LEARNING OBJECTIVES
-
Be aware of the frequency, associations and clinical significance of hallucinatory experiences in general populations of children and young people
-
Know how to conduct clinical assessments of children and young people presenting with hallucinatory experiences, taking into account developmental considerations
-
Be able to recognise the characteristics and clinical associations of hallucinations in children with psychotic and/or non-psychotic disorders and understand the therapeutic implications
From the earliest stages of life, the experiences of smelling, touching, tasting, hearing and seeing are the front door through which babies relate to the world that surrounds them. Sensations are interpreted as perceptions and processed into inner representations mediated by complex cognitive processing in the brain, involving the optimal combination of new sensory inputs with prior knowledge (Reference Jardri, Bartels-Velthuis and DebbaneJardri 2014). Human perception can be distorted in different ways. Taking into account the presence or absence of external stimuli, and the level of consciousness, a variety of perception distortions are defined (Table 1) (Reference Casey and BrendanCasey 2007).
TABLE 1 Psychopathology of human perception: sensory distortions
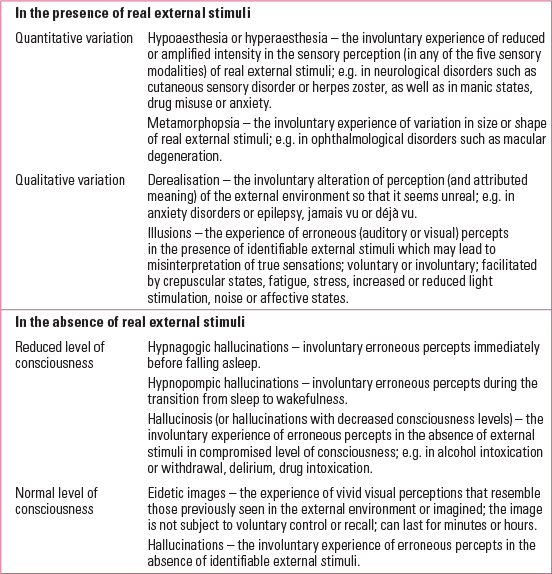
Hallucinations refer to sensory experiences that occur: (i) in the absence of corresponding external stimulation of the relevant sensory organ, (ii) in the awake state and (iii) with a sufficient sense of reality to resemble a veridical perception over which the individual does not feel that they have direct and voluntary control. Hallucinations have been considered one of the paradigmatic psychotic symptoms, together with their counterpart, alterations in thought content or delusions. Nonetheless, in both adult and child samples hallucinations are present not only in psychotic disorders such as schizophrenia spectrum or mood disorders, but also in other psychiatric disorders, including anxiety, stress reactions and conduct disorders, in substance misuse and medical conditions such as epilepsy and delirium, as well as in mentally healthy people.
Epidemiological findings
Over recent years it has become evident that hallucinatory experiences are common in general adult and child populations. Following the hypothesis of the continuum of psychopathology and medical help-seeking, psychopathological features would be present in the general population, although in an attenuated and/or isolated form and with lower levels of distress and impairment not leading to need for care. Epidemiological studies have explored their presence through questions that identify both clinical hallucinations (that fulfil the above criteria for the definition of hallucinations and cause distress and functional impairment significant enough to lead to help-seeking) and broader hallucinatory experiences (that do not cause sufficient distress or impairment to lead to help-seeking). Epidemiological questionnaires have used questions such as ‘Have you ever heard voices or sounds that no one else can hear?’ or ‘Have you ever heard voices when you were alone?’, which target a continuum of experience from single noises or words more in line with hallucinatory experiences to clinically relevant ongoing conversing voices. Overall, about 10% of children and young people in the general population report some type of hallucinatory experience (Reference Linscott and van OsLinscott 2013; Reference Jardri, Bartels-Velthuis and DebbaneJardri 2014).
Hallucinatory experiences and age
Although evidence on the associations between age and hallucinatory experiences is not unequivocal, recent studies on the trajectory of hallucinatory experiences over time have found higher prevalence rates in childhood (13–17% at age 9–12) and a decrease in adolescence (5–7.5% at age 13–18) (Reference Kelleher, Connor and ClarkeKelleher 2012a; Reference Thapar, Heron and JonesThapar 2012). However, it is of note that, whereas psychotic experiences may be highly reported by children, the prevalence of diagnosed psychosis conversely rises steeply in adolescence. This indicates that psychotic experiences are only rarely an expression of a psychotic disorder in children, and it further suggests either that hallucinatory experiences are part of normal developmental trajectories for a number of children or – as discussed later – that the high general population rates reflect difficulty in identifying hallucinations accurately in young children.
