Analysts of elections worldwide, from Albania to Zambia, would have a hard time denying that competing candidates and parties regularly ‘go negative’ on each other and attack their rivals’ ideas, policy proposals, past record and character flaws. Campaigns without any form of negativity are unlikely to exist in modern elections (Nai and Walter Reference Nai and Walter2015).
Few would also claim that negative campaigning is trivial or inconsequential (for a review, see Fridkin and Kenney Reference Fridkin and Kenney2012; Lau et al. Reference Lau, Sigelman and Rovner2007). Many suggest that negative campaigning is a detrimental force in modern democracies. Much evidence supports the ‘demobilization hypothesis’ (Ansolabehere and Iyengar Reference Ansolabehere and Iyengar1995; Ansolabehere et al. Reference Ansolabehere, Iyengar, Simon and Valentino1994), according to which negative campaigning depresses turnout and political mobilization both directly, by reducing the probability of voting for the target (as intended) but also for the sponsor, and indirectly, by lowering political efficacy and trust. Indeed, several studies have shown that negative campaigning has detrimental ‘systemic’ effects, fostering apathy and a gloomier public mood (Thorson et al. Reference Thorson, Ognianova, Coyle and Denton2000; Yoon et al. Reference Yoon, Pinkleton and Ko2005) in a ‘spiral of cynicism’ (Cappella and Jamieson Reference Cappella and Jamieson1997). Especially when combined with elements intended to trigger an emotional response, negative messages can depress political efficacy and trust in elected officials (Brader Reference Brader2005).
Not all studies agree that negative campaigning has a ‘corrosive’ effect (Jackson et al. Reference Jackson, Mondak and Huckfeldt2009; Lau and Rovner Reference Lau and Rovner2009). On the one hand, some have argued that the early ‘demobilization’ results were exaggerated and flawed by empirical inconsistencies (e.g. Wattenberg and Brians Reference Wattenberg and Brians1999). On the other hand, other studies highlight that negativity might have a positive role to play: negative messages can convey important and useful information to the voters (Finkel and Geer Reference Finkel and Geer1998), promote issue knowledge (Brians and Wattenberg Reference Brians and Wattenberg1996), cue the voters that the election is salient and thus worth the emotional and cognitive investment (Martin Reference Martin2004), and ultimately stimulate interest and participation (Geer Reference Geer2006).
Whether in a beneficial or detrimental way, negative campaigning is likely to play a role in modern democracies. Thus it seems important to understand its underpinnings: why, and under which conditions, do candidates ‘go negative’ on their rivals during election campaigns? This interrogation is not novel (e.g. Damore Reference Damore2002; Lau and Pomper Reference Lau and Pomper2001; see Lau and Rovner Reference Lau and Rovner2009 for a literature review), but very little is known today about the dynamics of negative campaigning outside the US case, and even less in a broader comparative perspective. Non-US evidence is scattered, and studies usually focus on specific cases, such as Denmark (Elmelund-Praestekaer Reference Elmelund-Præstekær2010; Hansen and Pedersen Reference Hansen and Pedersen2008), the Netherlands (Walter and Vliegenthart Reference Walter and Vliegenthart2010) or Germany (Maier and Jansen Reference Maier and Jansen2015). Furthermore, the few existing comparative studies (e.g. Curini Reference Curini2011; Walter et al. Reference Walter, van der Brug and van Praag2014) – although providing a fundamental contribution to the field of comparative political communication – have not yet been able to develop a large-scale overview of negative campaigning worldwide, because they have focused on only a handful of countries.
In this article, we take an important step towards this goal. We introduce an original comparative data set that contains systematic information about the campaigning strategies of 172 candidates in 35 different elections worldwide between June 2016 and May 2017 – virtually all elections that happened during that period, thus providing a comprehensive snapshot of the use of negative campaigning worldwide over the course of one year. The data set is based on expert ratings and includes information about elections in the US, France, Russia, the Netherlands, Spain, Austria, Australia and beyond. The data also include information about regions of the globe for which relatively less is known about electoral campaigning, such as African (e.g. Zambia, Ghana, Côte d’Ivoire, Morocco), Eastern Europe (e.g. Belarus, Bulgaria, Moldova, Romania), the Balkans (e.g. Serbia, Montenegro, Croatia, Macedonia) and East Asia (e.g. Japan, South Korea, Hong Kong). These elections span all types of electoral and party systems, and vary considerably in terms of competitiveness, closeness of the results and media coverage. Most importantly, the data contain detailed information about the use of negative campaigning for a wide palette of competing candidates across all ideologies, genders, incumbency statuses and electoral fortunes. These include, but are not limited to, Donald Trump and Hillary Clinton (US), Marine Le Pen and Emmanuel Macron (France), Geert Wilders (the Netherlands), Norbert Hofer (Austria), Dmitry Medvedev (Russia), Shinzo Abe (Japan), Hassan Rouhani (Iran), Mariano Rajoy and Pablo Iglesias (Spain) and many others (see Appendix A in the online supplementary material for the full list of elections and candidates).
Our aim is to study the drivers of negative campaigning in a comparative perspective, towards a universal understanding of the reasons why parties and candidates go negative on their rivals. We will focus our attention on the characteristics of the sponsors of negative messages (e.g. incumbency status, ideology, gender), the profile of the targets of attacks (e.g. competitive standing) and the relationship between sponsors and targets (e.g. ideological distance between them). Furthermore – made possible for the first time by the large-scale comparative scope of the data set – we will also assess how the context drives or moderates the use of negative campaigning.
Who goes negative and why?
The attacker
What are the reasons that make candidates more likely to campaign through negative messages? The usual assumption is that strategic considerations are at play, due to a trade-off between uncertain benefits and potential costs associated with attack messages (Lau and Pomper Reference Lau and Pomper2004). On the benefits side, candidates go negative hoping to attract undecided voters or to diminish positive feelings for their rivals, with clear direct or indirect benefits for them (Pinkleton Reference Pinkleton1997). On the costs side, negative campaigning strategies can be a liability. Attack politics is usually unpopular, and candidates that play with fire face a clear risk of getting burned in return. Many studies have shown the existence of such ‘backlash’ effects (Roese and Sande Reference Roese and Sande1993; Shapiro and Rieger Reference Shapiro and Rieger1992), even if the jury is still out concerning the net efficacy of attacks. If the candidate considers the potential risks to be greater than the uncertain benefits, he or she should not attack; inversely, if the backlash risk is considered small or inconsequential enough, the campaign will turn negative.
We focus here on two sets of characteristics of the candidates that are expected to drive their strategic calculations: their electoral profile (incumbency status and comparative standings) and their personal profile (ideology and gender). To be sure, most of these characteristics also reflect the characteristics of the party for which the candidates competed. The implications are that purely individual characteristics beyond ideology and gender, such as the candidates’ personality or reputation (Dietrich et al. Reference Dietrich, Lasley, Mondak, Remmel and Turner2012), are not taken into account in this article. Further research on those characteristics is, however, discussed elsewhere (Nai Reference Nai2018; Nai and Maier Reference Nai and Maier2018).
First, incumbent candidates should be comparatively less likely to go negative on their rivals than challengers (Lau and Pomper Reference Lau and Pomper2004; Walter and Nai Reference Walter and Nai2015). Incumbents, based on their experience, are usually able to promote themselves, their record and accomplishments – their experience in office should provide them with material over which to build positive self-promoting campaigns. Challengers usually do not have this option and are thus less likely to run positive campaigns. Furthermore, the record of incumbents while in office is closely scrutinized by the public at large, and much evidence exists that voters rely on retrospective evaluations to adjust their choices (Healy and Malhotra Reference Healy and Malhotra2013). Challengers do not have an office to lose, and naturally receive weaker coverage than incumbents (Hopmann et al. Reference Hopmann, de Vreese and Albæk2011), which should act as an incentive to find ways to increase their exposure in the media – for instance by using a more negative rhetoric; ‘candidates want to get their message out, hoping to control the terms of the debate. They can air a positive ad and seek to influence voters with that spot. But the news media will likely ignore it … A negative ad, however, can generate controversy and conflict, drawing attention from journalists’ (Geer Reference Geer2012: 423).
