CHD and stroke are leading causes of death in the USA and globally. Elevated serum LDL has been identified as a major risk factor for CHD(1). Data from epidemiological studies have shown a relationship between dietary cholesterol intake and CHD risk(Reference Shekelle, Shryock and Paul2, Reference Stamler and Shekelle3), and metabolic studies have shown that an increase in dietary cholesterol resulted in an increase in plasma total and LDL cholesterol(Reference Hegsted, McGandy and Myers4, Reference Keys and Parlin5). These findings, in part, have led to the guidelines from the American Heart Association (AHA) recommending that healthy adults limit their intake of dietary cholesterol to <300 mg/d. Since a large egg contains about 210 mg of cholesterol, or about 71 % of the corresponding recommended daily value, the AHA recommends restricting egg consumption unless dietary cholesterol intake from other sources is limited(Reference Kraus, Eckel and Howard6).
The AHA guidelines are inconsistent with international guidelines on egg consumption and cholesterol intake. The British Heart Foundation recently removed their advice to limit egg consumption to three per week and there is currently no restriction on egg consumption(7). The Food Standards Agency places an emphasis on reducing saturated fat intake while recommending that eggs are a good choice in a balanced diet(8). Australia recommends limiting cholesterol-rich foods but states that eggs are a good choice if you are healthy and have normal blood cholesterol levels(9). In addition, country-specific FAO food-based dietary guidelines indicate that many countries, including Thailand, Mexico, New Zealand and Japan, recommend eating eggs regularly as part of a healthy diet(10).
The AHA rationale is in conflict with a growing body of scientific literature. Observational epidemiological studies that used simple regression analyses indicated a positive relationship between dietary cholesterol and CHD risk, whereas results of multiple regression analyses tended to find no significant positive association(Reference Ascherio, Rimm and Giovannucci11–Reference Pietinen, Ascherio and Korhonen15). A cross-sectional study(Reference Song and Kerver16) found that egg consumption was not associated with elevated serum cholesterol concentrations. In addition, four prospective studies showed that after adjustment for other potential risk factors, there was no significant overall association between egg consumption and risk of stroke or CHD(Reference Hu, Stampfer and Manson17) or risk of stroke or CVD(Reference Nakamura, Iso and Kita18–Reference Qureshi, Suri and Ahmed20). A review of epidemiological studies by Kritchevsky and Kritchevsky(Reference Kritchevsky and Kritchevsky21) concluded that there was no significant positive association between consuming one or more eggs per day and CHD events, after adjustment for dietary confounders in addition to other known risk factors. A recent risk apportionment study looking at the contribution of egg consumption and other modifiable lifestyle factors to CHD risk determined that consuming one egg per day contributed to <1 % of the CHD risk in the majority of US adults 25 years of age and above when adjusting for other risk factors such as smoking, high BMI, poor dietary patterns and physical inactivity(Reference Barraj, Tran and Mink22).
In contrast, several studies have reported significant positive associations between egg intake and CHD mortality among persons with type 2 diabetes(Reference Hu, Stampfer and Manson17, Reference Djoussé and Gaziano19, Reference Qureshi, Suri and Ahmed20, Reference Houston, Ding and Lee23). In addition, an inverse association between egg intake and stroke risk was observed by Sauvaget et al.(Reference Sauvaget, Nagano and Allen24). While there are consistent findings in the scientific literature, several of the previous prospective studies have not controlled for dietary factors, in particular saturated fat intake(Reference Djoussé and Gaziano19, Reference Qureshi, Suri and Ahmed20). Therefore, the present prospective study to assess the impact of egg consumption on risk of death from CHD and stroke in the US population with data on potential dietary confounders will help to fill this gap in the literature. We also evaluated the relationship between egg consumption and CHD and stroke in subgroup analyses restricted to men and women with self-reported type 2 diabetes.
