Suicide is a leading cause of death and there is an urgent need for more research to understand, predict and prevent it.Reference Gordon, Avenevoli and Pearson1 Suicide research, however, comes with a unique set of ethical challenges.Reference Pearson, Stanley, King and Fisher2 A long-standing concern has been whether asking people about suicide might be harmful.Reference Blades, Stritzke, Page and Brown3 Prior research has found that asking about suicide at one point in time is not iatrogenic.Reference DeCou and Schumann4–Reference Gould, Marrocco, Kleinman, Thomas, Mostkoff and Cote6 Researchers are increasingly using real-time monitoring methods with multiple smartphone-based surveys each day.Reference Kleiman and Nock7 In clinical settings, patients are often asked repeatedly about their suicidal thinking to ascertain suicide risk. Therefore, it is important to know whether asking about suicide repeatedly is iatrogenic. Here we used a real-time monitoring design to test two questions about the safety of this approach: (a) does repeatedly assessing suicidal thinking over short periods of time increase suicidal thinking, and (b) is more frequent assessment of suicidal thinking associated with more severe suicidal thinking?
Method
Participants were 101 adults who had reported active suicidal thoughts in the previous week. Participants were recruited with online advertisements on Reddit and Craigslist. The history of suicidal thoughts and behaviours in the sample was 64% lifetime suicide attempt and 38% past year suicide attempt; the median number of lifetime days with active suicidal thoughts was 1825 (range 30–8000 days).
Each participant downloaded a smartphone-based survey app that sent them three types of survey over a 6-week period: daily surveys (1 time per day), momentary surveys (5 times per day) and burst surveys (6 times/h, 2 per day, 4 days/week). Four days a week, participants received 18 surveys per day (1 daily, 5 momentary and 12 burst surveys) and three days a week, participants received 6 surveys per day (1 daily and 5 momentary surveys). Each survey assessed the desire, urge and intent to kill oneself on a 0 (not at all) to 10 (very much) scale, and scores were combined to create a suicidal thinking severity score. At the end of every momentary and daily survey, participants were provided with a list of hotlines and resources.
The authors assert that all procedures contributing to this work comply with the ethical standards of the relevant national and institutional committees on human experimentation and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1975, as revised in 2008. All study procedures were approved by the Harvard University-Area Institutional Review Board (IRB no. 19-1819; ‘High-resolution real-time capture of suicidal thoughts and urges’). Written informed consent was obtained from all participants.
For question (a), we ran a three-level ordinal model in which responses were nested within participants and burst episodes (total number of surveys n = 10 479 over 2890 episodes). The predictor was time (i.e. minutes between the first completed burst survey and the last burst survey). If frequent assessments were iatrogenic, we would expect to see a positive association between the severity of suicidal thinking over time during a burst episode. To address the possibility that those with increased suicidal thoughts stopped completing surveys, we ran a multilevel survival analysis on missing data. The outcome was time (i.e. minutes between the first and the last completed burst surveys) with a binary variable (suicidal thinking increased versus no change/decreased) as the predictor. If assessments were iatrogenic, participants with increased suicidal thinking would stop assessments earlier. The survival analysis was estimated using the ‘coxme’ package.Reference Therneau8
For question (b), we ran a multilevel ordinal model in which the outcome was daily reports of the severity of suicidal thinking (total number of surveys n = 2314) and the predictor was a day with burst surveys (maximum n = 18 surveys sent) or without burst surveys (maximum n = 6 surveys sent). As a sensitivity analysis, we examined whether the effect of number of surveys per day differed by suicide attempt history (present versus absent). If high-risk participants were more affected by the assessments, we would expect there to be a significant interaction between number of surveys per day and suicide attempt history.
All multilevel models were estimated within a Bayesian framework with the ‘brms’ package.Reference Bürkner9 Results were interpreted by summarising the 95% highest density interval (HDI) around the median beta values. If the 95% HDI includes zero, it is indicative of a null effect.
Results
Frequently assessing suicidal thoughts was not associated with a change in the severity of suicidal thoughts (median 0.002, 95% HDI = 0.000–0.004). The trajectories of suicidal thinking are shown in Fig. 1. Those with increased suicidal thinking were less likely to stop completing assessments (HR = 0.90, 95% CI 0.84–0.96, P < 0.001). At the daily level, there was no association between the frequency of assessments and the severity of suicidal thoughts (median 0.068, 95% HDI −0.088 to 0.225, Fig. 1). There was no significant interaction between suicide attempt history and the frequency of assessments on the severity of suicidal thoughts (median 0.276, 95% HDI −0.077 to 0.594).
