Article contents
Twin wall distortions through structural investigation of epitaxial BiFeO3 thin films
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 04 November 2011
Abstract
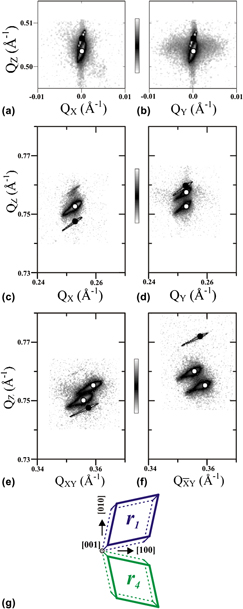
In this work, epitaxial (001) BiFeO3 thin films were deposited on SrTiO3 and TbScO3 single-crystal substrates and analyzed with high-resolution x-ray diffraction—reciprocal space mapping. A basic method was developed to extract structural details of the as-grown BiFeO3 film, including (i) epitaxial strain, (ii) ferroelastic domains, and (iii) lattice rotations. After demonstrating the method, extrinsic distortions at vertical twin walls were determined for specific BiFeO3 heterostructures. A relatively large distortion (0.20° ± 0.08°) was measured in a multidomain (12) and incoherent film, while a nearly intrinsic distortion (0.04° ± 0.03°) was measured in a two-domain coherent film. This work offers insights into the structure of multiferroic BiFeO3 thin films with a general approach that is appropriate for low symmetry epitaxial heterostructures.
- Type
- Articles
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 2011
References
REFERENCES
- 5
- Cited by