Methods
Study population
The Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES III) is a cross-sectional survey using a stratified, multi-stage probability sample of civilian, non-institutionalized individuals 2 months of age and above residing in the conterminous USA and is described in detail elsewhere(25). NHANES III was conducted by the National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS) from 1988 to 1994 and collected nutritional status, lifestyle factors, health-related behaviours, health status and physical examination data on 33 994 subjects interviewed in their homes and examined in mobile examination clinics(26). A semi-quantitative FFQ was administered during the home interviews among individuals of 17 years of age and above (n 20 050) to assess their qualitative dietary habits over the past month. Detailed methodology for the FFQ has been described previously(26).
NCHS conducted a follow-up study with NHANES III participants linking death records from the National Death Index (NDI) through 31 December 2000 for individuals aged 17 years and above at baseline. This linkage was based on a probabilistic match of the NHANES III records to the NDI and a sample of death certificates was collected for review and verification. The matching methodology, described in detail elsewhere(27), is based on twelve items that are collected in NHANES III and that are routinely used by NDI to match, including social security number, first and last name, birth date, sex, state of birth, race, state of residence and marital status. Among the eligible population that could be matched to the NDI (n 20 024), there were 3384 confirmed deaths (17 %) by 31 December 2000.
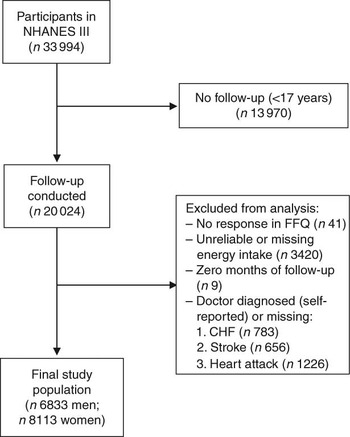
For the present study, we included all individuals at 17 years of age and above who had completed the FFQ at baseline (i.e. 1988–1994) and were eligible for follow-up (n 20 050). Of those eligible for follow-up, there were twenty-six individuals who did not provide sufficient information to match to the NDI. Individuals were excluded from the present analysis if they reported that they had been told by a doctor that they had congestive heart failure (n 783), stroke (n 656) or had previously suffered a heart attack (n 1226), if they did not respond to the relevant egg consumption question on the FFQ (n 41), or if their total energy intake was missing or implausibly low (<2510 kJ/d (<600 kcal/d)) or high (≥20 920 kJ/d (≥5000 kcal/d); n 3420). In addition, nine individuals who had zero total person-years were excluded. After these exclusions, 6833 men and 8113 women remained eligible for follow-up (Fig. 1).
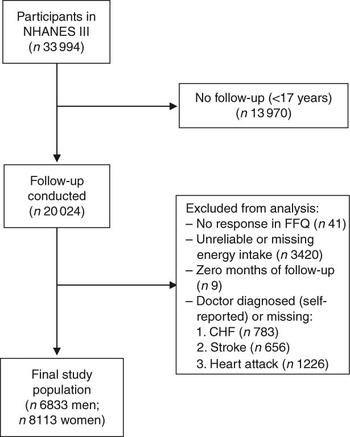
Fig. 1 Inclusion and exclusion criteria for the study population (NHANES III, the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 1988–1994; CHF, congestive heart failure)
Definition of mortality endpoints
Definitions for CHD mortality and stroke mortality were based on the International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision (ICD-10)(28). CHD deaths were defined by ICD-10 codes I20–I25. Stroke deaths were defined by ICD 10 codes I60–I69.
Egg consumption
The FFQ included sixty food categories and study participants were asked to report their frequency of consumption of each category over the past month. The question that provided the egg consumption data for the present analysis was: ‘How many times over the past month have you consumed eggs including scrambled, fried, omelettes, hard-boiled and egg salad?’ The implementation of the FFQ in NHANES III was intended to collect qualitative dietary data that allows for the assessment of general trends in the participant’s diet. NHANES III also collected 24 h dietary recalls on a subsample of the study population. However, this represents short-term intake and would not necessarily be representative of the participant’s typical diet. For this reason, we decided to use the FFQ as the method of measuring egg consumption and its association with mortality from CHD and stroke.
