Article contents
Penalization versus Goldenshluger − Lepski strategies in warped bases regression
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 17 May 2013
Abstract
This paper deals with the problem of estimating a regression function f,
in a random design framework. We build and study two adaptive estimators based on model
selection, applied with warped bases. We start with a collection of finite dimensional
linear spaces, spanned by orthonormal bases. Instead of expanding directly the target
function f on these bases, we rather consider the expansion of
h = f ∘ G-1, where
G is the cumulative distribution function of the design, following
Kerkyacharian and Picard [Bernoulli 10 (2004) 1053–1105].
The data-driven selection of the (best) space is done with two strategies: we use both a
penalization version of a “warped contrast”, and a model selection device in the spirit of
Goldenshluger and Lepski [Ann. Stat. 39 (2011) 1608–1632].
We propose by these methods two functions, ĥl
(l = 1, 2), easier to compute than least-squares estimators. We
establish nonasymptotic mean-squared integrated risk bounds for the resulting estimators,
\hbox{$\hat{f}_l=\hat{h}_l\circ G$}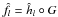 f̂l = ĥl°G if G is known, or
\hbox{$\hat{f}_l=\hat{h}_l\circ\hat{G}$}
f̂l = ĥl°G if G is known, or
\hbox{$\hat{f}_l=\hat{h}_l\circ\hat{G}$}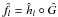 f̂l = ĥl°Ĝ
(l = 1,2) otherwise, where Ĝ is the
empirical distribution function. We study also adaptive properties, in case the regression
function belongs to a Besov or Sobolev space, and compare the theoretical and practical
performances of the two selection rules.
f̂l = ĥl°Ĝ
(l = 1,2) otherwise, where Ĝ is the
empirical distribution function. We study also adaptive properties, in case the regression
function belongs to a Besov or Sobolev space, and compare the theoretical and practical
performances of the two selection rules.
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- © EDP Sciences, SMAI, 2013
References
- 13
- Cited by