Hallucinatory experiences, emotional and behavioural symptoms
Cross-sectional studies have documented positive associations between hallucinatory experiences and a range of concurrent emotional and behavioural symptoms and disorders in children and young people (Reference Jardri, Bartels-Velthuis and DebbaneJardri 2014). As may be expected, professional help-seeking in children with abnormal auditory experiences is related to hallucination-related distress, including more emotional triggers of the voices, negative views towards them, and perceiving them as influencing their emotions and behaviour (Reference de Leede-Smith and Barkusde Leede-Smith 2013). Associations have also been reported between hallucinatory experiences, traumas such as bullying and suicidal symptomatology (Reference Jardri, Bartels-Velthuis and DebbaneJardri 2014). This work, however, has rarely controlled for the possible confounding effects of underlying or mediating neurodevelopmental and/or social anomalies, or the severity of the depressive symptoms; the significance of these associations thus requires further investigation.
Persistence of hallucinatory experiences
The majority of hallucinatory experiences are transitory (75–90%) and resolve spontaneously over time (Reference Linscott and van OsLinscott 2013). Traumatic events such as maltreatment, assault or bullying have been identified not only as potential triggers of hallucinatory experiences, but also as risk markers for their persistence (Reference Linscott and van OsLinscott 2013; Reference Jardri, Bartels-Velthuis and DebbaneJardri 2014). In addition, persistence has been shown to be predicted in some studies by: (i) higher severity, frequency and complexity of the perceptual phenomena (e.g. multiple voices with external attributions); (ii) the presence of emotional and behavioural symptoms and of drug use; and (iii) other risk factors, including adverse backgrounds, disturbed childhood development, low academic achievement and urbanicity, although these could be mediated, in part at least, by concurrent psychiatric disorders (Reference Dominguez, Wichers and LiebDominguez 2011; Reference van Rossum, Dominguez and Liebvan Rossum 2011; Reference Thapar, Heron and JonesThapar 2012; Reference Linscott and van OsLinscott 2013; Reference Jardri, Bartels-Velthuis and DebbaneJardri 2014).
Hallucinatory experiences and psychoses
The great majority of children reporting hallucinatory experiences do not have psychotic states, nor do they ever make the transition to a psychotic disorder. Earlier longitudinal studies showed an increased risk for schizophreniform diagnoses in adulthood in 25% of children reporting a combination of hallucinatory experiences and delusional thoughts aged 11. Later meta-analytic studies have estimated that only about 7% of children reporting hallucinatory experiences will suffer from a psychotic disorder later in life (Reference Linscott and van OsLinscott 2013). The positive predictive value of the presence of psychotic-like symptoms is consequently low and of limited use for psychosis prevention.
Even in young people with more troublesome psychotic symptoms – some of whom might qualify as having one of the ‘at-risk mental states’ – the risk of conversion to psychosis has been estimated as 26% (16% converting to schizophrenia) (Reference Fusar-Poli, Bechdolf and TaylorFusar-Poli 2013). Operationalised criteria developed to identify at-risk mental states usually require: attenuated positive psychotic symptoms; or full-blown psychotic symptoms although brief and self-limiting; or a significant decrease in functioning in the context of a genetic risk for schizophrenia; or basic symptoms together with distress, dysfunction and help-seeking (Reference Fusar-Poli, Bechdolf and TaylorFusar-Poli 2013).
It seems plausible that the predictive value of childhood hallucinatory experiences for adult psychoses will be accounted for by the experience of complex hallucinatory phenomena in the context of a summation of psychotic indicators, such as delusional beliefs, negative and disorganised symptoms, neurocognitive and social impairment, and behaviour and mood regulation anomalies, in combination with exposure to sufficient environmental stressors (Reference Dominguez, Saka and LiebDominguez 2010; Reference Smeets, Lataster and DominguezSmeets 2012; Reference Linscott and van OsLinscott 2013).
A developmental approach to hallucinations
Hallucinations are subjective phenomena and their assessment in children relies on the child's ability to understand and explain to others the difference between perceptions of externally and internally generated stimuli, and between those that are sleep-related or experienced in full awareness. At what age are children able to do this? In addition, young children have a rich fantasy life: when do they become able to differentiate this from sensory perceptions?
Fantasy and hallucinations
It has long been established that young children are able to differentiate between fantasy and reality. Reference DespertDespert (1948) studied the behaviour and communications during play of children aged 2–5 and showed that, although fantasy activities were not uncommon, hallucinations were absent. Some children talked about their fantasies repeatedly, but these lacked the characteristics of perceptions and those with the most creative imaginations were readily able to acknowledge their fantasies as ‘pretend’ rather than reality. This suggested that very young children are already able to appreciate when experiences are generated by them as fantasy and when they are not.