Statistical analyses
The data from NHANES III were extracted from the NCHS databases and the NHANES III baseline variables were merged with the NHANES III-linked mortality files using the SPSS for Windows statistical software package version 7·0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). Egg consumption was calculated by dividing the number of reported eating occasions (EO) per month by 30 d to get an estimate of the typical number of EO per day. We then categorized the egg consumption frequencies based on the examination of the distribution of egg consumption measured as the number of occasions each individual reported eating eggs (EO) per week to ensure an adequate sample size in each category. The following categories were used in the present study: less than one EO per week; one to six EO per week; and seven or more EO per week (one or more EO per day). These categories were also used by Qureshi et al.(Reference Qureshi, Suri and Ahmed20). Follow-up time was calculated for each participant as the time between the date of completion of the baseline questionnaire and the date of death or the end of the follow-up period (31 December 2000), whichever came first. We summarized the baseline characteristics of the study population and stratified by category of egg consumption. Mean values of the dietary variables were adjusted for total energy intake using the residual method(Reference Willett and Stampfer29). All analyses were run using SPSS for Windows version 7·0 (SPSS Inc.) and the STATA statistical software package version 10·0 (StataCorp, College Station, TX, USA).
We estimated hazard ratios (HR) of mortality from stroke and CHD associated with categories of egg consumption using the lowest category (less than one egg EO per week) as the reference group. HR were estimated using Cox proportional hazards analyses with the STCOX command in STATA version 10·0 (StataCorp). We evaluated and adjusted for potential confounders through a series of multivariate models stratified by gender. In the initial analyses (model 1), the HR were estimated after adjustment for age and energy intake (kJ/d (kcal/d)). We then continued to evaluate the association by adding covariates in groups to the initial model. Model 2 was adjusted for age and energy intake as well as health and lifestyle variables including baseline marital status, education level and smoking status (current/past v. never), baseline BMI, waist-to-hip ratio (WHR), hypertension and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Model 3 adjusted for the variables in model 2, plus intake of the following dietary/nutrient factors derived from each participant’s 24 h dietary recall record: number of servings per day of whole grains, fruit and vegetables, and daily intake of alcohol, saturated fat, unsaturated fat, polyunsaturated fat, cholesterol, dietary fibre, vitamins C and E, folate and β-carotene. Model 4 (or ‘parsimonious’ model) included all variables with a P < 0·15 in model 3. In order to investigate findings from previous studies of significant associations between egg intake and CHD risk(Reference Hu, Stampfer and Manson17, Reference Djoussé and Gaziano19, Reference Qureshi, Suri and Ahmed20, Reference Houston, Ding and Lee23), we re-ran the age- and energy-adjusted analysis among study participants who reported a previous doctor diagnosis of type 2 diabetes only.
All summary statistics and analyses were adjusted for survey design with appropriate statistical weights provided by NCHS and se (and associated CI) were derived using the Taylor series (linearization) method(30).
Results
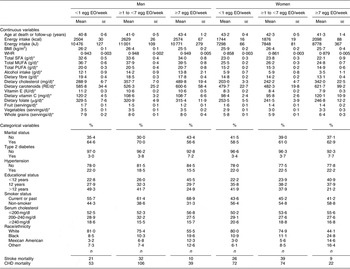
The mean number of EO of eggs in the study population was 0·25 EO/d (1·7 EO/week) and 0·19 EO/d (1·3 EO/week) among men and women, respectively. A summary of the baseline risk factors present in our study population stratified by egg consumption category is presented in Table 1. ‘High’ egg consumers (≥7 EO/week) were more likely to have diabetes, have fewer years of education, be current smokers and less likely to be white (non-Hispanic). Among men, but not women, ‘high’ egg consumption was associated with being unmarried. In addition, ‘high’ egg consumption was associated with higher WHR and energy intake as well as dietary intake of cholesterol, carotenoids and vitamin C, and daily servings of vegetables and whole grains in women. In men, higher reported egg consumption was also associated with higher dietary cholesterol and carotenoid intake, as well as dietary intake of fat (see Table 1; fat intake among women tended to be slightly lower among the ‘high’ consumers). Age was similar across the categories of intake and BMI and fruit intake were slightly lower among the ‘high’ consumers of eggs in both men and women.
