An integer n may be partitioned into the set of integers (α1, α2, …, αl), where 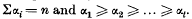 Whenever αi−1>αi the substitution of αi+1 for αi, where αi may be αi+1≡0, would give a partition of n+1 whilst the substitution of αi−1—1 for αi−1 would give a partition of n—1; partitions of n+1 and of n—1 so arising will be said to be associated with the given partition of n.
Whenever αi−1>αi the substitution of αi+1 for αi, where αi may be αi+1≡0, would give a partition of n+1 whilst the substitution of αi−1—1 for αi−1 would give a partition of n—1; partitions of n+1 and of n—1 so arising will be said to be associated with the given partition of n.