Imaginary friends are an example of fantasy activity by children. They have been reported in nearly half (46%) of 5- to 12-year-old children (Reference Pearson, Rouse and DoswellPearson 2001) and tend to disappear in middle childhood. They have been shown to be associated with positive developmental outcomes, such as superior performance on theory of mind tasks. From a clinical perspective, imaginary companions – in addition to lacking the characteristics of perceptions of seeing and hearing – differ from hallucinations in at least two respects: first, they can often be invoked by the child at will, in contrast to the involuntary nature of hallucinations, and second, they typically function as play partners associated with positive emotions.
Hallucinations in young children
In clinical samples, hallucinations seem to be especially rare under 7 years of age (Reference GarraldaGarralda 1984a). This has led to the suggestion that, in young children, limitations in cognitive development militate against the effective communication of hallucinations to others. They would have difficulty not in differentiating self-induced fantasies or ‘pretend’ activities from reality, but in knowing the difference between dreams and other subjective phenomena such as hallucinations. In Despert's study (Reference DespertDespert 1948), some 2- to 5-year-old children related hypnagogic experiences, but it proved impossible to obtain sufficient evidence from the children themselves to conclude that the experiences were hypnagogic hallucinations as opposed to dreams. Reference PiagetPiaget (1932) pointed out that until 7–8 years of age dreams are still systematically considered as objective reality, ‘as a sort of ethereal, rarefied picture floating in the air and fixed before our eyes’ (1997 reprint: p. 187). The comparatively high rates of hallucinations reported in epidemiological samples of schoolchildren in response to standardised questioning may therefore be partly an artefact of immature cognition in the younger among them.
Preschool children are more likely to demonstrate the presence of hallucinations through their behaviour – as outlined later – and to be particularly vulnerable to experiencing hallucinations and other abnormal phenomena in conditions of brain toxicity such as high fever and septic illness. In a sample of children and adolescents with meningococcal disease, ‘out-of-body’ type experiences were mainly reported by preschool children, possibly reflecting cognitive or brain immaturity through failure by the brain to integrate complex somatosensory and vestibular information (Reference Shears, Elison and GarraldaShears 2005).
Assessing hallucinations in clinical samples
When a child presents with hallucinatory experiences, the first step is to clarify whether these are:
-
illusions or misrepresentations of sensory inputs, fantasy-related, as with imaginary friends (‘Can you bring them on? Do you actually see them and hear them as you see and hear me now?’)
-
intrusive thoughts or inner images, as in obsessions, where ego-dystonic experiences are personalised and attributed to an external source (‘Are they like the voices you normally hear through your ears, or are they more like thoughts as when you are thinking about things?’)
-
post-traumatic flashbacks, as in involuntary and intrusive vivid inner images or sounds from past traumatic memories.
Once the presence of hallucinations is established, the second task is to document their complexity: simple hallucinations such as occasionally hearing one's own name being called or fleetingly seeing shadows out of the corner of one's eye are regarded as non-clinically significant.
Third, the clinician needs to ascertain whether hallucinations are linked to states of lowered awareness, as in sleep (hypnagogic or hypnopompic), fever, drug-taking, toxicity, epilepsy or migraine. Alice in Wonderland syndrome presents as a combination of migraine and a variety of hallucinations and illusions of size, time, colour, body shape and movement (Reference Smith, Wright and BennettSmith 2015). The differentiation of sleep-related phenomena and hallucinations merits particular note (Table 1). Although hypnagogic and hypnopompic hallucinations are usually without clinical significance, there are specific cases in which they may be part of a disabling childhood sleep disorder such as narcolepsy.
Finally, the fourth task involves assessing whether hallucinations are part of psychotic states and, if not, whether there are any pointers to why this symptom is presenting in this child at this particular time, including possible vulnerabilities and stressors in addition to other psychiatric morbidity. This assessment process is not always straightforward. In younger children or those with intellectual disability or in mistrustful and uncommunicative young people, it may require careful questioning by clinicians experienced in both interviewing children and diagnosing psychotic and other psychiatric states.
The detailed exploration of the symptom
Hallucinatory experiences can affect any of the five sensory modalities (Table 2). A comprehensive assessment requires detailed exploration of the symptom characteristics for each individual (Table 3). As a general rule, it is better to ask children and adolescents open questions where they can describe the experiences, or to provide a choice of answers from which they can choose, rather than closed questions that may guide and contaminate their answers. Descriptions of symptoms should be factual, avoiding florid interpretation.