Table 1 Baseline characteristics by category of egg consumption for 14 946 CVD-free men and women, NHANES III, 1988–1994
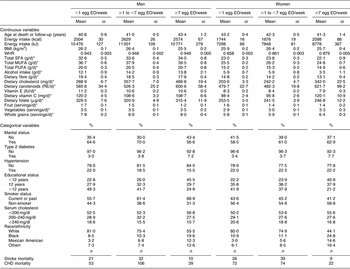
NHANES III, Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 1988–1994; EO, eating occasions; WHR, waist-to-hip ratio; RE, retinol equivalents.
*Adjusted for energy intake.
†Other includes all Hispanics who are not Mexican Americans and all other races that are neither white nor black.
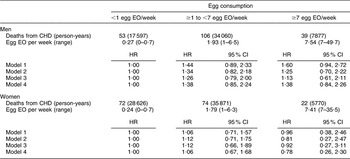
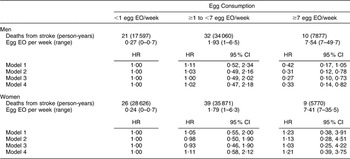
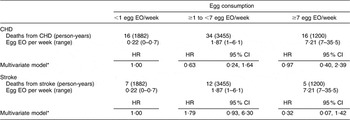
There were 168 CHD and seventy-four stroke deaths over an average follow-up time of 8·9 (range: 0·2–12·2) years in women, and 198 CHD and sixty-three stroke deaths over an average follow-up time of 8·8 (range: 0·1–12·2) years in men. After adjustment for age and energy, there was no statistically significantly increased relative risk of death from CHD (Table 2) or stroke (Table 3) in either men or women. The HR estimates for CHD mortality among men in the highest egg consumption category were attenuated with additional adjustment for baseline marital status, education level and smoking status (current/past v. never), BMI, WHR, hypertension and type 2 diabetes mellitus (HR = 1·25, 95 % CI 0·70, 2·22) and dietary variables (HR = 1·13, 95 % CI 0·61, 2·11). Marital status, race/ethnicity, diabetes and hypertension remained significant risk factors in the parsimonious CHD model among men and women as well as BMI and alcohol intake among men and educational status, WHR and vitamin E intake among women (HR for men = 1·38, 95 % CI 0·84, 2·26; HR for women = 0·78, 95 % CI 0·26, 2·30). There was no evidence of a trend of increased rate of CHD mortality with increasing egg consumption based on the lack of a monotonic pattern. In the stroke analysis in men, there was a significant reduction in the risk of mortality among the highest egg consumers compared with the lowest after adjustment for baseline marital status, education level, smoking status (current/past v. never), baseline BMI, WHR, hypertension and type 2 diabetes mellitus (HR = 0·31, 95 % CI 0·12, 0·78) and dietary variables (HR = 0·27, 95 % CI 0·10, 0·73). This association remained significant in the parsimonious model that adjusted for age and energy in addition to significant risk factors of race/ethnicity and alcohol and fibre intake (HR = 0·33, 95 % CI 0·14, 0·82). In contrast, we did not observe an inverse association between ‘high’ egg consumption and stroke mortality among women.
Table 2 Egg consumption and mortality from CHD in NHANES III mortality follow-up

NHANES III, Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 1988–1994; EO, eating occasion; HR, hazard ratio; WHR, waist-to-hip ratio.
Model 1: Age and energy.
Model 2: Age, energy, marital status, educational status, race/ethnicity, smoking status, BMI, WHR, hypertension, diabetes.
Model 3: Age, energy, marital status, educational status, race/ethnicity, smoking status, BMI, WHR, diabetes, hypertension and dietary variables.
Model 4: Men – age, energy, marital status, race/ethnicity, BMI, diabetes, hypertension and alcohol intake.
Model 4: Women – age, energy, marital status, educational status, race/ethnicity, WHR, diabetes, hypertension and vitamin E.
