Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by
Crossref.
Roghair, Ivo
Gallucci, Fausto
and
van Sint Annaland, Martin
2014.
Modeling and Simulation of Heterogeneous Catalytic Processes.
Vol. 45,
Issue. ,
p.
159.
Emre, Oğuz
O. Fox, Rodney
Massot, Marc
de Chaisemartin, Stéphane
Jay, Stéphane
and
Laurent, Frédérique
2014.
Towards Eulerian Modeling of a Polydisperse Evaporating Spray Under Realistic Internal-Combustion-Engine Conditions.
Flow, Turbulence and Combustion,
Vol. 93,
Issue. 4,
p.
689.
Capecelatro, Jesse
Pepiot, Perrine
and
Desjardins, Olivier
2014.
Numerical characterization and modeling of particle clustering in wall-bounded vertical risers.
Chemical Engineering Journal,
Vol. 245,
Issue. ,
p.
295.
Capecelatro, Jesse
Desjardins, Olivier
and
Fox, Rodney O.
2014.
Numerical study of collisional particle dynamics in cluster-induced turbulence.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 747,
Issue. ,
Richter, David H.
2015.
Turbulence modification by inertial particles and its influence on the spectral energy budget in planar Couette flow.
Physics of Fluids,
Vol. 27,
Issue. 6,
Capecelatro, Jesse
Desjardins, Olivier
and
Fox, Rodney O.
2015.
On fluid–particle dynamics in fully developed cluster-induced turbulence.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 780,
Issue. ,
p.
578.
Joshi, J.B.
and
Nandakumar, K.
2015.
Computational Modeling of Multiphase Reactors.
Annual Review of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering,
Vol. 6,
Issue. 1,
p.
347.
Vikhansky, Alexander
and
Splawski, Andrew
2015.
Adaptive multiply size group method for CFD‐population balance modelling of polydisperse flows.
The Canadian Journal of Chemical Engineering,
Vol. 93,
Issue. 8,
p.
1327.
Xue, Qingluan
and
Fox, Rodney O.
2015.
Computational Modeling of Biomass Thermochemical Conversion in Fluidized Beds: Particle Density Variation and Size Distribution.
Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research,
Vol. 54,
Issue. 16,
p.
4084.
Capecelatro, Jesse
and
Desjardins, Olivier
2015.
Mass Loading Effects on Turbulence Modulation by Particle Clustering in Dilute and Moderately Dilute Channel Flows.
Journal of Fluids Engineering,
Vol. 137,
Issue. 11,
Fang, Chenchen
Xu, Jianliang
Zhao, Hui
Li, Weifeng
and
Liu, Haifeng
2015.
Experimental investigation on particle entrainment behaviors near a nozzle in gas–particle coaxial jets.
Powder Technology,
Vol. 286,
Issue. ,
p.
55.
Sarkar, Avik
Milioli, Fernando E.
Ozarkar, Shailesh
Li, Tingwen
Sun, Xin
and
Sundaresan, Sankaran
2016.
Filtered sub-grid constitutive models for fluidized gas-particle flows constructed from 3-D simulations.
Chemical Engineering Science,
Vol. 152,
Issue. ,
p.
443.
Capecelatro, Jesse
Desjardins, Olivier
and
Fox, Rodney O.
2016.
Strongly coupled fluid-particle flows in vertical channels. II. Turbulence modeling.
Physics of Fluids,
Vol. 28,
Issue. 3,
Capecelatro, Jesse
Desjardins, Olivier
and
Fox, Rodney O.
2016.
Effect of Domain Size on Fluid–Particle Statistics in Homogeneous, Gravity-Driven, Cluster-Induced Turbulence.
Journal of Fluids Engineering,
Vol. 138,
Issue. 4,
Capecelatro, Jesse
Desjardins, Olivier
and
Fox, Rodney O.
2016.
Strongly coupled fluid-particle flows in vertical channels. I. Reynolds-averaged two-phase turbulence statistics.
Physics of Fluids,
Vol. 28,
Issue. 3,
Fox, Rodney O.
2016.
Handbook of Multiphase Flow Science and Technology.
p.
1.
Ozel, Ali
Kolehmainen, Jari
Radl, Stefan
and
Sundaresan, Sankaran
2016.
Fluid and particle coarsening of drag force for discrete-parcel approach.
Chemical Engineering Science,
Vol. 155,
Issue. ,
p.
258.
Kellogg, Kevin M.
Liu, Peiyuan
LaMarche, Casey Q.
and
Hrenya, Christine M.
2017.
Continuum theory for rapid cohesive-particle flows: general balance equations and discrete-element-method-based closure of cohesion-specific quantities.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 832,
Issue. ,
p.
345.
Fullmer, William D.
Liu, Guodong
Yin, Xiaolong
and
Hrenya, Christine M.
2017.
Clustering instabilities in sedimenting fluid–solid systems: critical assessment of kinetic-theory-based predictions using direct numerical simulation data.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 823,
Issue. ,
p.
433.
Doisneau, François
Arienti, Marco
and
Oefelein, Joseph C.
2017.
A semi-Lagrangian transport method for kinetic problems with application to dense-to-dilute polydisperse reacting spray flows.
Journal of Computational Physics,
Vol. 329,
Issue. ,
p.
48.
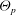 $\Theta _\textit {p}$, which appears in the KT constitutive relations, and the particle-phase turbulent kinetic energy
$\Theta _\textit {p}$, which appears in the KT constitutive relations, and the particle-phase turbulent kinetic energy  $k_\textit {p}$, which appears in the turbulent transport coefficients. The exact RA equations contain unclosed terms due to nonlinearities in the hydrodynamic model and we briefly discuss the available closures for these terms. Finally, we demonstrate by comparing model predictions with direct numerical simulation results that even for non-collisional fluid–particle flows it is necessary to provide separate models for
$k_\textit {p}$, which appears in the turbulent transport coefficients. The exact RA equations contain unclosed terms due to nonlinearities in the hydrodynamic model and we briefly discuss the available closures for these terms. Finally, we demonstrate by comparing model predictions with direct numerical simulation results that even for non-collisional fluid–particle flows it is necessary to provide separate models for 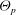 $\Theta _\textit {p}$ and
$\Theta _\textit {p}$ and 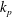 $k_\textit {p}$ in order to correctly account for the effect of the particle Stokes number and mass loading.
$k_\textit {p}$ in order to correctly account for the effect of the particle Stokes number and mass loading.



