42 results
Introduction
-
-
- Book:
- The Cambridge Handbook of Private Law and Artificial Intelligence
- Published online:
- 21 March 2024
- Print publication:
- 28 March 2024, pp 1-17
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Contributors
-
- Book:
- The Cambridge Handbook of Private Law and Artificial Intelligence
- Published online:
- 21 March 2024
- Print publication:
- 28 March 2024, pp xvii-xx
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Part IV - Comparative Perspectives
-
- Book:
- The Cambridge Handbook of Private Law and Artificial Intelligence
- Published online:
- 21 March 2024
- Print publication:
- 28 March 2024, pp 597-656
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Index
-
- Book:
- The Cambridge Handbook of Private Law and Artificial Intelligence
- Published online:
- 21 March 2024
- Print publication:
- 28 March 2024, pp 657-672
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Abbreviations
-
- Book:
- The Cambridge Handbook of Private Law and Artificial Intelligence
- Published online:
- 21 March 2024
- Print publication:
- 28 March 2024, pp xxiii-xxvi
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Figures
-
- Book:
- The Cambridge Handbook of Private Law and Artificial Intelligence
- Published online:
- 21 March 2024
- Print publication:
- 28 March 2024, pp xiii-xiv
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Contents
-
- Book:
- The Cambridge Handbook of Private Law and Artificial Intelligence
- Published online:
- 21 March 2024
- Print publication:
- 28 March 2024, pp ix-xii
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Part III - Corporate and Commercial Law
-
- Book:
- The Cambridge Handbook of Private Law and Artificial Intelligence
- Published online:
- 21 March 2024
- Print publication:
- 28 March 2024, pp 407-596
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Copyright page
-
- Book:
- The Cambridge Handbook of Private Law and Artificial Intelligence
- Published online:
- 21 March 2024
- Print publication:
- 28 March 2024, pp vi-vi
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Table
-
- Book:
- The Cambridge Handbook of Private Law and Artificial Intelligence
- Published online:
- 21 March 2024
- Print publication:
- 28 March 2024, pp xv-xvi
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Acknowledgements
-
- Book:
- The Cambridge Handbook of Private Law and Artificial Intelligence
- Published online:
- 21 March 2024
- Print publication:
- 28 March 2024, pp xxi-xxii
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
6 - Tort Law and AI
- from Part I - Law of Obligations
-
-
- Book:
- The Cambridge Handbook of Private Law and Artificial Intelligence
- Published online:
- 21 March 2024
- Print publication:
- 28 March 2024, pp 135-171
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Part I - Law of Obligations
-
- Book:
- The Cambridge Handbook of Private Law and Artificial Intelligence
- Published online:
- 21 March 2024
- Print publication:
- 28 March 2024, pp 69-304
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Reviews
-
- Book:
- The Cambridge Handbook of Private Law and Artificial Intelligence
- Published online:
- 21 March 2024
- Print publication:
- 28 March 2024, pp ii-iv
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Part II - Property
-
- Book:
- The Cambridge Handbook of Private Law and Artificial Intelligence
- Published online:
- 21 March 2024
- Print publication:
- 28 March 2024, pp 305-406
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Dedication
-
- Book:
- The Cambridge Handbook of Private Law and Artificial Intelligence
- Published online:
- 21 March 2024
- Print publication:
- 28 March 2024, pp vii-viii
-
- Chapter
- Export citation

The Cambridge Handbook of Private Law and Artificial Intelligence
-
- Published online:
- 21 March 2024
- Print publication:
- 28 March 2024
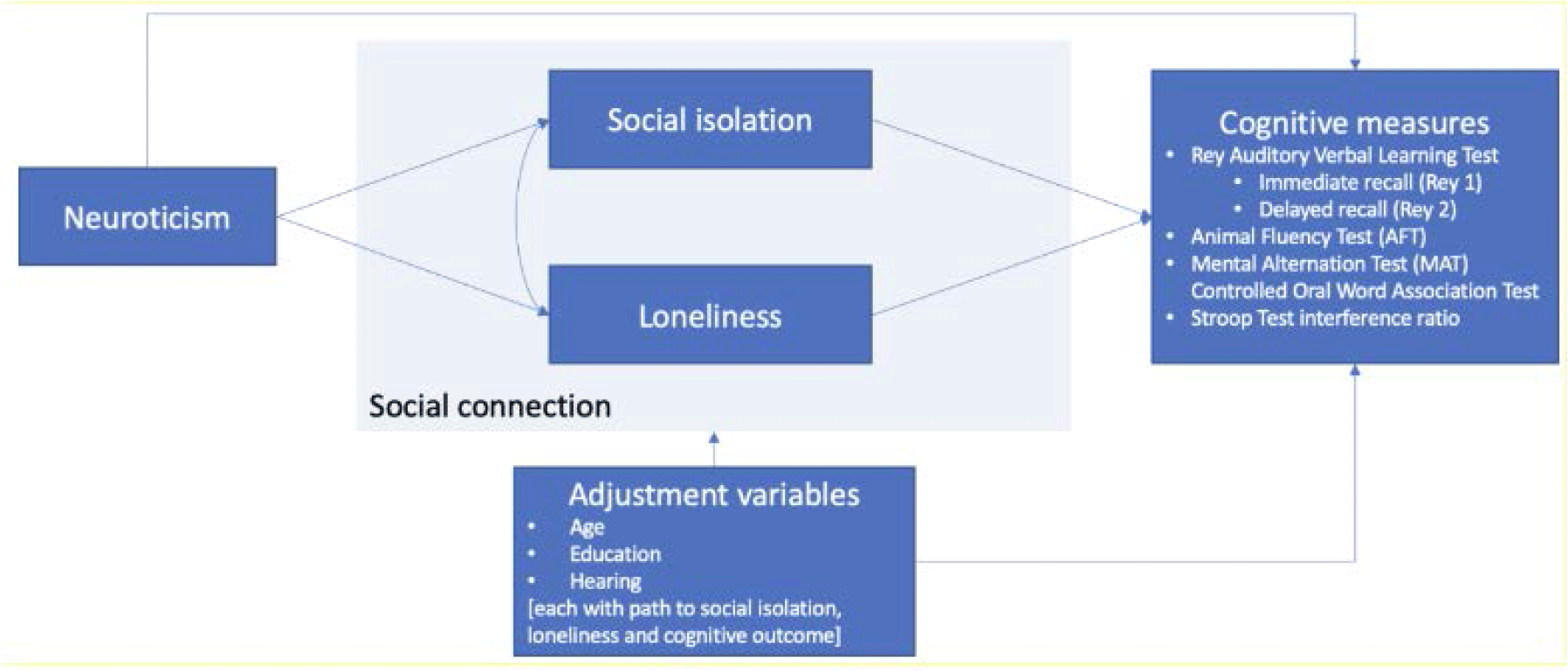
FC30: The relationships between neuroticism, social connection and cognition
-
- Journal:
- International Psychogeriatrics / Volume 35 / Issue S1 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 February 2024, pp. 92-94
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Interactions between profit and welfare on extensive sheep farms
-
- Journal:
- Animal Welfare / Volume 21 / Issue S1 / May 2012
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2023, pp. 57-64
-
- Article
- Export citation
On the occurrence of varlamoffite at the Sardine tin mine, North Queensland, Australia
-
- Journal:
- Mineralogical Magazine / Volume 37 / Issue 289 / March 1970
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 July 2018, pp. 624-628
-
- Article
- Export citation