Table 3 Egg consumption and mortality from stroke in NHANES III mortality follow-up
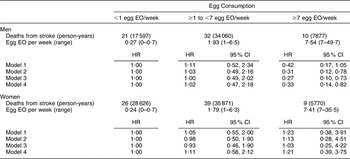
NHANES III, Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 1988–1994; EO, eating occasion; HR, hazard ratio; WHR, waist-to-hip ratio.
Model 1: Age and energy.
Model 2: Age, energy, marital status, educational status, race/ethnicity, smoking status, BMI, WHR, hypertension, diabetes.
Model 3: Age, energy, marital status, educational status, race/ethnicity, smoking status, BMI, WHR, diabetes, hypertension and dietary variables.
Model 4: Men – age, energy, race/ethnicity, alcohol and fibre intake.
Model 4: Women – age, energy, BMI and grain intake.
When we restricted the analysis to men and women with self-reported type 2 diabetes, we did not observe a significant association between egg consumption and CHD or stroke mortality (Table 4). We were not able to stratify the present analysis by gender because of the small sample size and limited covariate adjustment to age, energy intake and gender. The adjusted HR comparing the highest egg consumers to the lowest were 0·97 (95 % CI 0·40, 2·39) for CHD mortality and 0·32 (95 % CI 0·07, 1·42) for stroke mortality.
Table 4 Egg consumption and mortality from CHD and stroke among diabetics in NHANES III mortality follow-up
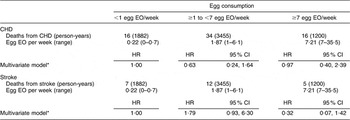
NHANES III, Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 1988–1994; EO, eating occasion; HR, hazard ratio.
*Adjusted for age, energy intake and sex.
Discussion
The present prospective study used the most recent follow-up of a nationally representative sample of US men and women to assess the association between egg consumption and cardiovascular health. We found that self-reported egg consumption frequency was not associated with increased mortality from CHD or stroke in men or women after adjustment for established risk factors. In addition, we did not observe increased CHD or stroke mortality among diabetics with ‘high’ egg consumption (v. ‘low’) in subgroup analyses. A unique finding was the reduction in stroke mortality among men reporting ‘high’ egg consumption, but the 95 % CI was wide, indicating imprecision, and the results should be interpreted in the present context.
These results are consistent with findings from the previous studies. A review of epidemiological studies by Kritchevsky and Kritchevsky(Reference Kritchevsky and Kritchevsky21) concluded that there was no significant positive association between consuming one or more eggs per day and CHD events, after adjustment for dietary confounders in addition to other known risk factors. Hu et al.(Reference Hu, Stampfer and Rimm31) evaluated the relationship between egg consumption and risk of CHD and stroke using the Health Professionals’ Follow-up Study (1986–1994) and the Nurses’ Health Study (1980–1994) and reported no significantly increased risk of disease in men or women after adjustment for smoking, age, BMI and many other risk factors for coronary artery disease. In an earlier nationally representative sample using NHANES I (1971–1975), Qureshi et al.(Reference Qureshi, Suri and Ahmed20) also reported no significant positive association between egg consumption and risk of incident stroke and stroke mortality or death from coronary artery disease in a combined analysis of men and women. Using data from the Physicians’ Health Study I (1981), a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial designed to study the use of low-dose aspirin and β-carotene for the prevention of CVD and cancer, Djoussé and Gaziano(Reference Djoussé and Gaziano19) evaluated the association between egg consumption and risk of incident stroke, myocardial infarction (MI) and death. That study found no evidence of a significant positive association between egg consumption and incident MI or strokes. They did find a significant positive trend for risk of all-cause mortality with increasing egg consumption (P for trend <0·0001)(Reference Djoussé and Gaziano19); however, the study lacked detailed data on dietary variables as well as other important covariates associated with risk for CVD.
