Article contents
Optical and electron spin resonance studies of coprecipitated Cd1–xCuxS (x = 0–0.15) semiconductor nanoparticles capped with thiophenol
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 14 February 2011
Abstract
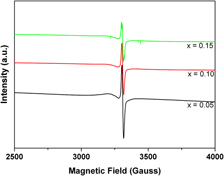
Nanoparticles of Cd1–xCuxS (x = 0–0.15) were synthesized by chemical coprecipitation using thiophenol as a capping agent. The x-ray diffraction patterns reveal that the pure and doped CdS nanoparticles are single phase with cubic zinc blende structure. The transmission electron microscopy shows the average size of the nanoparticles is about 8.5 nm. Optical absorption spectra indicate the energy gap decreases with increasing Cu2+ concentration. The broad emission peak around 520 nm is completely quenched with increasing Cu2+ content. The electron spin resonance analysis also confirms the Cu (II) ion to be doped substitutionally in CdS nanoparticles and the Lande factor of all the samples with sharp resonance is g = 2.0.
- Type
- Articles
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 2011
References
REFERENCES
- 2
- Cited by