Second, the prospect of electoral failure should act as an incentive to attack rivals (Harrington and Hess Reference Harrington and Hess1996; Nai and Sciarini Reference Nai and Sciarini2015; Walter et al. Reference Walter, van der Brug and van Praag2014). Positive campaigning is principally used to attract voters, whereas ‘negative campaigning is used to reduce the support of the opponent. [… Thus], the one lagging behind in the polls has not succeeded in attracting undecided voters and, therefore, has to scare off the opponent’s voters to stand a better chance’ (Elmelund-Praestekaer Reference Elmelund-Præstekær2010: 141). Actors who are lagging behind have little to lose – and much to gain – from a negative strategy. Negative campaigns are risky businesses, but in a situation where candidates face unfavourable odds the potential benefits of going negative outweigh the risks associated with attack politics. When they are facing defeat, potential ‘backlash’ effects that reduce support for the sponsor of the negative advertisement are less consequential. Inversely, when facing the prospect of electoral success, candidates should be particularly willing to avoid strategies that could damage their image and spoil their win.
Turning to the candidates’ personal profile, circumstantial evidence exists to expect higher bellicosity from right-wing candidates. In the US, some studies show that Republicans are more likely to go negative than Democrats (Lau and Pomper Reference Lau and Pomper2001), perhaps due to the fact that GOP strategists tend to be more open to the idea of strategic attacks (Theilmann and Whilhite Reference Theilmann and Wilhite1998), whereas evidence exists that voters identifying with the Democrats are, under some conditions, less sympathetic towards negativity than Republicans or independents (Ansolabehere and Iyengar Reference Ansolabehere and Iyengar1995; Mattes and Redlawsk Reference Mattes and Redlawsk2015). Only scattered evidence exists, however; outside the US case – for instance, the far-right Schweizerische Volkspartei (SVP – Swiss People’s Party) in Switzerland is by far the most negative during referendum campaigns (Nai and Sciarini Reference Nai and Sciarini2015) – and globally, this effect suffered in the past from under-theorization (Walter and Nai Reference Walter and Nai2015). This effect could partially be driven by differences in psychological orientations between left- and right-leaning individuals. Right-wing ideology, especially in its extreme version of right-wing authoritarianism, is closely associated with social dominance orientations (Heaven and Bucci Reference Heaven and Bucci2001), promoting tough-mindedness and ‘a view of the world as a ruthlessly competitive jungle in which the strong win and the weak lose’ (Duckitt Reference Duckitt2006: 685), which can be expected to lead to a greater tolerance for negativity and a more aggressive rhetoric; indeed, Alain Van Hiel et al. (Reference Van Hiel, Mervielde and De Fruyt2004) show that right-wing individuals are more likely to engage in compulsive acts and show low agreeableness.
Beyond the left or right positioning of candidates, their distance from the ideological centre is also expected to drive negativity. More extreme parties and candidates are less likely to participate in coalitions or policy agreements. Especially in multiparty systems, negativity has been shown to be inversely proportional to coalition potential: parties seeking to enter coalition negotiations, in either the pre- or post-electoral phase, have strategic incentives to keep their negative rhetoric at bay if they want to avoid nefarious backlash effects (Hansen and Pedersen Reference Hansen and Pedersen2008; Walter and Van der Brug Reference Walter and van der Brug2013). Indeed, preliminary results outside the US case seem to confirm that parties far from the ideological centre are more likely to engage in negative campaigning techniques (Elmelund-Praestekaer Reference Elmelund-Præstekær2010; Walter et al. Reference Walter, van der Brug and van Praag2014).
Finally, evidence exists that links candidates’ gender to their use of negative messages. The rationale supporting the relationship between gender and negativity is non-essentialist and argues that female candidates have a strategic disadvantage, when compared to male candidates, in going negative. Female candidates that go negative on their opponents face a situation that contrasts with social stereotypes and shared expectations of their behaviour as passive, kind and sympathetic (Fridkin et al. Reference Fridkin, Kenney and Woodall2009; Huddy and Terkildsen Reference Huddy and Terkildsen1993; Krupnikov and Bauer Reference Krupnikov and Bauer2014). This disruption of gender stereotypes can potentially have substantial electoral consequences, in the form of the increased likelihood of backlash effects (Kahn Reference Kahn1996; Trent and Friedenberg Reference Trent and Friedenberg2008). Although the existence of gender differences in negativity is contested elsewhere (e.g. Maier Reference Maier2015), the rationale supporting a strategic incentive for female candidates not to go negative seems sound enough to test for it through our large-scale comparative data.
The context
Of course, candidates’ electoral and personal characteristics cannot be the only determinants of campaign strategies, and good reasons exist to expect that the context helps define the limits of what is acceptable during campaigns. We focus here on two major components of the context: the state of the race (competitiveness) and the rules of the game (electoral system, party fragmentation).
First, the competitiveness of the race – that is, how close or undecided the outcome of the election is expected to be during the campaign – is likely to alter the strategic considerations of candidates. Strong evidence exists that more competitive or ‘close’ races lead to higher negativity (Elmelund-Praestekaer Reference Elmelund-Præstekær2008; Fowler et al. Reference Fowler, Franz and Ridout2016b; Kahn and Kenney Reference Kahn and Kenney1999; Lau and Pomper Reference Lau and Pomper2004), even though the opposite is found by Peter Francia and Paul Herrnson (2007), who show that candidates in non-competitive races are more likely to go negative because they are ‘the most desperate to make gains in the polls’ (Francia and Herrnson Reference Francia and Herrnson2007: 260). Damian Bol and Marian Bohl (2015) suggest that competitiveness is especially relevant in elections held under plurality or majority electoral rules – in proportional representation (PR) elections competitiveness should only play a marginal role, as electoral results are only a part of the equation and post-election coalition building matters. Indeed, several studies on elections held under non-majority rules seem to show that competitiveness plays only a minimal role (Elmelund-Praestekaer Reference Elmelund-Præstekær2010; Walter et al. Reference Walter, van der Brug and van Praag2014). The electoral system should also have a direct effect on the use of negativity, as elections held under PR should have lower negativity because parties and candidates have additional incentives for cooperative behaviour due to the possibility of post- or pre-election coalition bargaining. These formal or informal interparty agreements should shape the strategic underpinnings of negativity and make the risk of alienating potential coalition allies too great to bear; this is in line with the general idea that the ‘consensus’ model, in which PR plays a major role, yields naturally a ‘kinder, gentler’ form of democracy (Lijphart Reference Lijphart1999).
A similar argument can be made with regards to the party system: when a higher number of parties or candidates compete, negativity should decrease. This is, mathematically, a result of the relationship between the number of actors and the chances of direct returns when making attacks on competitors: in a simple two-party system, a zero-sum game exists in which any strategy that reduces support for the rivals should naturally increase support for the sponsor (excluding extreme forms of demobilization); quite logically, the higher the number of competing actors, the lower the chances of such direct returns, as attacks on a competitor could lead to virtually no direct electoral gains for the sponsor – while still remaining quite a risky tactic in terms of backlash effects (Walter and Nai Reference Walter and Nai2015; but see Elmelund-Praestekaer and Svensson Reference Elmelund-Praestekaer and Svensson2014).Footnote 1
Aiming for the right target
By their very definition, political attacks in campaigns have a relational and directional nature: they necessarily involve one actor (the sponsor) that goes negative against another actor (the target). Most of the literature on the use of negativity in election campaigns has focused on the characteristics of the sponsor, but good reasons exist to focus on the target of attacks, and on the relationship between the sponsor and the target.