Meta-analyses by Howell et al.(Reference Howell, McNamara and Tosca32) and Clarke et al.(Reference Clarke, Frost and Collins33) indicated that saturated fat, not dietary cholesterol, is the major contributor to high blood cholesterol levels in the general population. Our analysis did not control for blood cholesterol levels because we assumed that it was a potential mediator of the effect of egg consumption on CHD and stroke. However, we also ran the analysis controlling for baseline total blood cholesterol levels (blood LDL levels were available only for a subset of our population) and found no measurable difference in the results (data not shown). A review by McNamara(Reference McNamara34) concluded that ‘egg restrictions would be predicted to have little effect on plasma cholesterol levels or on CHD risk’ (p. 546S). Given the epidemiological and clinical evidence(Reference McNamara35), it is unclear whether an intervention strategy of limiting egg consumption in healthy adults would lead to a significant reduction in LDL levels or CHD risk(Reference Fernandez36–Reference Lee and Griffin38). Using a risk apportionment model, Barraj et al.(Reference Barraj, Tran and Mink22) reported that regular daily egg consumption contributed to <1 % of the CHD risk in the majority of US adults 25 years of age and above when adjusting for other risk factors such as smoking, high BMI, poor dietary patterns and physical inactivity.
Our study did not observe increased CHD or stroke mortality among people with diabetes; however, the study power to detect an association was limited by the relatively smaller number of observed cases and the relatively short duration of follow-up. Hu et al.(Reference Hu, Stampfer and Manson17), Qureshi et al.(Reference Qureshi, Suri and Ahmed20), Djoussé and Gaziano(Reference Djoussé and Gaziano19), and Houston et al.(Reference Houston, Ding and Lee23) reported an increased risk of CHD among diabetics in subgroup analyses. Hu et al.(Reference Hu, Stampfer and Manson17) reported a 2-fold increase in risk among diabetic men when comparing more than one egg per day with less than one egg per day (P for trend = 0·04) and a relative risk estimate of 1·49 among diabetic women (P for trend = 0·008)(Reference Hu, Stampfer and Manson17). Qureshi et al.(Reference Qureshi, Suri and Ahmed20) reported a similar 2-fold increase among diabetics (men and women combined) who consumed more than six eggs per week(Reference Qureshi, Suri and Ahmed20). Djoussé and Gaziano reported a statistically significant 2-fold increase among men who reported five or more eggs per week (P for trend = 0·0005) after multivariate adjustment(Reference Djoussé and Gaziano19). In the prospective Health ABC Study, CVD HR comparing the upper to lower category of egg intake (≥3/week v. <1/week) and tertile of cholesterol intake were >3·0 among older persons with type 2 diabetes (P for trend = 0·005 (eggs) and 0·04 (cholesterol))(Reference Houston, Ding and Lee23). Evidence of abnormal cholesterol transport among diabetics with decreased levels of apolipoprotein E(Reference Fielding, Castro and Donner39) could be contributing to the increased risk of CHD. A previous study found that among persons with type 2 diabetes, egg consumption and saturated fat and cholesterol intake had a negative effect on glucose tolerance in 394 non-diabetic men, which could be accounting for an increased risk of CHD in diabetics(Reference Feskens and Kromhout40). Unfortunately, we were not able to control or evaluate markers of insulin resistance or other potentially relevant biomarkers such as lipoproteins on the association between egg consumption and risk in persons with diabetes.
We observed a statistically significant reduction in stroke mortality among men reporting ‘high’ egg consumption. A similar inverse association was observed by Sauvaget et al.(Reference Sauvaget, Nagano and Allen24) with the evaluation of the relationship between consumption of animal products, including eggs, and stroke using data from the Life Span Study that followed survivors of the Hiroshima/Nagasaki bombings. They found a significant reduction in risk among men and women reporting almost daily egg consumption (RR = 0·70, 95 % CI 0·51, 0·95) after adjusting for sex, birth cohort, city, radiation dose, BMI, smoking, alcohol, education, diabetes and hypertension(Reference McNamara35). Similar results were not observed in the previous prospective studies that looked at the relationship of egg consumption with stroke(Reference Hu, Stampfer and Manson17, Reference Djoussé and Gaziano19, Reference Qureshi, Suri and Ahmed20); however, our analysis did allow for the control of several dietary factors that may be confounders in this relationship. Men in the highest egg consumption category had higher intake of saturated fats. Model 3 with the inclusion of the dietary variables resulted in the lowest HR estimate of 0·27 (95 % CI 0·10, 0·73); however, the only remaining significant dietary factor in model 4 was alcohol and fibre intake. One possible mechanism for this protective association with stroke may be due to the potential association of egg intake, and more specifically protein intake, with reduced blood pressure(Reference Takashima, Iwase and Yoshida41, Reference Umesawa, Sato and Imano42). A healthier nutrient profile among egg consumers may also contribute to the inverse relationship, though we attempted to adjust for this by including nutrient intakes in our analysis. However, there may be residual confounding and unmeasured variables that are influencing our results. Based on the inconsistency in the current research and the small number of cases in our analysis, further evaluation in a controlled experimental design is warranted.
