Article contents
Effect of inclination angle on heat transport properties in two-dimensional Rayleigh–Bénard convection with smooth and rough boundaries
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 18 October 2022
Abstract
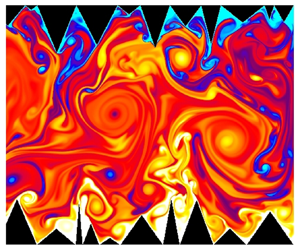
Using direct numerical simulations, two-dimensional tilted Rayleigh–Bénard convection (RBC) is studied in both smooth and roughness-facilitated convection cells of double aspect ratio ( $\varGamma =2$) for air as a working fluid. We investigate the effect of inclination angle (
$\varGamma =2$) for air as a working fluid. We investigate the effect of inclination angle ( $0^{\circ } \leq \phi \leq 90^{\circ }$) on heat flux (
$0^{\circ } \leq \phi \leq 90^{\circ }$) on heat flux ( $Nu$), Reynolds number (
$Nu$), Reynolds number ( $Re$) and flow structures. In a Rayleigh number range
$Re$) and flow structures. In a Rayleigh number range  $10^{6}\leq Ra\leq 10^{9}$, we address the
$10^{6}\leq Ra\leq 10^{9}$, we address the  $Ra$ dependence of
$Ra$ dependence of  $Nu(\phi )$ trend. In the smooth case, while greater tilt results in highest heat flux below
$Nu(\phi )$ trend. In the smooth case, while greater tilt results in highest heat flux below  $Ra=10^{8}$,
$Ra=10^{8}$,  $Nu$ drops with
$Nu$ drops with  $\phi$ monotonically above it (RBC transports heat most efficiently), which explains the different
$\phi$ monotonically above it (RBC transports heat most efficiently), which explains the different  $Nu(\phi )$ trend observed in the previous studies due to
$Nu(\phi )$ trend observed in the previous studies due to  $Ra$ dependence (Guo et al., J. Fluid Mech., vol. 762, 2015, pp. 273–287; Shishkina & Horn, J. Fluid Mech., vol. 790, 2016, R3; Khalilov et al., Phys. Rev. Fluids, vol. 3, 2018, 043503). For the smooth case, we identify the control parameters (
$Ra$ dependence (Guo et al., J. Fluid Mech., vol. 762, 2015, pp. 273–287; Shishkina & Horn, J. Fluid Mech., vol. 790, 2016, R3; Khalilov et al., Phys. Rev. Fluids, vol. 3, 2018, 043503). For the smooth case, we identify the control parameters ( $\phi =75^{\circ }$ and
$\phi =75^{\circ }$ and  $Ra=10^{7}$) that yield maximum heat flux (an increment of
$Ra=10^{7}$) that yield maximum heat flux (an increment of  $18\,\%$ with respect to the level case). On the other hand, among the three roughness set-ups used in the present study, the tallest roughness configuration yields the maximum increment in heat flux (
$18\,\%$ with respect to the level case). On the other hand, among the three roughness set-ups used in the present study, the tallest roughness configuration yields the maximum increment in heat flux ( $25\,\%$) in vertical convection (
$25\,\%$) in vertical convection ( $\phi =90^{\circ }$) at
$\phi =90^{\circ }$) at  $Ra=10^{6}$. With increase in
$Ra=10^{6}$. With increase in  $Ra$,
$Ra$,  $Re$ changes with
$Re$ changes with  $\phi$ marginally in the smooth case, whereas it shows notable changes in its roughness counterpart. We find that the weakening of thermal stratification is related directly to the height of roughness peaks. While
$\phi$ marginally in the smooth case, whereas it shows notable changes in its roughness counterpart. We find that the weakening of thermal stratification is related directly to the height of roughness peaks. While  $Ra$ delays the onset of thermal stratification (in terms of inclination angle) in the smooth case, an increase in roughness height plays the same role in roughness-facilitated convection cells.
$Ra$ delays the onset of thermal stratification (in terms of inclination angle) in the smooth case, an increase in roughness height plays the same role in roughness-facilitated convection cells.
JFM classification
Information
- Type
- JFM Papers
- Information
- Copyright
- © The Author(s), 2022. Published by Cambridge University Press
References
- 12
- Cited by