First, we discussed above reasons why incumbents should be less likely to go negative, while simultaneously providing reasons why challengers should be more likely to do so. Assessing the use of negativity within a relational and dyadic system, where the characteristics of both the sponsor and the target are taken into account, allows us to go a step further and combine those two sets of rationales. Not only should incumbents be less likely and challengers more likely to attack, but incumbents should, comparatively, receive more attacks than other candidates – that is, the frequency of attacks within any given dyad should be higher when the target is the incumbent. Second, and similarly, candidates should logically attack ‘upwards’ – that is, target attacks towards rivals ahead in the race. The rationale supporting this trend is relatively straightforward: according to a simple competition model (Damore Reference Damore2002; Haynes and Rhine Reference Haynes and Rhine1998), frontrunners should logically attract more attacks because their position is more likely to pose a threat to the remaining candidates. This effect complements, at the dyad level, the expectation at the candidate level that lagging behind in the polls should increase the likelihood of attacking (Harrington and Hess Reference Harrington and Hess1996; Nai and Sciarini Reference Nai and Sciarini2015; Walter et al. Reference Walter, van der Brug and van Praag2014).
Third, candidates that are ideologically distant are expected to engage in more negative campaigning than ideologically close candidates. Empirical evidence for this effect is mixed – some studies find that distance increases negativity (Dolezal et al. Reference Dolezal, Ennser-Jedenastik and Müller2015; Elmelund-Praestekaer Reference Elmelund-Præstekær2008), while other find exactly the opposite (Curini and Martelli Reference Curini and Martelli2010; Walter Reference Walter2014). We believe that ideological distance between candidates provides incentives to attack for the same reason that increasing polarization of party systems has been shown to foster negativity (e.g. Geer Reference Geer2006, Reference Geer2012): distance between competing actors escalates disagreements on key issues, which opens the window of opportunity for ideologically based attacks.
Fourth, we expect negativity within dyads to be a function of negativity in the reverse dyad – that is, when the target becomes the sponsor of the attack. In lay terms, this simply equals expecting that candidates are more likely to attack each other than attack other candidates in the race. The rationale for such expectation draws from the literature showing a ‘logic of retaliation’ in negative campaigning (Damore Reference Damore2002; Dolezal et al. Reference Dolezal, Ennser-Jedenastik and Müller2016; Druckman et al. Reference Druckman, Kifer and Parkin2010; Song et al. Reference Song, Nyhuis and Boomgaarden2017), according to which negativity can be induced by attacks from opponents. The reasons supporting this trend remain under-theorized, but seem relatively intuitive nonetheless (Dolezal et al. Reference Dolezal, Ennser-Jedenastik and Müller2016): candidates have a strategic incentive to respond to negativity with another attack, because failing to do so might create in the eyes of the voter the image that candidates are ineffective or uncommitted to the issues at stake. Furthermore, some evidence exists that backlash effects are less severe for counterattacks, which tips the balance towards going negative (Krupnikov and Bauer Reference Krupnikov and Bauer2014); when voters witness an attack against an actor they almost naturally expect a counterattack, the absence of which might be perceived as cognitively dissonant (De Nooy and Kleinnijenhuis Reference De Nooy and Kleinnijenhuis2015). All in all, retaliation ‘enables those being attacked to offset the relative losses by damaging the competitors’ standing’ (Song et al. Reference Song, Nyhuis and Boomgaarden2017), which means that candidates are often ‘better served by counterattacking’ (Damore Reference Damore2002: 673). In our case, because we are unable to test for the dynamic of attacks (we do not know who attacked first and when), we simply assume that when both candidates in a dyad attack each other a great deal, this reflects an overall and repeated logic of retaliation or ‘tit-for-tat’, regardless of the sequence of attacks.
Fifth, extending the logic of gendered stereotypes and social expectations described above (Huddy and Terkildsen Reference Huddy and Terkildsen1993; Krupnikov and Bauer Reference Krupnikov and Bauer2014), we anticipate that female candidates are less often the target of attacks than male candidates, especially when the sponsor is a female candidate. Kim Fridkin et al. (Reference Fridkin, Kenney and Woodall2009) discuss two main reasons why female candidates can be expected to receive fewer attacks than male candidates. First, they argue, ‘political messages launched against women candidates may be viewed as unfair because women are seen as less likely to have provoked negative attacks and may be seen as less likely to respond to these messages (e.g., women are less aggressive)’ (Fridkin et al. Reference Fridkin, Kenney and Woodall2009: 56); in this sense, gender stereotypes are at play in that we expect less ‘aggressive’ behaviour not only from women, but also against them. Second, because people are more likely to evaluate women as agents driven by compassion, warmth and empathy, political attacks against them ‘may be viewed as unwarranted or even unfair’ (Fridkin et al. Reference Fridkin, Kenney and Woodall2009: 56). Although it might be naive to assume that practitioners and candidates are aware of this scholarship and adapt their behaviour accordingly, it nonetheless seems safe to suggest that gender stereotypes at play at the sponsor level also find an echo in the selection of targets of attacks. Overall, political attacks turned towards female candidates can be expected to be less effective because they are likely to be perceived as unfair and unwarranted.
Data and methods
Negative campaigning worldwide: a new comparative data set
We test our expectations through a new comparative data set on campaigning strategies of candidates competing in elections worldwide (NEGex).Footnote 2 The data set covers all national elections held worldwide between June 2016 and May 2017. Data were gathered through a systematic survey distributed to election-specific samples of national and international scholars in the weeks following each election.Footnote 3 Experts were contacted via a personalized email during the week following the election and received two reminders, respectively one and two weeks after the first invitation. The invitation email contained the link to the questionnaire, administered through Qualtrics. The average response rate across all elections is 19.7%, relatively high for expert surveys.
After the exclusion of missing values on all relevant variables, and considering only elections for which at least five different experts provided independent evaluations, our models were run on 172 candidates who competed in 35 elections worldwide. Information is based on answers provided by 675 experts, aggregated at the candidate–election level. Appendix A in the online supplementary material lists all elections and candidates in our data set and specifies the number of opinions gathered for each election.
On average, experts in the whole sample lean slightly to the left (M=4.35/10, St. dev.=1.84), 75% are domestic (that is, work in the country for which they were asked to evaluate the election) and 36% are female. Overall, experts declared themselves very familiar with the elections (M=8.05/10, St. dev.=1.77) and estimated that the questions in the survey were relatively easy to answer (M=6.47/10, St. dev.=2.39). Table E2 (in online Appendix E) shows the composition of each sample of experts, by election, along these five characteristics. The effect of the experts’ profile on their evaluations will also be controlled in our analyses (see below).
Measuring negativity
Experts were asked to evaluate the overall campaign tone (positive/negative) for up to 10 candidates competing in the election they were surveyed for. Asking experts to evaluate the content of campaigns might seem unorthodox. Scholars usually measure the use of negative campaigning through a content analysis of specific communication channels, such as party manifestos (Curini Reference Curini2011), newspaper advertisements (Nai Reference Nai2013, Reference Nai2014), TV spots (Benoit Reference Benoit2007; Martin Reference Martin2004), debates (Maier and Jansen Reference Maier and Jansen2015; Walter and Vliegenthart Reference Walter and Vliegenthart2010), newspaper reports on campaigns (Lau and Pomper Reference Lau and Pomper2004) and so on.
Although it can provide precise measures and allows the temporal evolution of candidate campaigns to be taken into account, this usual approach has three main disadvantages within the framework of a large-scale comparative design. First, from a logistical standpoint, it would require a level of resources that is unheard of in contemporary social sciences research – imagine retrieving, transcribing, classifying and coding campaign materials for virtually all countries across the globe in as many different languages. Second, from an empirical standpoint, it cannot be assumed that any given communication channel is used in an equivalent way (or, even, exists) in all elections worldwide. For example, TV ads might be the primary vehicle for negativity in the US, but they are banned in Switzerland; measuring negative campaigning on candidates’ websites might be a good idea in countries where internet penetration is high, but this is far from being the case everywhere. Third, from a theoretical standpoint, content analysis of specific communication channels provides a channel-specific image of the campaign and is unable to qualify the campaign of candidates as a whole. Some candidates might go negative during debates, and not at all in TV commercials; coding only one or the other would, necessarily, provide a skewed image of their overall campaign. Indeed, evidence exists that negativity differs across different communication channels (Elmelund-Praestekaer Reference Elmelund-Præstekær2010; Walter and Vliegenthart Reference Walter and Vliegenthart2010). Asking experts to assess the tone of the overall campaign circumvents these problems and provides a measure of campaign tone that is not channel-specific, thus allowing for a broader understanding of the phenomenon.
