7 results
Authoritarianism, perceptions of security threats, and the COVID-19 pandemic: A new perspective
-
- Journal:
- Politics and the Life Sciences / Volume 43 / Issue 1 / Spring 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 October 2023, pp. 60-82
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Citizens’ Attitudes to Contact Tracing Apps
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Experimental Political Science / Volume 9 / Issue 1 / Spring 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 September 2020, pp. 118-130
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Iron Silicide Nanostructures Prepared by E-Gun Evaporation and Annealing on Si(001)
-
- Journal:
- MRS Online Proceedings Library Archive / Volume 1534 / 2013
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 March 2013, pp. A31-A36
- Print publication:
- 2013
-
- Article
- Export citation
Groups with few conjugacy classes
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society / Volume 54 / Issue 2 / June 2011
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 March 2011, pp. 423-430
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
P. oxy. lxx - (N.) Gonis (J.D.) Thomas (R.) Hatzilambrou (edd., trans.) The Oxyrhynchus Papyri. Volume LXX. (Graeco-Roman Memoirs 90.) Pp. xii + 164, colour pls. London: Egypt Exploration Society, 2006. Cased, £65. ISBN: 978-0-85698-173-9.
-
- Journal:
- The Classical Review / Volume 58 / Issue 2 / October 2008
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 December 2008, pp. 408-409
- Print publication:
- October 2008
-
- Article
- Export citation
Duration of Tell Settlements at Four Prehistoric Sites in Hungary
-
- Journal:
- Radiocarbon / Volume 40 / Issue 2 / 1997
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 July 2016, pp. 659-665
- Print publication:
- 1997
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Re-Evaluation of the Neolithic in Eastern Hungary Based on Calibrated Radiocarbon Dates
-
- Journal:
- Radiocarbon / Volume 37 / Issue 2 / 1995
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 July 2016, pp. 239-244
- Print publication:
- 1995
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation



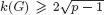 with equality if and only if if
with equality if and only if if 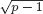 is an integer,
is an integer, 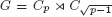 and
and 