TABLE 2 Hallucinatory experiences in five sensory modalities: description and differential diagnosis
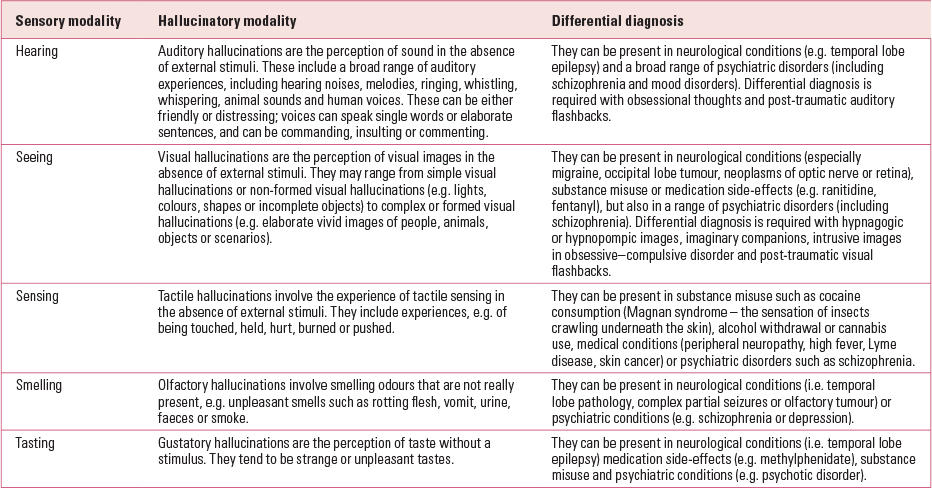
TABLE 3 The detailed exploration of hallucinations
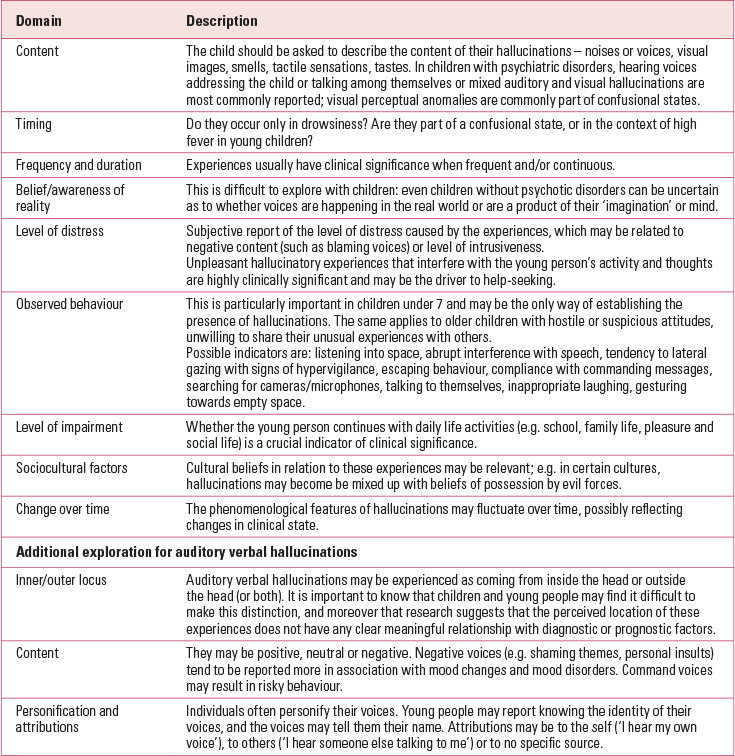
In children, hallucinations are regarded as having clinical significance when: (i) they occur without clouding of consciousness, and (ii) they are either comparatively complex (e.g. voices containing a narrative or that are multiple, elaborate visions, multisensory experiences), or are distressing and impairing, or are linked to physical illness and/or active psychopathology and/or suicidality. Adult studies have identified markers of risk in the case of auditory verbal hallucinations. These include emotional valence driven by negative content, appraisal of the identity, intent and power of voices as a source of distress, perceived lack of control and presence of command hallucinations that may encourage harm to self or others (Reference de Leede-Smith and Barkusde Leede-Smith 2013). However, these findings are yet to be replicated in child and adolescent populations.
Clinical scales to assist the assessment of hallucinations
A number of clinician-rated scales have been used to assess the severity of hallucinations in adults with psychotic disorders (e.g. the Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS; Reference Kay, Fiszbein and OplerKay 1987)) and these may be useful to quantify treatment progress in young people with psychoses.
More recently validated instruments explore the characteristics of psychotic symptoms regardless of diagnosis. For example, the Psychotic Symptoms Rating Scales (PSYRATS, 17 items; Reference Haddock, McCarron and TarrierHaddock 1999) quantifies in considerable detail the multidimensional features of hallucinations (frequency, duration, location, loudness, origin, negativity, distress, disruption and controllability) and delusions, and has been validated in clinical and non-clinical samples; the Questionnaire for Psychotic Experiences (QPE, 50 items; Reference NijboerNijboer 2015) measures the presence, severity and phenomenological characteristics of auditory, visual and other sensory hallucinations and delusions. The PSYRATS is increasingly being used clinically as a measure of symptom change, whereas the QPE is a promising clinical scale at the earliest stages of research and clinical development. However, although these scales look promising, there is as yet little evidence on their use with children and young people.