Experts evaluated the tone of candidates’ campaignsFootnote 4 on a scale ranging between −10 (the campaign was exclusively negative) and 10 (the campaign was exclusively positive); their answers were then aggregated to provide a score of campaign negativity for each competing candidate. In the absence of independent evidence (e.g. alternative measures of campaign negativity) covering the large-scale scope of our data set, it is virtually impossible to run extensive tests for the external validity of this measure. In the only study comparing expert evaluations with content-based measures of negative campaigning (Gélineau and Blais Reference Gélineau and Blais2015), however, the authors highlight that there is a great degree of convergence between the two measures and make a preliminary conclusion that ‘expert surveys should be considered as a serious option, especially in the context of cross-national research’ (Gélineau and Blais Reference Gélineau and Blais2015: 74), which we find encouraging.
Furthermore, to get a more precise idea about what the experts were evaluating, we also asked them to rate the negativity of six vignettes (from −10 ‘very negative’ to 10 ‘very positive’), framed as examples of campaign messages that were either positive, comparative or negative. The aggregated evaluation of those vignettes by all of our experts jointly is illustrated in Figure 1. As the figure shows, experts tend to evaluate as more negative the vignettes that are harsher in tone, which suggests that their shared understanding of ‘negativity’ goes beyond the simple direction of the messages. For instance, the vignette with a negative character-oriented attack (V5) was evaluated on average as substantially more negative than the vignette with a comparable issue-oriented attack (V4); similarly, the harsh character attack in V6 was evaluated as more negative than the character attack in V5. The aggregate measure of negativity that results from experts’ evaluations is general in scope, tackling both issue and character (valence) attacks. However, these results suggest that the experts also take into account the perceived ‘harshness’ of the attacks when evaluating the tone of candidates’ campaigns.
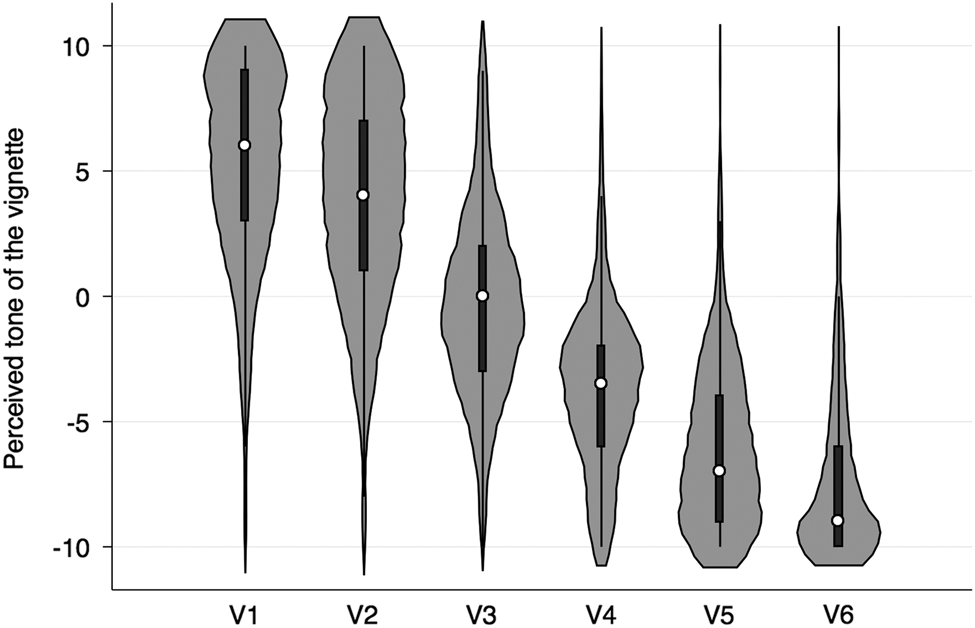
Figure 1 Experts’ Evaluations of Campaign Vignettes Note: All vignettes were evaluated on a scale ranging from −10 ‘very negative’ to 10 ‘very positive’. For each vignette, the ‘violins’ represent how the expert evaluations (N=481–601) are distributed.
The six vignettes read as follows:
V1. ‘I care about people’ [positive, character]
V2. ‘Inflation dropped during my term in office’ [positive, issue]
V3. ‘Unemployment dropped during my term in office, whereas under my opponent it increased’ [comparative, issue]
V4. ‘Under my opponent’s administration the economy has stagnated’ [negative, issue]
V5. ‘You cannot trust my opponent’ [negative, character]
V6. ‘My opponent is dishonest and corrupt’ [negative, character harsh]
The original measure might suffer from cross-cultural comparability issues due to the fact that ‘negativity’ might not have the same meaning everywhere. Even though experts were provided with a clear definition of negative and positive campaigning, it is suitable in this case to ‘anchor’ their judgements based on vignettes (Hopkins and King Reference Hopkins and King2010; King et al. Reference King, Murray, Salomon and Tandon2004); we used the six vignettes presented in Figure 1 to set up a benchmark for comparison across respondents. More specifically, we ran a series of parametric adjustments (Hopkins and King Reference Hopkins and King2010; King et al. Reference King, Murray, Salomon and Tandon2004) through ordered probit models (gllamm models). The models estimated the adjusted measure of campaign negativity simultaneously via the values assigned to all vignettes and five set parameters: the unique election identifier to control the fact that experts are clustered within different elections, and four at the expert level: gender, domestic/international, self-reported familiarity with the election, and left–right positioning. This last control is important, as political orientations have been shown in the past to affect experts’ evaluations (e.g. Curini Reference Curini2010). The adjusted variable is a continuous measure of campaign negativity that ranges between 1 ‘very positive’ and 7 ‘very negative’, and is used as the dependent variable in models at the candidate level.
Table A2 (in online Appendix A) presents, for each candidate, the tone of his or her campaign based on the aggregated scores provided by our experts; the table provides both the adjusted score (used in our analyses) and the original unadjusted score. It is not our goal in this article to comment on the campaign tone of specific candidates (for that, see e.g. Nai and Maier Reference Nai and Maier2018); nonetheless, a few examples can be used to illustrate our data.
Our data suggest that Donald Trump was substantially more negative than Hillary Clinton in the 2016 election. To be sure, evidence exists that Clinton attacked Trump more than the other way around during the campaign (Fowler et al. Reference Fowler, Ridout and Franz2016a); however, the nature of Trump’s campaign was significantly higher in incivility and contempt (Ott Reference Ott2017; Redlawsk et al. Reference Redlawsk, Roseman, Mattes and Katz2018), as well as blame attribution (Oliver and Rahn Reference Oliver and Rahn2016), which was undoubtedly picked up by our experts when assigning scores for Trump. Remember, as discussed before, that our measure goes beyond simple directionality (defence vs. attacks) and also considers, de facto, the harshness of the attacks. Across the Atlantic, our results for the 2017 French election show that the two most extreme candidates – far-right Marine Le Pen and far-left Jean-Luc Mélenchon – went substantially more negative than their rivals; although we do not have independent evidence supporting this claim for this election, this is exactly what Kevin Brookes et al. (Reference Brookes, Le Gall and Berton2014) find for these two candidates for the previous election (2012), thus suggesting that these two candidates have a tendency to run negative campaigns (and providing a good example for our intuition that more extreme candidates are more likely to go on the offensive). A similar trend can also be observed for the 2017 Dutch election, where the far-right Geert Wilders, often accused of displaying a ‘controversial attitude and aberrant political style’ (De Landsheer and Kalkhoven Reference De Landsheer and Kalkhoven2014) and of ‘not trying at all to be agreeable’ (McBride Reference McBride2017) was evaluated with the second highest scores for negativity in our whole sample.
