No CrossRef data available.
Article contents
Intense optical absorption of defects created in Er3+-diffused layer in MgO (5 mol%)-doped LiNbO3 crystal by local Er3+ diffusion under Li-poor atmosphere
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 26 April 2012
Abstract
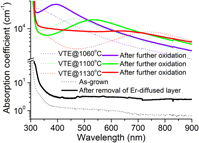
Intense broad absorption bands centered around 1.7, 2.5, 3.1, and 3.7 eV take place in Er3+-diffused layer formed near MgO (5 mol%)-doped LiNbO3 crystal surface by in-diffusion of Er metal under Li-poor atmosphere. These bands are tentatively attributed to the defect absorption of small polarons, bipolarons, F-centers, and Q-polarons created due to Er3+ in-diffusion and Li2O loss from the crystal. It is interesting that the number, type, area, and peaking position of the bands can be controlled by the diffusion temperature and further oxidation treatment. Such material is a promising medium for data storage based upon two-color holography.
- Type
- Articles
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 2012