Differential diagnosis
Hallucinations and paediatric organic conditions
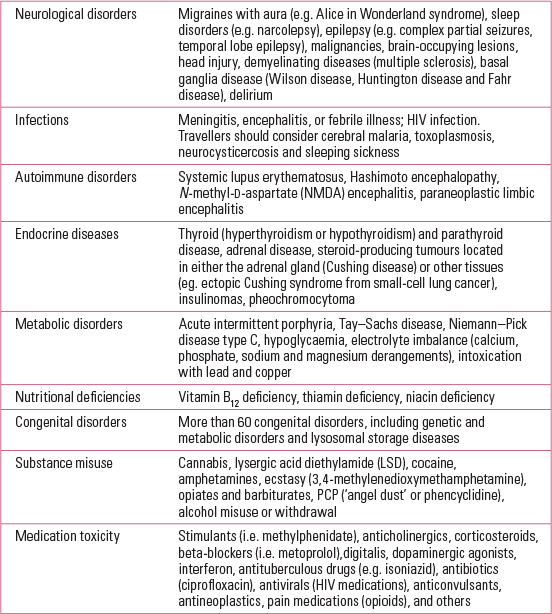
A variety of paediatric organic conditions need to be considered and investigated when there are relevant clinical indicators based on detailed medical history and physical exploration. Reference Freudenreich, Schulz and GoffFreudenreich (2009) and Reference Algon, Yi, Calkins and KohlerAlgon (2012) have outlined broad and specific screening for medical disorders in first-episode psychosis (Table 4).
TABLE 4 Paediatric organic conditions that may present with hallucinations or related perceptual phenomena – with or without reduced levels of consciousness
Hallucinations and paediatric psychiatric conditions
As important as carefully exploring the nature of hallucinatory experiences is to assess the constellation of symptoms of which hallucinatory experiences form part for each particular child or adolescent. The psychiatric differential diagnosis of hallucinations includes:
-
psychiatric disorders where psychotic symptoms are a hallmark (hereafter: psychotic disorders), as in schizophrenia spectrum (i.e. schizophrenia, schizoaffective, schizotypal, acute and transient psychotic disorders) and mood disorders (i.e. bipolar disorder and major depression with psychotic symptoms); each of these requires specific symptom combinations and time frames to reach clinical diagnosis level (World Health Organization 1992); for an initial psychotic presentation, all these disorders are grouped into first-episode psychosis
-
psychiatric disorders where hallucinations are not a hallmark but an associated symptom, e.g. emotional and behavioural disorders
-
psychiatric disorders with psychopathological features which may resemble those of hallucinations, such as intrusive obsessions in obsessive– compulsive disorder, intrusive images/thoughts in post-traumatic stress disorder, or elaborate magical bizarre thoughts in autism spectrum disorder.
Hallucinations and psychotic disorders
First-episode psychosis is defined as more than a week of unremitting frank psychotic symptoms, namely clinically defined delusions, hallucinations, passivity experiences or severe thought disorder. Psychotic symptoms are considered frank if they score higher than 4 (moderate) on the PANSS (the scale runs from 1 to 7: absent to extreme). In psychotic states, hallucinations co-occur with a constellation of symptoms, as part of the clinical psychosis phenotype described by five psychopathological dimensions (Reference Dikeos, Wickham and McDonaldDikeos 2006):
-
the positive dimension: delusions, ideas of reference, unusual thought content, hallucinations, grandiosity and suspiciousness/persecution
-
the negative dimension: alogia, affective flattening, avolition, apathy, anhedonia, asociality, social withdrawal, stereotyped thinking and motor retardation
-
the disorganised dimension: conceptual disorganisation, positive formal thought disorder, difficulty in abstract thinking, derailment, tangentiality, incoherence, illogicality, circumstantiality, associative loosening, inattention/distractibility, disorientation, inappropriate affect, bizarre behaviour, mannerisms and posturing
-
the depressive dimension: observed depression, hopelessness, self-deprecation, feelings of guilt, guilty ideas of reference, early wakening, suicidal ideation, anxiety and active social avoidance
-
the manic/excitement dimension: pressured speech, excessive activity, racing thoughts, elevated mood, increased sociability, reduced need for sleep, reckless activity, irritable mood, increased self-esteem and grandiose delusions.
An individual can score high or low on the different dimensions, which may coexist. Close monitoring over time will be required to observe the direction in which psychopathology evolves. It may veer towards a schizophrenia spectrum or mood disorder picture.