The table also presents, for each candidate, a measure of ratings consistency (calculated starting from the standard deviation of the experts’ original assessments); overall, experts in our database tend to agree with each other, even if variations between candidates appear. Most importantly, the consistency seems slightly lower for elections with an overall lower number of experts consulted; this suggests that, in some cases, differences between experts might have played a role – one reason why we run robustness checks that control for the aggregated experts profile (see below).
A series of tests were also performed to check for the presence of biases due to the specific profile of experts (and the interaction between the profile of experts and the profile of candidates – for example, male experts evaluating the tone of female candidates); our analyses reveal scattered and negligible biases, which reassures us on the measure of reliability (analyses reported in online Appendix E).
Finally, the questionnaire also asked experts to evaluate, for each competing candidate, the primary target of their attacks (if any). We unfortunately do not have a measure of the intensity of attacks from all candidates towards all rivals, as this would have implied a complex set-up and increased substantially the length of the questionnaire, which was already relatively demanding. However, the existing variable provides a relevant measure of attacks among candidates and allows us to specify the relationship between candidates in unique dyads (i.e. a sponsor and a target). The answers provided by experts are aggregated at the dyad level and vary between 0 (no expert mentioned that candidate A attacked candidate B the most) and 100 (all experts mentioned that candidate A attacked candidate B the most).
Covariates
Incumbency status is a simple binary variable that takes the value 1 if the candidate ran as an incumbent. Unfortunately, no existing data set provides information about the left–right positioning of parties and candidates worldwide – at least, no data set exists that covers the full scope of our data. Measures such as the ones in the Chapel Hill Expert Survey (CHES; Polk et al. Reference Polk, Rovny, Bakker, Edwards, Hooghe, Jolly, Koedam, Kostelka, Marks, Schumacher, Steenbergen, Vachudova and Zilovic2017), in the study by Benoit and Laver (Reference Benoit and Laver2007, henceforth B&L) or in the Manifesto Project Dataset (MPD; Volkens et al. Reference Volkens, Lehmann, Matthiess, Merz and Regel2016) cover only subsets of countries and are therefore not tailored for our large-scale comparative purpose.Footnote 5 We thus relied on information provided by the Wikipedia pages for each political party, based on the affiliation of the competing candidates. Although not ideal, due to its open source nature, information diffused through this channel has been shown to provide quality factual information when it comes to electoral results and party competition (Brown Reference Brown2011). Based on the existing information, we created a scale ranging from 1 ‘far left’ to 7 ‘far right’. We verified the external validity of our variable by comparing it with other existing measures; the picture that emerges is one of good external validity, as our measure correlates strongly with the other variables (R=0.88*** with the CHES measure, R=0.89*** with the B&L measure, and R=0.64*** with the MPD measure; see online Appendix D).Footnote 6 Our left–right variable is then folded on itself to create the ‘extremism’ variable, which takes the value 0 for low extremism (this includes candidates from centre left to centre right), 1 for moderate extremism (left and right candidates) and 2 for high extremism (far left and far right candidates). An alternative variable as the squared term of left–right yields very similar results (Table B5 in the online Appendix). We measure competitive standings via the candidate’s success, as the absolute percentage of votes a candidate received in the election. Ideally, we would have a measure of the candidate competitive standings before election day (e.g. opinion polls). Such a measure is, however, problematic for two reasons: first, the number and availability (and quality) of pre-election polls vary drastically across countries. Second, using the value for a specific poll introduces an arbitrary temporal component into the analysis; although the relationship between standing and negativity should be tested dynamically, our dependent variable captures the overall negativity of a candidate’s campaign and does not include a dynamic component.
At the contextual level, we use a binary variable that sorts countries with a PR electoral system (including mixed member proportional) from countries with a plurality/majority system (including mixed member majoritarian; Gallagher Reference Gallagher2014); a more fine-grained measure will be used in robustness checks (see Tables B6 and C3 in the online Appendix), yielding identical results. A simple binary variable distinguishes between presidential (2) and legislative (1) elections. We use the formula proposed by Markku Laakso and Rein Taagepera (Reference Laakso and Taagepera1979) for the effective number of parties (ENPP) to measure the total (effective) number of candidates; this measure takes into account the differences in candidates’ support and yields a number to be interpreted as the number of competing candidates with a similar strength. To measure competitiveness of the election we rely on a question in the expert survey that asked experts to evaluate how much they agree that ‘the race was not competitive, the winner was clearly known beforehand’ (from 0 ‘very low competitiveness’ to 4 ‘very high competitiveness’). Models are also controlled by a binary variable that sorts OECD from non-OECD countries. Finally, all models are controlled by the negativity of the whole campaign, also assessed by all experts (as an additional question at the beginning of the questionnaire, on top of the specific questions for each candidate); this is a further control that the effects we find are specific to the use of negative campaigning by individual candidates, regardless (or, better, controlling for) the overall negativity of the campaign.Footnote 7
Most variables at the dyad level are straightforward (e.g. ‘target is incumbent’). Difference in score is calculated by subtracting the percentage of votes for the sponsor from the percentage of votes for the target; a positive score thus means that the target is ahead in the score. The level of attacks received from the target is simply the value of the dependent variable (how frequently the sponsor attacks the target) for the reversed dyad. Descriptive statistics for all variables at the candidate, dyad and election levels are in Table F1 in the online Appendix.
Models: candidates and dyads
The next section discusses two sets of analyses which are run on two different data sets. The first set of models (Tables 1 and 2) is run at the candidate level and estimates the candidates’ use of negative campaign messages; models are hierarchical regressions, where competing candidates are nested within elections and countries. This first set of models tests the validity of our expectations concerning how the characteristics of the attacker determine the campaign strategies, first concerning the direct effect of candidate and context characteristics (Table 1), and then concerning the effect of candidate characteristics mediated by the context (Table 2). These models are run on the data structured at the candidate level (that is, unit of observations are competing candidates, N=172 after exclusion of missing values).
Table 1 Determinants of Negativity

Note: All models are random-effect hierarchical linear regressions (HLM) where candidates are nested within elections. Models run only on elections evaluated by five experts or more. Dependent variable is the tone of the candidate’s campaign and varies between 1 ‘very positive’ and 7 ‘very negative’.
*** p<0.001, ** p<0.01, * p<0.05, † p<0.1.
Table 2 Determinants of Negativity, Context-Specific Effects

Note: Each row represents a separate model, in which the cross-level interaction term is added to the base model (M1 in Table 2). Full results are available upon request from the author. All models are random-effect hierarchical linear regressions (HLM) where candidates are nested within elections. Models run only on elections evaluated by five experts or more. Dependent variable is the tone of the candidate’s campaign and varies between 1 ‘very positive’ and 7 ‘very negative’.
*** p<0.001, ** p<0.01, * p<0.05, † p<0.1.
The second set of models is run on a reshaped data set in which the unit of observation is candidate dyads – that is, unique combinations of two candidates (sponsor, target) competing in any given election. For each election in the data set, the number of dyads is D=N*(N−1), where N is the number of candidates competing in the election. For instance, for an election with three competing candidates A, B and C, six unique dyads exist as combinations of those three candidates either as sponsors or targets of attacks (AB, AC, BA, BC, CA and CB). The reshaped data set includes 811 unique dyads (after exclusion of missing values), with information about the sponsor, the attacker and the specific dyadic relationship (e.g. ideological distance between the two candidates in the dyad). Tables 3 and 4 present results for models run at the dyad level; the models are used to test the validity of our expectations concerning the effects of target characteristics, as well as characteristics of the relationship between the sponsor (attacker) and the target. These models are also hierarchical in nature, in that dyads and their characteristics are nested within elections and countries at the upper level.