An inherent limitation in the data set and our analysis is the use of 24 h recall to assess dietary and nutrient intake associated with a chronic outcome. Egg consumption was based on ‘usual’ consumption patterns reported through a 30 d FFQ, while the other dietary variables were based on what the individual reported consuming on a particular day. The major limitation of the 24 h recall method is related to the variation from day to day, making it impossible to identify a representative day(Reference Buzzard43). Long-term dietary intakes are often skewed to the right; however, single-day intake often results in a flattened distribution that overestimates the low and high intake(44). In addition, egg consumption was based on a semi-quantitative FFQ that reported the EO per month. The amount of eggs consumed at each EO is not represented in this measure, and therefore it is difficult to evaluate the potential for a dose–response pattern of association. However, the 24 h dietary recall data for the individuals included in the present study showed that the average amount of eggs consumed per reported EO of foods similar to those reported in the FFQ was 66·3 g/EO, which is slightly more than one large egg (50 g)(45).
There is the potential for misclassification of dietary exposure due to the collection of data at one point in time to the extent that behaviour has changed over follow-up, as well as the potential for recall issues with reporting diet over an extended period of time (i.e. 30 d). In addition, we only included consumption from food sources in which egg was the main ingredient. This would represent a potential residual confounder in our analysis. However, Hu et al.(Reference Hu, Stampfer and Manson17) reported no measurable difference in estimates when recent egg consumption was used instead of baseline estimates or when egg from other foods were included in the analysis. In addition, our high egg consumer group included those people who reported the consumption of seven or more eggs per week, which could still represent a large proportion of consumers with daily cholesterol intake that is within the current AHA guidelines. However, our sample size did not allow us to investigate the effect a higher cut-off could have on the association. Hu et al.(Reference Hu, Stampfer and Rimm31) were able to look at this question in some detail and reported that there was no significant difference between extreme groups of consumers (‘never’ consumers compared with consumers of two or more eggs per day) in the association with fatal CHD or non-fatal MI.
The strengths of the present study include the population-based design that provides information representative of the US population. The extensive data available in NHANES III allowed us to evaluate the effect of dietary factors as well as health and lifestyle factors on the association between egg consumption and CHD and stroke mortality. In addition, the use of the NDI allows for a complete assessment of outcomes. In conclusion, we observed a lack of association between regular egg consumption and increased risk of CHD or stroke among a sample representative of the US adult population, which is consistent with previous findings. Our findings contribute additional scientific evidence that is inconsistent with the AHA guidelines to limit cholesterol intake through limited egg consumption. The implication of our findings supports a re-evaluation of the recommendations regarding egg consumption for the US population that is more consistent with the international community.
Acknowledgements
The present study was funded by the Egg Nutrition Center (C.G.S., L.M.B. and N.L.T.) and National Institutes of Health Training Grant T32HD046405 (C.G.S). The authors have no conflicts of interest. The opinions expressed herein are those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of the Egg Nutrition Center. C.G.S. and L.M.B. developed the concept and design of the present study and processed the NHANES III consumption and mortality follow-up data for use in the analyses. C.G.S., L.M.B., N.L.T. and P.J.M. designed the statistical analyses. C.G.S. and L.M.B. conducted and interpreted the results of the analyses. C.G.S. wrote the draft of the manuscript and all four authors contributed to the critical review and revision of that draft. The present paper was presented in part at Experimental Biology 2009, New Orleans, LA, USA during 18–22 April.