. First, there are unresolved issues regarding how to properly adjust for the multiple testing of correlated measures. Second, there is a potential loss in power when not analysing all of the correlated traits simultaneously (Boomsma & Dolan, Reference Boomsma and Dolan1998). Bivariate genetic linkage analysis may have some advantages in resolving these problems (Marlow et al., Reference Marlow, Fisher, Francks, MacPhie, Cherny, Richardson, Talcott, Stein, Monaco and Cardon2003) and may provide greater power than univariate analysis for identifying QTLs with pleiotropic effects.
In this study, two interesting regions at 20p12 and 3p26-25 were found to have pleiotropic effects on TBFM and TBLM. Region 20p12 contains several obesity-related genes such as the McKusick–Kaufman syndrome (MKKS) (Katsanis et al., Reference Katsanis, Beales, Woods, Lewis, Green, Parfrey, Ansley, Davidson and Lupski2000, Reference Katsanis, Ansley, Badano, Eichers, Lewis, Hoskins, Scambler, Davidson, Beales and Lupski2001; Slavotinek et al., Reference Slavotinek, Stone, Mykytyn, Heckenlively, Green, Heon, Musarella, Parfrey, Sheffield and Biesecker2000), VSX1 (Hayashi et al., Reference Hayashi, Huang and Deeb2000; Semina et al., Reference Semina, Mintz-Hittner and Murray2000) and FOXA2 (Wolfrum et al., Reference Wolfrum, Shih, Kuwajima, Norris, Kahn and Stoffel2003). Among these genes, MKKS is the most intriguing candidate gene, because mutations in MKKS gene have been shown to cause the Bardet–Biedl syndrome (BBS), characterized by obesity and diabetes (Green et al., Reference Green, Parfrey, Harnett, Farid, Cramer, Johnson, Heath, McManamon, O'Leary and Pryse-Phillips1989). It has also been reported that among middle-aged men, the codon 517 MKKS variant was more prevalent among lean men than among obese men (Andersen et al., Reference Andersen, Echwald, Larsen, Hamid, Glumer, Jorgensen, Borch-Johnsen, Andersen, Sorensen, Hansen and Pedersen2005) and it has been proposed that MKKS is involved in molecular mechanisms governing the regulation and distribution of body fat (Katsanis et al., Reference Katsanis, Beales, Woods, Lewis, Green, Parfrey, Ansley, Davidson and Lupski2000).
Region 3p26-25 also contains several candidate genes related to obesity, such as peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPARG) (Agarwal & Garg, Reference Agarwal and Garg2002; Savage et al., Reference Savage, Tan, Acerini, Jebb, Agostini, Gurnell, Williams, Umpleby, Thomas, Bell, Dixon, Dunne, Boiani, Cinti, Vidal-Puig, Karpe, Chatterjee and O'Rahilly2003), GHRL (Miraglia et al., Reference Miraglia del Giudice, Cirillo, Santoro, D'Urso, Carbone, Di Toro and Perrone2001; Ukkola et al., Reference Ukkola, Ravussin, Jacobson, Snyder, Chagnon, Sjostrom and Bouchard2001; Korbonits et al., Reference Korbonits, Gueorguiev, O'Grady, Lecoeur, Swan, Mein, Weill, Grossman and Froguel2002), HRH1 (Masaki et al., Reference Masaki, Chiba, Yasuda, Noguchi, Kakuma, Watanabe, Sakata and Yoshimatsu2004) and PPP1R3A (Savage et al., Reference Savage, Tan, Acerini, Jebb, Agostini, Gurnell, Williams, Umpleby, Thomas, Bell, Dixon, Dunne, Boiani, Cinti, Vidal-Puig, Karpe, Chatterjee and O'Rahilly2003). Among these potential candidate genes, we are particularly interested in PPARG because it has been associated with human lipodystrophy (Hegele et al., Reference Hegele, Cao, Frankowski, Mathews and Leff2002) and because several oxidative genes are under the transcriptional control of PPARG coactivator-1α (PPARGC1A), which stimulates oxidative phosphorylation, mitochondrial biogenesis and the generation of oxidative type 1 muscle fibres (Lin et al., Reference Lin, Wu, Tarr, Zhang, Wu, Boss, Michael, Puigserver, Isotani, Olson, Lowell, Bassel-Duby and Spiegelman2002).
In summary, our study represents a further effort to identify the QTLs having pleiotropic effect on TBFM and TBLM, with several genomic regions showing suggestive linkage. Our study provides a basis for further endeavours to find the genes, and their functions, contributing to variation in both TBFM and TBLM and eventually help uncover the mechanism underlying the complicated aetiology of obesity.
The authors were partially supported by grants from the NIH (R01 AR050496, K01 AR02170-01, R01 AR45349-01 and R01 GM60402-01A1) and an LB595 grant from the State of Nebraska. The study also benefited from grants from Project 30570875 supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, Xi'an Jiaotong University and the Ministry of Education of China. The genotyping experiment was performed by the Marshfield Center for Medical Genetics and was supported by the NHLBI Mammalian Genotyping Service (contract number HV48141).