Table 3 Target of Attacks, Candidate Dyads
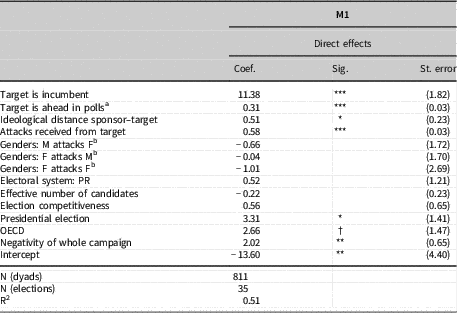
Notes: All models are random-effect hierarchical linear regressions (HLM) where dyads of candidates are nested within elections. Models run only on elections evaluated by five experts or more. Dependent variable measures the intensity of attacks from the sponsor to the target in the dyad, and varies between 0 ‘target not attacked’ and 100 ‘target strongly attacked’.
a The variable is computed as the absolute score of the target minus the absolute score of the sponsor; thus, a positive score means that the target performed better in the election (he or she is ahead in the final tally) when compared to the sponsor of the attack.
b Reference category: M attacks M (M=Male candidate, F=Female candidate).
*** p<0.001, ** p<0.01, * p<0.05, † p<0.1.
Table 4 Target of Attacks, Candidate Dyads, Context-Specific Effects
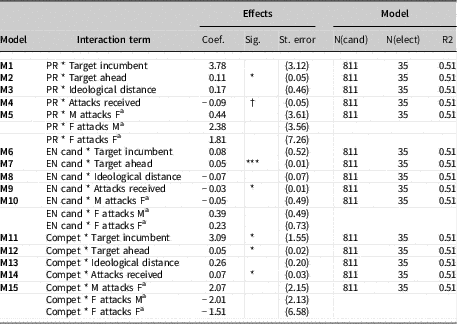
Notes: Each row represents a separate model (except for gender, given that the term is a 2×2 interaction; M5, M10 and M15), in which the cross-level interaction term is added to the base model (M1 in Table 4). Full results are available upon request from the author. All models are random-effect hierarchical linear regressions (HLM) where dyads of candidates are nested within elections. Models run only on elections evaluated by five experts or more. Dependent variable measures the intensity of attacks from the sponsor to the target in the dyad, and varies between 0 ‘target not attacked’ and 100 ‘target strongly attacked’.
a Reference category: M attacks M (M=Male candidate, F=Female candidate).
*** p<0.001, ** p<0.01, * p<0.05, † p<0.1.
Results
Conditions promoting negativity
Looking first at candidate characteristics (Table 1, Model M1), we find strong confirmation that challengers are more likely to go negative on their rivals, in line with the idea that incumbents have much more to lose in going negative (and, potentially, less material on which to base the attacks against challengers). We also find consistent support that candidates far from the ideological centre are significantly and substantially more likely to go negative, as are candidates on the far-right ideological spectrum.
We find, however, no evidence that female candidates are less likely to do so. Still at the candidate level, our models also yield a rather surprising result: although the effect is not extremely strong, candidates with a comparative advantage in the race were more likely to go negative, and not less likely as expected. We cannot fully exclude the possibility that this effect is due to a reversed causality, where going negative explains greater success. To be sure, the relationship between campaigning and competitive standings is a dynamic one, where both aspects influence each other mutually (Blackwell Reference Blackwell2013); our data give a picture of the election campaign as a whole and are not tailored to test for such dynamic effects.
At the contextual level, our results suggest that differences in electoral systems, number of competing candidates and election competitiveness are not direct drivers of negativity (competitiveness also does not seem to have a significantly different effect under PR, as suggested by Bol and Bohl Reference Bol and Bohl2015; M2). We do find that campaigns tend to be less negative in presidential contests (an effect that exists also in a bivariate way); due to the different nature of presidential elections, and the radically different extent of powers of presidents themselves, across different political systems (e.g. the president is the key political figure in US politics but has extremely limited powers in Iceland), it is hard to provide a coherent narrative supporting this effect.
As we discuss below, however, contextual differences interact significantly, in some cases, with determinants at the candidate level and moderate their effects. To allow for a straightforward comparison across all effects, Figure 2 plots the regression coefficients for a model where all variables have been standardized (mean=0, St. dev.=1).
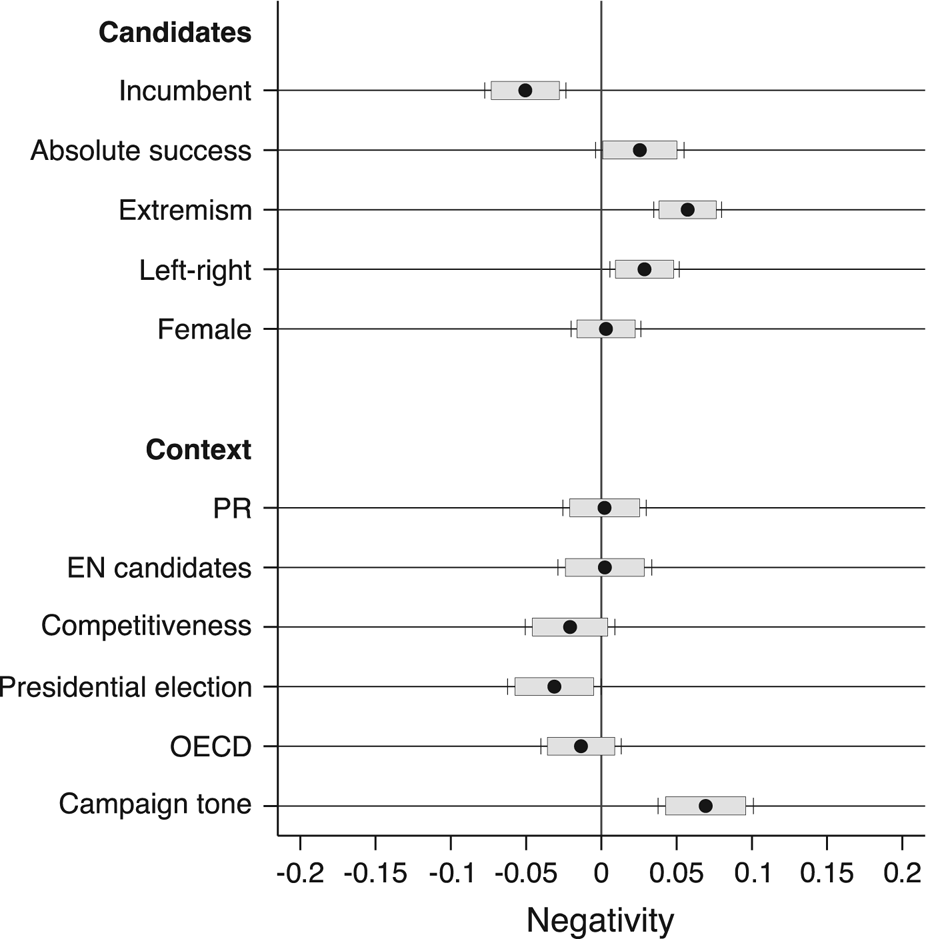
Figure 2 Determinants of Negativity, Standardized Effects Notes: N (candidates)=172, N (elections)=35. Confidence intervals are presented at both 90% (boxes) and 95% (capped whiskers) levels.
All independent variables are standardized (mean=0, St. dev.=1) to allow comparison of effect magnitudes; the dependent variable measures the candidates’ use of negative campaigning and has been put in a 0 to 1 scale where 1 signals a very negative campaign and 0 a very positive campaign.
If the context does not seem to play a major direct role, we find some evidence that it acts instead as a moderating force on the effects of candidates’ characteristics (Table 2).
First, female candidates go negative significantly less than male candidates during elections under PR; although neither of those two elements had a significant effect on its own, they concur to reduce negativity. Seen from the other side, this also simply means that male candidates are especially likely to go negative during elections played under majoritarian rules, which seems intuitively defendable given the rationales discussed above for both gender and electoral systems. The data we dispose of are not fine-grained enough to uncover the underlying mechanisms supporting such interaction. Nonetheless, we believe that this effect, if confirmed by additional evidence, could shed some light on the differential use of attack politics among male and female candidates; increasing evidence seems to suggest that this difference is most of the time only marginal (e.g. Maier Reference Maier2015), and our result could suggest that the difference, rather, depends on the specific contextual conditions at play.
