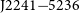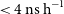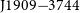81 results
MWA rapid follow-up of gravitational wave transients: Prospects for detecting prompt radio counterparts
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 40 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 October 2023, e050
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Characteristics of Adults Hospitalized for a Major Depressive Disorder: Results from the Multicenter OASIS-D Study
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 66 / Issue S1 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2023, pp. S346-S347
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
WALLABY pilot survey: The diversity of HI structural parameters in nearby galaxies
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 40 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 June 2023, e032
-
- Article
- Export citation
Examining associations between genetic and neural risk for externalizing behaviors in adolescence and early adulthood
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 54 / Issue 2 / January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 May 2023, pp. 267-277
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The prescriber’s guide to classic MAO inhibitors (phenelzine, tranylcypromine, isocarboxazid) for treatment-resistant depression
-
- Journal:
- CNS Spectrums / Volume 28 / Issue 4 / August 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 July 2022, pp. 427-440
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
In situ, broadband measurement of the radio frequency attenuation length at Summit Station, Greenland
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Glaciology / Volume 68 / Issue 272 / December 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 May 2022, pp. 1234-1242
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Early-time searches for coherent radio emission from short GRBs with the Murchison Widefield Array
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 39 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 February 2022, e003
-
- Article
- Export citation
Investigation of convergent and divergent genetic influences underlying schizophrenia and alcohol use disorder
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 53 / Issue 4 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 July 2021, pp. 1196-1204
-
- Article
- Export citation
Murchison Widefield Array rapid-response observations of the short GRB 180805A
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 38 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 June 2021, e026
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Preparedness and response to an emerging health threat—Lessons learned from Candida auris outbreaks in the United States
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 42 / Issue 11 / November 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 February 2021, pp. 1301-1306
- Print publication:
- November 2021
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Neutron Star Extreme Matter Observatory: A kilohertz-band gravitational-wave detector in the global network
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 37 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 November 2020, e047
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
MWA tied-array processing III: Microsecond time resolution via a polyphase synthesis filter
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 37 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 August 2020, e034
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of neuroangiostrongyliasis: updated recommendations
-
- Journal:
- Parasitology / Volume 148 / Issue 2 / February 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 July 2020, pp. 227-233
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The MeerKAT telescope as a pulsar facility: System verification and early science results from MeerTime
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 37 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 July 2020, e028
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
MP50: Vaping, tobacco and cannabis among patients presenting to the emergency department: a cross-sectional study
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Emergency Medicine / Volume 22 / Issue S1 / May 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 May 2020, pp. S60-S61
- Print publication:
- May 2020
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
MP17: Evaluation of a national competency-based assessment system in emergency medicine: A CanDREAM study
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Emergency Medicine / Volume 22 / Issue S1 / May 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 May 2020, p. S48
- Print publication:
- May 2020
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
P078: Impact of vaping on lung health and visits to the emergency department: a cross-sectional study
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Emergency Medicine / Volume 22 / Issue S1 / May 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 May 2020, p. S92
- Print publication:
- May 2020
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Responsiveness of subjective quality of life assessment in schizophrenic patients: a quasi-experimental pilot study
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 16 / Issue 2 / March 2001
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 April 2020, pp. 99-103
-
- Article
- Export citation
Science with the Murchison Widefield Array: Phase I results and Phase II opportunities – Corrigendum
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 37 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 March 2020, e014
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
The Portuguese Participation in the Actifcare (Access to Timely Formal Care in Dementia) European Study: Preliminary Results of Systematic Reviews, Qualitative and Quantitative Data
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 41 / Issue S1 / April 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 March 2020, p. S652
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation