Airy Functions
The functions ![]() and
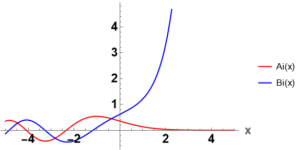
and ![]() are called “Airy functions” of the first and second kind respectively. Their plots are shown below.
are called “Airy functions” of the first and second kind respectively. Their plots are shown below.
For negative ![]() both functions oscillate and approach 0 as
both functions oscillate and approach 0 as ![]() . For positive
. For positive ![]() the function
the function ![]() monotonically decays towards zero and the function
monotonically decays towards zero and the function ![]() approaches
approaches ![]()
![]() .
.
The values of ![]() where
where ![]() (all at
(all at ![]() ) can’t be expressed in a simple form, so we label them
) can’t be expressed in a simple form, so we label them ![]() , where
, where ![]() is the first one,
is the first one, ![]() is the second one, and so on. Similarly, the zeroes of
is the second one, and so on. Similarly, the zeroes of ![]() are
are ![]() ,
, ![]() , and so on.
, and so on.
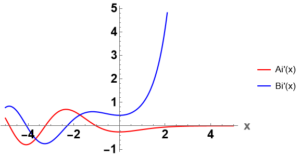
The derivatives of the Airy functions look similar.
We can label the zeroes of the derivatives in the same way: ![]() ,
, ![]() , and so on.
, and so on.
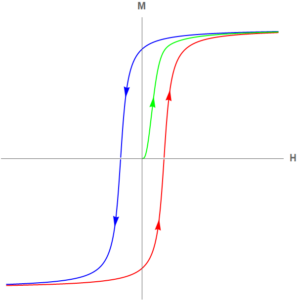
Hysteresis loop
M (internally generated field) vs H (externally applied field)
The green curve represents the initial change starting from the origin (no field of any kind). Thereafter the curve never returns to the origin, because when the external field is zero, the aligned domains still create a non-zero internal field.