Second, competitiveness reduces the differences between challengers and incumbents. If challengers are, in general, more likely to attack, this is especially the case when the election is not competitive. High competitiveness increases the stakes for incumbents as well, and the chances that they decide ultimately to go negative on their rivals (Fowler et al. Reference Fowler, Franz and Ridout2016b). Figure 3 plots the marginal effects for this interaction; the strong contrast between challengers and incumbents only at low levels of competitiveness appears clearly. A similar effect also exists for the interaction between competitiveness and electoral success.
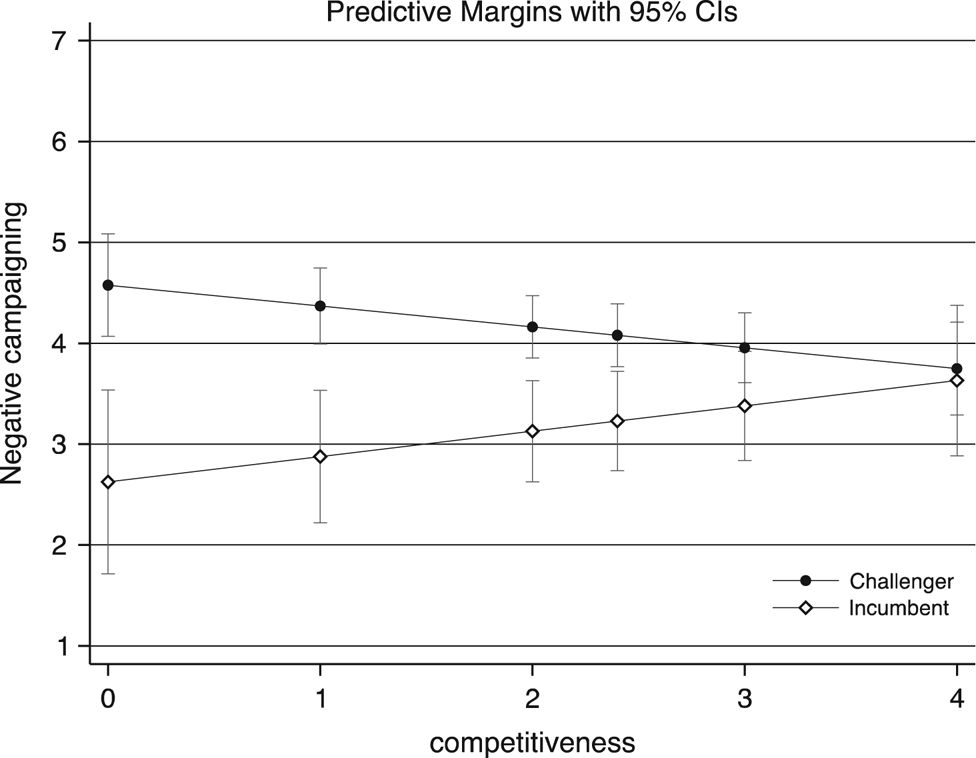
Figure 3 Negative Campaigning, by Competitiveness of the Election and Incumbency Status, Marginal Effects Note: Marginal effects with 95% CIs, based on coefficients in Model M11 (Table 2). Competitiveness of the election ranges between 0 ‘very low’ and 4 ‘very high’. All other variables fixed at the median value.
Targeted attacks
Turning to specific attack behaviours within dyads of candidates, our analyses provide strong support for most expectations, even though we find no significant effect for gender combinations (Tables 3 and 4). Incumbents are strongly and significantly more likely to be targeted, and so are candidates with a comparative standing advantage. This trend resists all robustness checks and additional controls (see online Appendix C) and thus confirms the exportability of a well-known trend in the specific case of US elections: attacks are used strategically to scare off voters from candidates with an initial advantage over the sponsor of attacks, either because they benefit from an incumbency bonus or simply because they are ahead in the score. Targeting attacks towards candidates ahead in the polls, although present in all our models, seems furthermore more likely when the (effective) number of competing candidates increases and during competitive elections. Our models also confirm the intuition that candidates direct their attacks towards rivals far from them on the ideological spectrum; the ideological distance between sponsor and target of attacks is a significant positive predictor of attacks within dyads. It is also interesting to note that this effect exists regardless of the electoral system at play: we could have expected that ideological proximity between candidates reduces the likelihood of attacks, especially in systems where post-election negotiations are likely (e.g. PR), but this does not seem to be the case and the effect exists across all electoral systems and number of competing candidates (Table 4).
We also find strong confirmation that a ‘logic of retaliation’ (Dolezal et al. Reference Dolezal, Ennser-Jedenastik and Müller2016; Song et al. Reference Song, Nyhuis and Boomgaarden2017) is generally at play, because within dyads attacks are significantly more likely when the sponsor is also strongly attacked by the target. Due to the nature of the data, we cannot break down this effect further and assess the dynamics of who attacks first and who reacts; what appears from our results, though, is that, ceteris paribus, pairs of candidates are more likely to attack each other than attack a third candidate, which responds to the logic of targeted retaliation described in the literature. Furthermore, this logic seems to be more likely during elections held under plurality/majority, with a comparatively smaller number of competing candidates (which makes sense), and characterized by higher competitiveness (Table 4). Figure 4 substantiates this last effect through marginal effects.
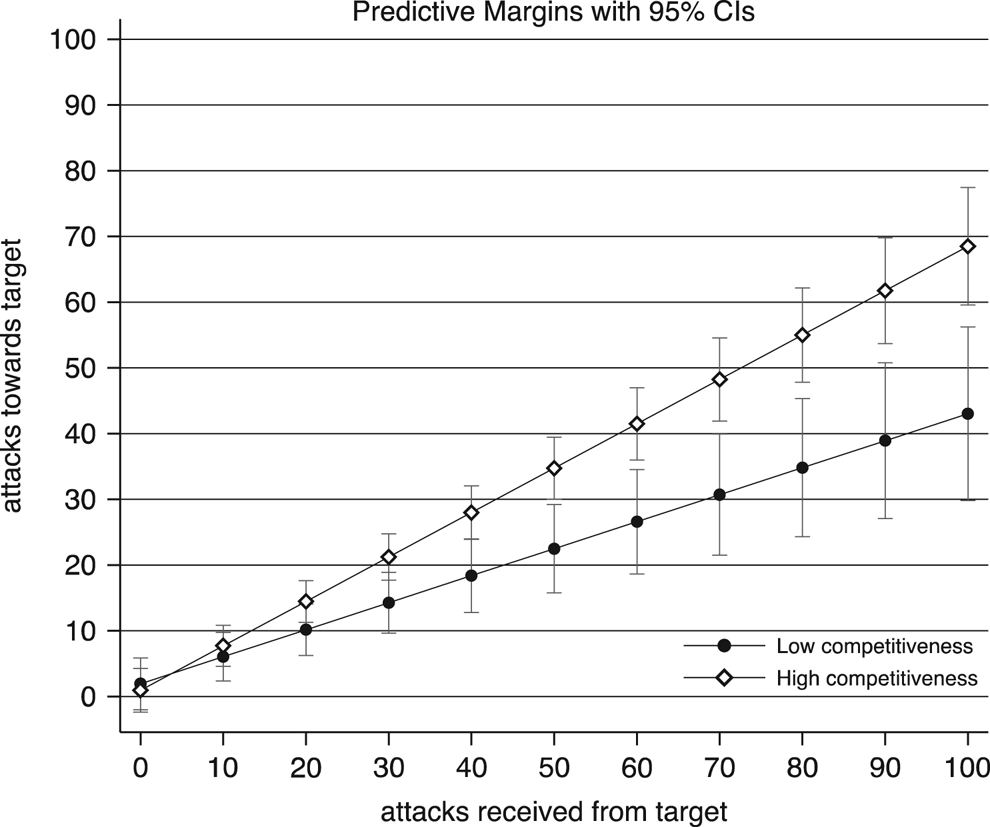
Figure 4 Attacks Against the Target within Dyads, by Intensity of Attacks Received from the Target and Election Competitiveness (Marginal Effects) Note: Marginal effects with 95% CIs, based on coefficients in Model M14 (Table 4). Competitiveness of the election varies between 0 ‘very low’ and 4 ‘very high’. All other variables fixed at the median value.
