Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by
Crossref.
Vreugdenhil, Catherine A.
and
Taylor, John R.
2019.
Stratification Effects in the Turbulent Boundary Layer beneath a Melting Ice Shelf: Insights from Resolved Large-Eddy Simulations.
Journal of Physical Oceanography,
Vol. 49,
Issue. 7,
p.
1905.
Pegler, Samuel S.
and
Davies Wykes, Megan S.
2020.
Shaping of melting and dissolving solids under natural convection.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 900,
Issue. ,
Malyarenko, Alena
Wells, Andrew J.
Langhorne, Patricia J.
Robinson, Natalie J.
Williams, Michael J.M.
and
Nicholls, Keith W.
2020.
A synthesis of thermodynamic ablation at ice–ocean interfaces from theory, observations and models.
Ocean Modelling,
Vol. 154,
Issue. ,
p.
101692.
Gwyther, David E.
Kusahara, Kazuya
Asay-Davis, Xylar S.
Dinniman, Michael S.
and
Galton-Fenzi, Benjamin K.
2020.
Vertical processes and resolution impact ice shelf basal melting: A multi-model study.
Ocean Modelling,
Vol. 147,
Issue. ,
p.
101569.
Cheng, Chen
Jenkins, Adrian
Wang, Zhaomin
and
Liu, Chengyan
2020.
Modeling the vertical structure of the ice shelf–ocean boundary current under supercooled condition with suspended frazil ice processes: A case study underneath the Amery Ice Shelf, East Antarctica.
Ocean Modelling,
Vol. 156,
Issue. ,
p.
101712.
Rosevear, Madelaine Gamble
Gayen, Bishakhdatta
and
Galton-Fenzi, Benjamin Keith
2021.
The role of double-diffusive convection in basal melting of Antarctic ice shelves.
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences,
Vol. 118,
Issue. 6,
Begeman, Carolyn Branecky
Asay-Davis, Xylar
and
Van Roekel, Luke
2022.
Ice-shelf ocean boundary layer dynamics from large-eddy simulations.
The Cryosphere,
Vol. 16,
Issue. 1,
p.
277.
Schulz, K.
Nguyen, A. T.
and
Pillar, H. R.
2022.
An Improved and Observationally‐Constrained Melt Rate Parameterization for Vertical Ice Fronts of Marine Terminating Glaciers.
Geophysical Research Letters,
Vol. 49,
Issue. 18,
Rosevear, Madelaine G.
Gayen, Bishakhdatta
and
Galton-Fenzi, Benjamin K.
2022.
Regimes and Transitions in the Basal Melting of Antarctic Ice Shelves.
Journal of Physical Oceanography,
Vol. 52,
Issue. 10,
p.
2589.
McCutchan, Aubrey
and
Johnson, Blair
2022.
Laboratory Experiments on Ice Melting: A Need for Understanding Dynamics at the Ice-Water Interface.
Journal of Marine Science and Engineering,
Vol. 10,
Issue. 8,
p.
1008.
Vreugdenhil, Catherine A.
Taylor, John R.
Davis, Peter E. D.
Nicholls, Keith W.
Holland, Paul R.
and
Jenkins, Adrian
2022.
The Ocean Boundary Layer beneath Larsen C Ice Shelf: Insights from Large-Eddy Simulations with a Near-Wall Model.
Journal of Physical Oceanography,
Vol. 52,
Issue. 8,
p.
1903.
Na, Ji Sung
Kim, Taekyun
Jin, Emilia Kyung
Yoon, Seung-Tae
Lee, Won Sang
Yun, Sukyoung
and
Lee, Jiyeon
2022.
Large-eddy simulations of the ice-shelf–ocean boundary layer near the ice front of Nansen Ice Shelf, Antarctica.
The Cryosphere,
Vol. 16,
Issue. 9,
p.
3451.
Rosevear, Madelaine
Galton-Fenzi, Benjamin
and
Stevens, Craig
2022.
Evaluation of basal melting parameterisations using in situ ocean and melting observations from the Amery Ice Shelf, East Antarctica.
Ocean Science,
Vol. 18,
Issue. 4,
p.
1109.
Washam, Peter
Lawrence, Justin D.
Stevens, Craig L.
Hulbe, Christina L.
Horgan, Huw J.
Robinson, Natalie J.
Stewart, Craig L.
Spears, Anthony
Quartini, Enrica
Hurwitz, Benjamin
Meister, Matthew R.
Mullen, Andrew D.
Dichek, Daniel J.
Bryson, Frances
and
Schmidt, Britney E.
2023.
Direct observations of melting, freezing, and ocean circulation in an ice shelf basal crevasse.
Science Advances,
Vol. 9,
Issue. 43,
Schmidt, B. E.
Washam, P.
Davis, P. E. D.
Nicholls, K. W.
Holland, D. M.
Lawrence, J. D.
Riverman, K. L.
Smith, J. A.
Spears, A.
Dichek, D. J. G.
Mullen, A. D.
Clyne, E.
Yeager, B.
Anker, P.
Meister, M. R.
Hurwitz, B. C.
Quartini, E. S.
Bryson, F. E.
Basinski-Ferris, A.
Thomas, C.
Wake, J.
Vaughan, D. G.
Anandakrishnan, S.
Rignot, E.
Paden, J.
and
Makinson, K.
2023.
Heterogeneous melting near the Thwaites Glacier grounding line.
Nature,
Vol. 614,
Issue. 7948,
p.
471.
Wang, Zhaomin
Liu, Chengyan
Cheng, Chen
Qin, Qing
Yan, Liangjun
Qian, Jiangchao
Sun, Chong
and
Zhang, Li
2023.
On the Multiscale Oceanic Heat Transports Toward the Bases of the Antarctic Ice Shelves.
Ocean-Land-Atmosphere Research,
Vol. 2,
Issue. ,
Howland, Christopher J.
Verzicco, Roberto
and
Lohse, Detlef
2023.
Double-diffusive transport in multicomponent vertical convection.
Physical Review Fluids,
Vol. 8,
Issue. 1,
Cenedese, Claudia
and
Straneo, Fiamma
2023.
Icebergs Melting.
Annual Review of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 55,
Issue. 1,
p.
377.
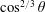 $\cos ^{2/3}\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$
, where
$\cos ^{2/3}\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$
, where
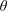 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$
is the angle of the sloping surface to the vertical. The analysis is tested by comparing it with laboratory measurements of the ablation of a sloping ice wall in contact with salty water. We apply the model to make predictions of the turbulent convective dissolution of a sloping ice shelf in the polar oceans.
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}$
is the angle of the sloping surface to the vertical. The analysis is tested by comparing it with laboratory measurements of the ablation of a sloping ice wall in contact with salty water. We apply the model to make predictions of the turbulent convective dissolution of a sloping ice shelf in the polar oceans.