Characteristics of hallucinations in psychotic disorders
A retrospective study of hallucinations in children and adolescents referred to the Maudsley Hospital in London identified auditory hallucinations as the most common psychotic symptom in those with psychotic disorders (schizophrenia, manic–depressive illness, schizoaffective or unspecified psychoses), present in three-quarters of the sample, and it described their clinical manifestations (Reference GarraldaGarralda 1984b, Reference Garralda1985). In terms of content, voices tended to tell the children to carry out actions which, in half the cases, could be considered as wrongdoings. Some contained suicidal instigations, and occasionally there was a direct relationship with suicidal symptoms. Their tone was equally likely to be unpleasant as pleasant, and the voices were varyingly attributed to unspecified or familiar people such as school contacts or parents; more rarely they were thought to be God. Some children interpreted the voices as their own thoughts being spoken aloud or other people speaking their thoughts. Visual hallucinations were less common, variously described as of unidentified people or family members, animals or objects; rarely would a child report seeing the devil.
Hallucinations co-occurred with delusional beliefs (mainly of a paranoid or persecutory nature, such as complaining that people were poisoning or conspiring against them), abnormalities in language production (incoherence, mutism or laconism, repetitive speech), inappropriate affect (including giggling), bizarre behaviour, hypoactivity and social withdrawal. Schneiderian first-rank symptoms were rare, present in 15% of the sample.
The presence of hallucinations in this sample (when compared with children with psychoses who did not report hallucinations) was linked to reporting precipitants of illness, symptoms of depression and anxiety, and problems with reading (Reference GarraldaGarralda 1984b), suggesting a role of stressors, mood changes and cognitive vulnerability in the experience of hallucinations in children and young people with psychotic disorders.
Psychotic schizophrenia spectrum disorders
Youth-onset schizophrenia is an infrequent but important cause of hallucinations in young people. The prevalence of schizophrenia increases rapidly from age 14 and accounts for 24% of UK psychiatric admissions of young people aged 10–18 (National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) 2013). Schizophrenia spectrum disorders are commonly preceded by the so-called prodromal period, lasting up to 12 months, in which the child or young person's behaviour and experience are altered, leading to social withdrawal or impaired functioning. In the especially rare prepubertal or childhood-onset schizophrenia (Reference David, Greenstein and ClasenDavid 2011), auditory and visual hallucinations have been documented in 95% and 80% of children respectively during their hospital admissions. In this group, visual hallucinations showed a significant relationship with lower IQ and earlier age at onset, and tactile (60%) and olfactory (30%) hallucinations were observed only in children with visual hallucinations.
Psychotic mood disorders
Mood changes are a particularly common association of hallucinations in children and should therefore be explored carefully. Both extremes of mood disorder (i.e. the manic phase of bipolar disorder as well as the depressive phase of major depression) may present with psychotic hallucinatory experiences, which tend to be mood congruent. In paediatric populations with bipolar disorder (Reference Kowatch, Youngstrom and DanielyanKowatch 2005), increased energy, distractibility and pressured speech, followed by racing thoughts, decreased need for sleep and poor judgement, are the most common symptoms of mania, in contrast to flight of ideas and hypersexuality, which are less frequently present. It is of note that irritability and dysphoria are not distinctive features of mania, as they may be the predominant mood state in young people presenting with the constellation symptomatology of depression (i.e. anhedonia, fatigue and suicidal ideation) (Reference ChangChang 2009). In a sample of 257 children and adolescents with bipolar I disorder (Reference Tillman, Geller and KlagesTillman 2008), excluding the perceptual experiences of imaginary companions or voices calling their name (which occurred in 43.6% of cases), visual hallucinations were the most frequent hallucination type (16%), followed by command auditory hallucinations (15.6%), tactile (10.1%) and olfactory (8.2%) hallucinations, and conversing voices (7.4%), commenting voices (6.6%) and other verbal hallucinations (5.4%).
Hallucinations and non-psychotic psychiatric disorders
Population studies show that children who report hallucinatory experiences score significantly higher than those who do not on general and specific measures of psychopathology, including both internalising and externalising features (Reference Scott, Martin and BorScott 2009; Reference Kelleher, Keeley and CorcoranKelleher 2012b). This has been replicated in clinical samples, where hallucinations co-occur in children and young people presenting with anxiety disorders, stress reactions and conduct/oppositional disorders (Reference GarraldaGarralda 1984a; Reference Askenazy, Lestideau and MeynadierAskenazy 2007; Reference Braakman, Kortmann and Van den BrinkBraakman 2009). Hallucinations are, however, not a frequent feature of clinical presentations: in Reference Ulloa, Birmaher and AxelsonUlloa et al 's (2000) study of children and adolescents referred to a mood and anxiety disorders clinic, psychotic symptoms (mainly hallucinations) were reported by 4% and suspected in a further 4%: definite symptoms were associated with mood disorders and suicidal ideation, the latter mediated by the presence of a mood disorder.
