Book contents
- Frontmatter
- Dedication
- Contents
- List of Contributors
- Preface
- Part I Clinical syndromes: general
- Part II Clinical syndromes: head and neck
- Part III Clinical syndromes: eye
- Part IV Clinical syndromes: skin and lymph nodes
- Part V Clinical syndromes: respiratory tract
- Part VI Clinical syndromes: heart and blood vessels
- Part VII Clinical syndromes: gastrointestinal tract, liver, and abdomen
- Part VIII Clinical syndromes: genitourinary tract
- Part IX Clinical syndromes: musculoskeletal system
- Part X Clinical syndromes: neurologic system
- 74 Bacterial meningitis
- 75 Aseptic meningitis syndrome
- 76 Acute viral encephalitis
- 77 Intracranial suppuration
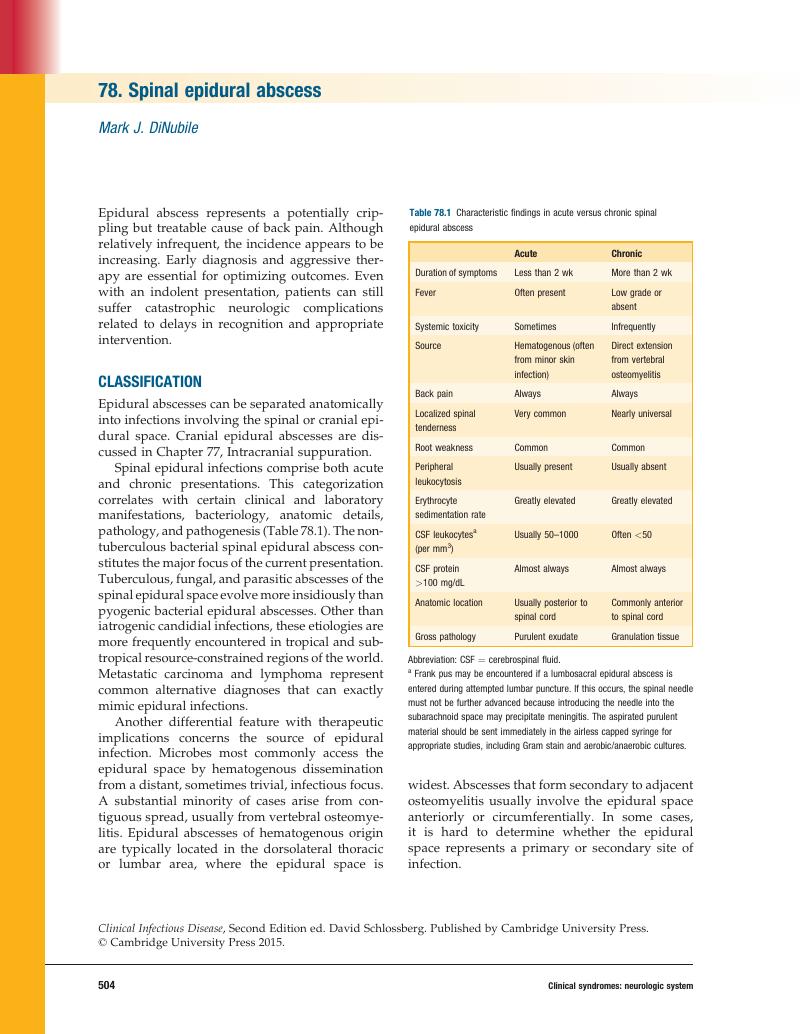
- 78 Spinal epidural abscess
- 79 Myelitis and peripheral neuropathy
- 80 Reye syndrome
- 81 Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy
- 82 Cerebrospinal fluid shunt infections
- 83 Prion diseases
- Part XI The susceptible host
- Part XII HIV
- Part XIII Nosocomial infection
- Part XIV Infections related to surgery and trauma
- Part XV Prevention of infection
- Part XVI Travel and recreation
- Part XVII Bioterrorism
- Part XVIII Specific organisms: bacteria
- Part XIX Specific organisms: spirochetes
- Part XX Specific organisms: Mycoplasma and Chlamydia
- Part XXI Specific organisms: Rickettsia, Ehrlichia, and Anaplasma
- Part XXII Specific organisms: fungi
- Part XXIII Specific organisms: viruses
- Part XXIV Specific organisms: parasites
- Part XXV Antimicrobial therapy: general considerations
- Index
- References
78 - Spinal epidural abscess
from Part X - Clinical syndromes: neurologic system
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 05 April 2015
- Frontmatter
- Dedication
- Contents
- List of Contributors
- Preface
- Part I Clinical syndromes: general
- Part II Clinical syndromes: head and neck
- Part III Clinical syndromes: eye
- Part IV Clinical syndromes: skin and lymph nodes
- Part V Clinical syndromes: respiratory tract
- Part VI Clinical syndromes: heart and blood vessels
- Part VII Clinical syndromes: gastrointestinal tract, liver, and abdomen
- Part VIII Clinical syndromes: genitourinary tract
- Part IX Clinical syndromes: musculoskeletal system
- Part X Clinical syndromes: neurologic system
- 74 Bacterial meningitis
- 75 Aseptic meningitis syndrome
- 76 Acute viral encephalitis
- 77 Intracranial suppuration
- 78 Spinal epidural abscess
- 79 Myelitis and peripheral neuropathy
- 80 Reye syndrome
- 81 Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy
- 82 Cerebrospinal fluid shunt infections
- 83 Prion diseases
- Part XI The susceptible host
- Part XII HIV
- Part XIII Nosocomial infection
- Part XIV Infections related to surgery and trauma
- Part XV Prevention of infection
- Part XVI Travel and recreation
- Part XVII Bioterrorism
- Part XVIII Specific organisms: bacteria
- Part XIX Specific organisms: spirochetes
- Part XX Specific organisms: Mycoplasma and Chlamydia
- Part XXI Specific organisms: Rickettsia, Ehrlichia, and Anaplasma
- Part XXII Specific organisms: fungi
- Part XXIII Specific organisms: viruses
- Part XXIV Specific organisms: parasites
- Part XXV Antimicrobial therapy: general considerations
- Index
- References
Summary
- Type
- Chapter
- Information
- Clinical Infectious Disease , pp. 504 - 509Publisher: Cambridge University PressPrint publication year: 2015