Finally, our results suggest that the context moderates the effects of competitive standings, although the marginal effects are relatively small in magnitude.
Robustness checks
We ran several sets of robustness tests, for both the analyses at the candidate (online Appendix B) and dyad levels (online Appendix C). Results discussed above are overall robust, and resist controlling for the geographic region of the country and when using alternative measures for both the dependent variable (unadjusted negativity) and some independent variables (left–right, extremism, and a more fine-grained measure of electoral systems). Furthermore, which is perhaps the most important set of controls, all models yield virtually identical results when controlled by the profile of experts (election averages on several expert profile variables, which signal how skewed – and thus potentially biased – the election samples of experts are).
Conclusion and discussion: five general trends
Few would disagree that the typical modern electoral campaign is a hard-fought battle for the hearts and minds of voters, during which competing parties and candidates alternate between self-promotion and attacks on rivals. Negative campaigning seems to exist virtually everywhere, although in varying proportions and with as-yet unclear short-term and systemic effects (Lau et al. Reference Lau, Sigelman and Rovner2007; Nai and Walter Reference Nai and Walter2015). This being so, our global understanding of the phenomenon and its underpinnings is quite incomplete, as evidence existing beyond the US case is very limited. Furthermore, due to the complex discursive nature of attack politics, which creates very concrete obstacles to large-scale systematic research, only scattered comparative evidence exists (e.g. Curini Reference Curini2011; Walter et al. Reference Walter, van der Brug and van Praag2014). All in all, we are far from a global overview of the factors that promote the use of negative campaigns in elections across the world – or even from knowing if any such ‘universal’ factors exist in the first place.
In this article, we aimed to take an important step towards this goal. We introduced an original comparative data set with systematic information about campaigning strategies of 172 candidates who competed in 35 different elections worldwide between June 2016 and May 2017 – a snapshot of the use of negative election campaigning worldwide over the course of one year. By paying special attention to the profile of the sponsor and the target of attacks, as well as the characteristics of the context in which those candidates competed, analyses based on this novel data set yielded some systematic results. Although these results should not be considered as ‘universal laws’ – their importance can be expected to be driven, at least partially, by geographic, cultural and political differences across the candidates, countries and elections under investigation – they nonetheless suggest the existence of five general trends regarding the reasons to ‘go negative’ during leadership-level contests – that is, presidential elections and party leader campaigns in parliamentary elections. The main results can be illustrated as follows:
(1) Incumbents go positive but are attack magnets. Having much to lose and thus few incentives to attack, incumbents are more likely to go positive and promote themselves, but attract negativity and are often the target of attacks. Inversely, challengers have less material upon which to build positive campaigns, and much to say about the past actions and deeds of incumbents, who naturally become the target of attacks.
(2) Extremism and ideological distance from the target drive negativity. Our results at the candidate level show that more extreme candidates, and those on the right end of the political spectrum, are more likely to go negative. Furthermore, ideological distance between candidates fosters negativity: Et tu, Brute? Not according to our data, as candidates seems more likely to attack ideologically distant rivals expected to disagree with them on issues and policy. It is important to note that the effects of ideology also exist when controlling for the ideology of experts who have provided the evaluations.
(3) Candidates attack upwards. Regardless of their competitive standing, incumbency status or ideology, candidates target their attacks towards rivals that have a greater chance of electoral success. The clear trend in analyses at the dyad level is that when the target is ahead in the ratings (or the average polls result) when compared to the sponsor, it is more likely to attract attacks. Even more specifically, the greater the distance, the higher the attack within the dyad.
(4) A logic of retaliation and reciprocity drives negativity. Regardless of their ideology and competitive standings, incentives seem to exist for candidates to go negative on rivals that attack them in return. More research is needed to untangle whether this is due to candidates being perceived as weak and ineffective if they do not retaliate, or simply because being attacked gives candidates a good excuse to unleash attacks that are less likely to backfire. All in all, our results show a strong trend towards attack reciprocity, regardless of who went negative first.
(5) The context matters, indirectly. The decision to go negative might or might not be a strategic one, but regardless of this consideration the context sets up incentives to attack (and pressures not to). It does so mostly indirectly, however, in altering the importance of individual characteristics (e.g. incumbency status) depending on specific election dynamics (e.g. high competitiveness). Direct contextual effects remain limited, suggesting that actors have the last word. From a comparative perspective, this also suggests that the validity of the first four findings can be a function of contextual differences.
Our results face several limitations. First, because the data we rely upon provide a snapshot of negativity during the whole campaign, we were unable to discuss temporal campaign dynamics, such as the interplay between campaign tone, evolution of poll support and subsequent campaign tone (Blackwell Reference Blackwell2013), or a dynamic logic of retaliation based on attacks and counterattacks (Dolezal et al. Reference Dolezal, Ennser-Jedenastik and Müller2016). Second, we were unable to assess the differential use of campaign strategies across different channels, as our measure is (voluntarily) broad and not related to a specific medium or channel; scholars investigating those variations will have to look elsewhere. Third, we understand that expert evaluations are sometimes met with scepticism; we hope, however, to have provided enough material, including several robustness and reliability checks, to convince that this alternative approach has considerable merits for large-scale comparative research on negative campaigning, which is virtually non-existent so far.
Those limitations notwithstanding, our study contributes to the existing literature in four ways. First, empirically, it provides the first large-scale comparative evidence about the use of negative campaigning worldwide, including for regions of the globe that seldom attract the attention of the scientific community at large when it comes to electoral competition. In this sense, the study takes an important step outside the comfort zone of studying campaign dynamics in well-known cases.
Second, also empirically, our article is among the first attempts to assess the effects of individual and contextual characteristics simultaneously when it comes to model a candidate’s decision to ‘go negative’. Further research should expand on this logic and include additional elements at both levels. For instance, at the candidate level, mounting evidence suggests that the personality profile of candidates matters for their communication style and electoral success (Dietrich et al. Reference Dietrich, Lasley, Mondak, Remmel and Turner2012; Nai Reference Nai2018; Nai and Maier Reference Nai and Maier2018); at the context level, formal differences between countries should ideally be studied, for instance in terms of campaign finance regulations – it is a well-known fact that the existence of regulations allowing for ‘anonymous’ advertising (in sharp progression in the US after the 2010 landmark Supreme Court ruling Citizens United v FEC) increases the overall use of negative advertising (Brooks and Murov 2012; Franz et al. Reference Franz, Freedman, Goldstein and Ridout2008).
Third, theoretically, it indirectly supports the universality of strategic underpinnings to campaign messages – for instance, the fact that incumbents have a strategic disadvantage to attack, or that candidates should normally attack upwards. Much evidence exists that electoral campaigns are facing a process of international standardization (Plasser Reference Plasser2000), and our results indirectly support this idea.
Fourth, normatively, it deepens our knowledge of a ubiquitous phenomenon that has the potential to exert a profound influence on modern representative democracies; whether negative campaigning is a positive or disruptive force remains to be seen, but its centrality in modern electoral contests is uncontested, and strengthening our understanding of what it is and where it comes from seems necessary.
Acknowledgements
I am very grateful to the anonymous reviewers and the journal editors for their constructive comments, which helped greatly in improving the article. Despite my best efforts, this article might still contain mistakes that are my responsibility alone. I acknowledge financial support from the Swiss National Science Foundation (Grant ref P300P1_161163) and the support provided by the Electoral Integrity Project (Harvard and University of Sydney), where an early version of this article was drafted; many thanks to colleagues at the EIP, and in particular to Pippa Norris, for their inputs. The data set discussed in this article can be accessed at www.alessandro-nai.com/negative-campaigning-comparative-data.
Supplementary material
To view supplementary material for this article, please visit https://doi.org/10.1017/gov.2018.32