There has been comparatively little work to characterise hallucinations in children with emotional and behavioural disorders (Ulloa et al looked only at mood disorders), but the above-mentioned paediatric hallucinations study at the Maudsley Hospital described in some detail the experiences of a group of children with hallucinations in the context of emotional and conduct disorders (Reference GarraldaGarralda 1984a). As in the children with psychotic states, auditory hallucinations predominated, and visual phenomena were reported by about half. The length of time hallucinations had been present ranged from 1 week to several years, and episodes tended to be brought on by stressful events, distress, naughtiness or temper. Three-quarters of the children reported that voices addressed them. In half of these cases the voices asked them to do something wrong and unpleasant, and in over a third they made threatening comments. About half of the children said that they were anxious and frightened during these experiences, and a quarter said they fought the voices, refusing to obey orders. There was a trend for the voices to be located predominantly in the child's internal space before the age of 13 and in external space after that age. Visual hallucinations included seeing frightening objects such as skeletons or ghosts, but a number of children also talked about seeing recently deceased people.
The children with hallucinations and non-psychotic diagnoses were found to be older and with lower IQ than the majority of clinic attenders and they were also more likely to be admitted as inpatients, a proxy for illness severity. In comparison with a matched control group of children without hallucinations, they were found to have experienced more stressors precipitating illness, and they displayed more mood changes, and dissociative symptoms (e.g. derealisation) and episodes, as well as more neurodevelopmental deficits (e.g. problems with reading, and discrepancies in verbal and performance IQ). Hallucinations were not linked to lower socioeconomic backgrounds, social deprivation, sensory deficits, vivid imagination or daydreaming. At long-term follow-up in adulthood (Reference GarraldaGarralda 1984c), the psychiatric adjustment of children with a history of hallucinations was comparable with that of controls, but although rates of psychoses were not increased among these children, they continued to be more likely to experience complex hallucinations and dissociative phenomena (e.g. depersonalisation and derealisation, déjà vu and short dissociative episodes) over the years.
These findings are in keeping with the increasing evidence of: first, a relationship between early traumatic events and stress reactions, including hallucinations (Reference Braakman, Kortmann and Van den BrinkBraakman 2009) and in a minority of individuals psychotic disorders (Reference de Leede-Smith and Barkusde Leede-Smith 2013); and, second, the possibility of dissociation as a mediator in the relationship between childhood trauma and hallucination proneness (Reference Varese, Barkus and BentallVarese 2012). Links between hallucinations and dissociation, low intellectual functioning and emotional dysregulation have since been confirmed by epidemiological findings and clinical reports (Reference Linscott and van OsLinscott 2013; Reference Jardri, Bartels-Velthuis and DebbaneJadri 2014). This points to the relevance of emotional dysregulation and its perceptual correlates in young people's responses to traumatic events. For the clinician, the findings indicate the advisability of exploring the presence of possibly unacknowledged traumas and losses, as well as dissociative tendencies and cognitive vulnerabilities in these children, in addition to assessing mood regulation and suicidality.
There is little information on the short-term outcome of hallucinations in clinical samples. In a small group of 13 prepubertal out-patients with hallucinatory experiences, half were free of these 3 months following assessment and at 1-year followup, about 1 in 10 had recovered but had had a relapse following new stresses, and the rest (under one-third) continued to report hallucinatory experiences (Reference Askenazy, Lestideau and MeynadierAskenazy 2007).
Schizotypal disorder and autism spectrum presentations
Psychotic-like features such as hallucinations pose a further challenge to clinicians when they occur in the context of either an autism spectrum or a schizotypal disorder. Schizotypal disorder is characterised by eccentric behaviour and anomalies of thinking and affect that resemble those seen in schizophrenia, and may include unusual perceptual experiences, as well as transient quasi-psychotic episodes with intense hallucinations. Schizotypal disorder is rarely diagnosed in children, but in adolescents it may overlap with autistic disorders (Reference Barneveld, Pieterse and de SonnevilleBarneveld 2011) and account for psychotic symptoms in some adolescents with autism. The differentiation of transient quasi-psychotic states from full-blown schizophrenic disorder may require particularly careful assessment and observation over time in young people with autism and hallucinations.
Management plans
Childhood hallucinatory experiences in nonclinical samples rarely cause substantial suffering in children's lives, and high rates of symptom discontinuation make treatment usually unnecessary. In clinical samples of children presenting with psychotic disorders, specific treatment strategies will be put into place, while in those with non-psychotic disorders, treatment of the associated psychiatric disorder and/or therapeutic work aimed at stress/anxiety reduction and mood regulation may be expected to improve hallucination-related distress. Occasionally, and in the face of persisting hallucinations that do not respond to appropriate interventions, antipsychotic medication may be helpful (Reference VickersVickers 2002).