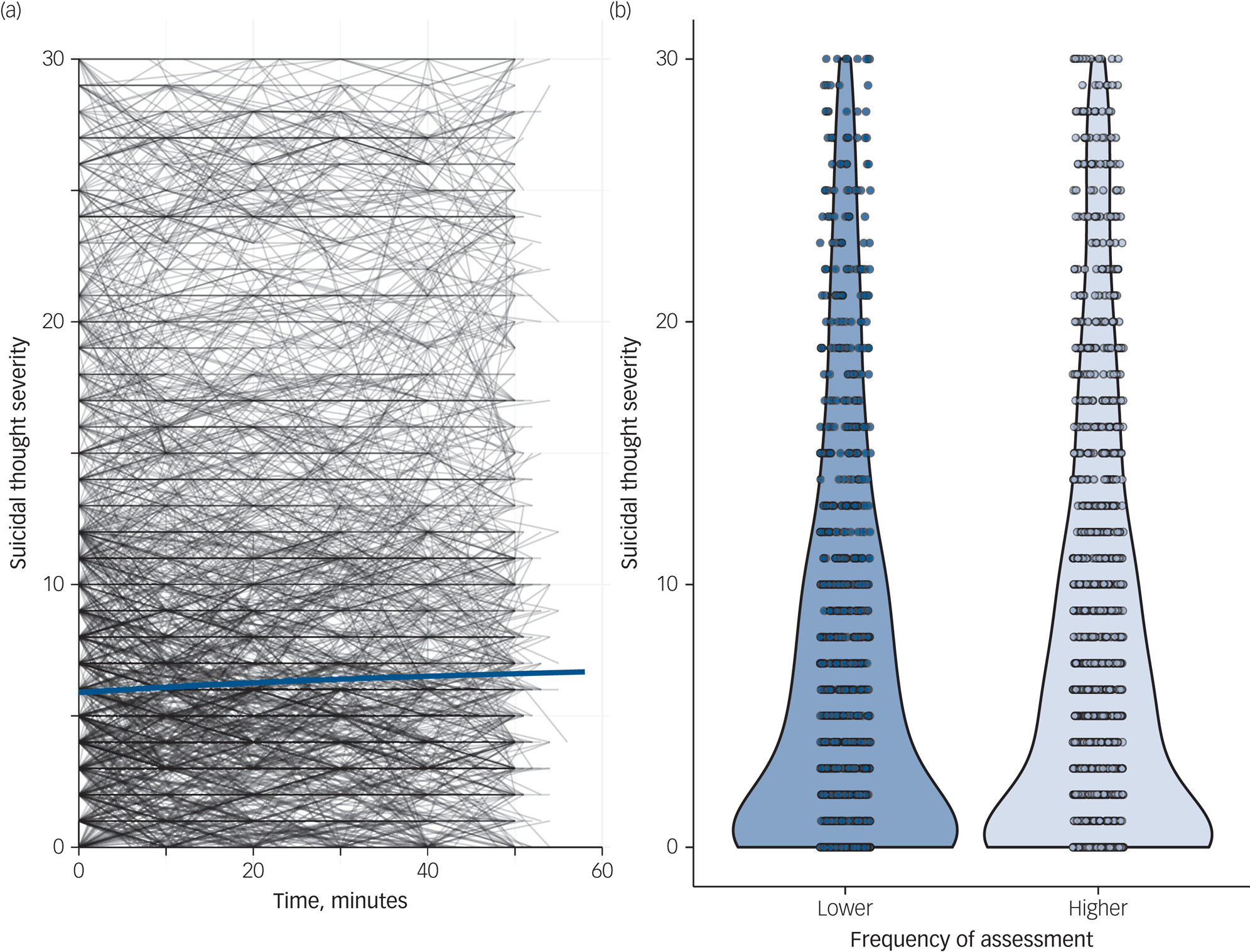
Fig. 1 The effects of frequent assessment of suicidal thinking.
(a) Suicidal thought severity trajectories over 1 h: the blue line represents a smoothed average. (b) Daily suicidal thought severity by frequency of real-time assessments: lower, maximum of 6 surveys per day; higher, maximum of 18 surveys per day.
Discussion
This is the highest-resolution study to date on the potential iatrogenic effects of assessing suicidal thoughts. We found no evidence to support the notion that repeated assessment of suicidal thoughts is iatrogenic. These findings align with prior research on longer-term reactivity.Reference Law, Furr, Arnold, Mneimne, Jaquett and Fleeson10 A limitation of the current study is the potential selection biases of the recruitment strategy. An important future direction would be to replicate these findings among high-risk populations (e.g. psychiatric in-patients). For both participant safety and scientific ecological validity, the lack of reactivity to frequent assessments supports the safety of the frequent assessment of suicidal thoughts.
Funding
This research was supported by the Pershing Square Venture Fund for Research on the Foundations of Human Behavior, the Chet and Will Griswold Suicide Prevention Fund, the Knox Fund at Harvard University, and the Sydney DeYoung Foundation. D.D.L.C. is supported by the National Science Foundation Graduate Research Fellowship under grant no. DGE-1745303. This content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Science Foundation.
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Author contributions
D.D.L.C. and R.G.F. collected the data for the study and take responsibility for the integrity of the data and analysis. D.D.L.C., R.G.F., E.M.K., A.J.M. and M.K.N. conceptualised the design of the study. D.D.L.C. and P.M. conducted the analyses. D.D.L.C., R.G.F., P.M. and M.K.N. interpreted the analyses. D.D.L.C. drafted the initial version of the manuscript. All authors provided critical revisions of the manuscript. All authors reviewed the final version of the draft.
Declaration of interest
M.K.N. has in the past year received consulting fees for a legal case about suicide and is an unpaid scientific advisor for TalkLife and Empatica.




eLetters
No eLetters have been published for this article.