Psychotic disorders
When hallucinations are part of a first psychotic episode, early identification and treatment are indicated. NICE guidelines recommend urgent specialist referral to either child and adolescent mental health services (CAMHS) or an early intervention in psychosis service (NICE 2013). The currently recommended treatment includes the use of antipsychotic medication (risperidone or aripiprazole, for at least 12 months) in conjunction with psychological interventions, namely psychoeducation, discontinuation of illicit drug use, reduction of stresses, family intervention and individual cognitive–behavioural therapy. Duration of untreated psychosis (DUP), which refers to the time between the onset of psychotic symptoms continuous with the presenting episode and the initiation of continuous (>30 days) antipsychotic medication, has become established as an important factor associated with outcome: the longer the DUP, the worse the subsequent psychosis, so early diagnosis and treatment are called for.
Antipsychotic medication is not recommended for psychotic symptoms that are not sufficient for a diagnosis of first-episode psychosis, nor should it be used with the aim of decreasing the risk of psychosis (NICE 2013). However, young people with an at-risk mental state should be carefully monitored for signs of transition to frank psychosis.
Non-psychotic presentations
When hallucinations are part of anxiety, post-traumatic stress, disruptive or substance misuse disorders, treatment of the disorder is indicated. The hallucinations themselves deserve particular attention and monitoring if they are complex (e.g. containing a narrative, involving multiple voices, multisensory), distressing and impairing even after the accompanying psychopathology has subsided or if it does not respond to treatment.
Psychological therapy for hallucinations
Since distress is one of the risk markers for hallucinations, stress management can be a major target of specific psychological therapies. In addition, psychological theories of auditory hallucinations have been developed over the years, with related therapeutic modalities (Reference Thomas, Hayward and PetersThomas 2014).
Cognitive–behavioural therapy (CBT) for psychotic symptoms has been evaluated as an adjunct to routine care in the context of psychotic states; results suggest a modest reduction in symptom severity, but there have been few trials focusing on hallucinations themselves. Recent developments in the management of hallucinations include mindfulness-based therapies, competitive memory training and compassionate mind training, which aim to promote greater resilience to critical commenting. Another recent direction has been the use of computer-generated avatars that enable the therapist to role-play the voice to help the person practise different responses to the experience. These techniquesFootnote † have been used primarily with adults and require further evaluation, and their suitability and efficacy for children are not known.
Reference EdelsohnEdelsohn (2006) described a modification of CBT as a brief intervention for hallucinations in children presenting to psychiatric emergency services. It consists of gaining an appreciation of the child's beliefs about the hallucinations (‘What do they mean?’), details of how they started, and whether the child can start or stop them, followed by helping the child identify alternative explanations for the hallucinations and introducing coping strategies.
Psychoeducation when hallucinations are part of non-psychotic disorders
If hallucinations present in the context of non-psychotic disorders, psychoeducation for the child and family about the symptoms is important. The popular understanding of hallucinations is that they are an expression of severe mental illness. The symptoms can therefore be very alarming, which may partly explain why they tend to present as psychiatric emergencies (Reference EdelsohnEdelsohn 2006). This may be compounded by concern arising because of a family history of psychotic illness. It is therefore highly relevant for the clinician to carry out a careful differential diagnosis and share this with the family, explaining the potential presence of hallucinations across a number of child psychiatric diagnoses and their response to treatment and conveying information about the limited predictive value of childhood hallucinatory experiences for adult psychotic states.
Destigmatisation and normalisation, alongside attention to concurrent stressors and psychiatric disorders (including mood disorders and suicidality as well as any concurrent neurodevelopmental risks), are thus key elements of therapeutic input.
MCQs
Select the single best option for each question stem
-
1 The frequency of hallucinatory experiences in children and young people in the general population is closest to:
-
a 0.1%
-
b 1%
-
c 10%
-
d 20%
-
e 30%.
-
-
2 The rate of discontinuation over time of hallucinatory experiences in children in the general population is closest to:
-
a 20%
-
b 40%
-
c 60%
-
d 80%
-
e 100%.
-
-
3 The risk of a future psychotic state in children in the general population with psychotic symptoms/hallucinations is closest to:
-
a 1%
-
b 10%
-
c 20%
-
d 30%
-
e 40%.
-
-
4 In clinical samples of children with non-psychotic states, hallucinations have been found to be associated with:
-
a imaginary companions
-
b a rich fantasy life
-
c severe social deprivation
-
d dissociative experiences and emotional dysregulation
-
e parental psychotic states.
-
-
5 The clinical management of hallucinations in children primarily involves:
-
a CBT for psychotic states
-
b treatment of the concurrent psychiatric disorder
-
c antipsychotic medication
-
d reduction of the duration of untreated psychosis
-
e mindfulness training.
-
MCQ answers
| 1 | c | 2 | d | 3 | b | 4 | d | 5 | b |









eLetters
No eLetters have been published for this article.