185 results

Worlds of Byzantium
- Religion, Culture, and Empire in the Medieval Near East
- Coming soon
-
- Expected online publication date:
- June 2024
- Print publication:
- 31 May 2024
-
- Book
- Export citation
Shifting the paradigm of research-to-policy impact: Infrastructure for improving researcher engagement and collective action
-
- Journal:
- Development and Psychopathology , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 March 2024, pp. 1-14
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Changes in evening-shifted loss of control eating severity following treatment for binge-eating disorder
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 February 2024, pp. 1-8
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Is it time to abandon the concept of treatment-resistant depression?
-
- Journal:
- Research Directions: Depression / Volume 1 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 February 2024, e19
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
What are the best strategies for stratification of clinical cohorts with depression and other mood disorders?
-
- Journal:
- Research Directions: Depression / Volume 1 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 February 2024, e18
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
FC17: Effects of the CarFreeMe driving cessation intervention to identify and improve transport and lifestyle issues for people with dementia: Participant feedback and satisfaction after program completion
-
- Journal:
- International Psychogeriatrics / Volume 35 / Issue S1 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 February 2024, pp. 79-80
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Potential underreporting of treated patients using a Clostridioides difficile testing algorithm that screens with a nucleic acid amplification test
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 45 / Issue 5 / May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 January 2024, pp. 590-598
- Print publication:
- May 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
3 Development of a Computerized Neurocognitive Battery for Children and Adolescents Affected by Human Immunodeficiency Virus in Botswana
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 29 / Issue s1 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 December 2023, pp. 211-212
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
What is the place of universal, selective, and indicated prevention strategies for depression and other mood disorders?
-
- Journal:
- Research Directions: Depression / Volume 1 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 December 2023, e17
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Effectiveness of Bio-K+ for the prevention of Clostridioides difficile infection: Stepped-wedge cluster-randomized controlled trial
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 45 / Issue 4 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 December 2023, pp. 443-451
- Print publication:
- April 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Is the concept of clinical staging a useful way of matching levels of intervention to the needs of young people with depressive or other mood disorders?
-
- Journal:
- Research Directions: Depression / Volume 1 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 December 2023, e16
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Is immune activation simply a non-specific marker of depression severity or chronicity or does it indicate an underlying pathophysiological path to depressive or other mood disorders?
-
- Journal:
- Research Directions: Depression / Volume 1 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 November 2023, e15
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Building strong health and career trajectories through translational research
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Developmental Origins of Health and Disease / Volume 14 / Issue 5 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 October 2023, pp. 570-575
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Will new brain stimulation techniques precipitate a new wave of therapies?
-
- Journal:
- Research Directions: Depression / Volume 1 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 October 2023, e10
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
What is the true nature of the relationship between metabolic disturbance, specifically of glucose and insulin metabolism, and depressive and other mood disorders?
-
- Journal:
- Research Directions: Depression / Volume 1 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 October 2023, e2
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
What are the likely impacts of climate change on rates of depression and other mood disorders? What actions can be taken by individuals, communities or nations to reduce those impacts?
-
- Journal:
- Research Directions: Depression / Volume 1 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 October 2023, e3
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Are depressive and other mood disorders best conceptualized as disorders of energy, and related motor activity, rather than mood?
-
- Journal:
- Research Directions: Depression / Volume 1 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 October 2023, e4
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
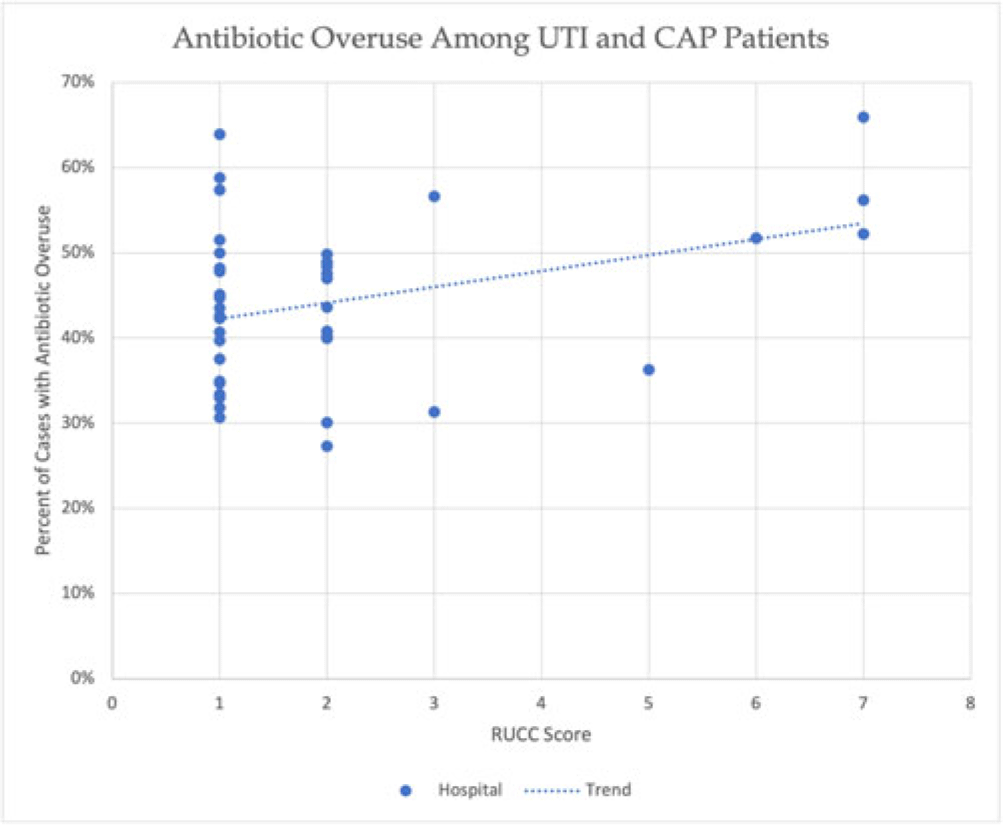
Identifying the relationship between hospital rurality and antibiotic overuse
-
- Journal:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship & Healthcare Epidemiology / Volume 3 / Issue S2 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 September 2023, pp. s34-s35
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
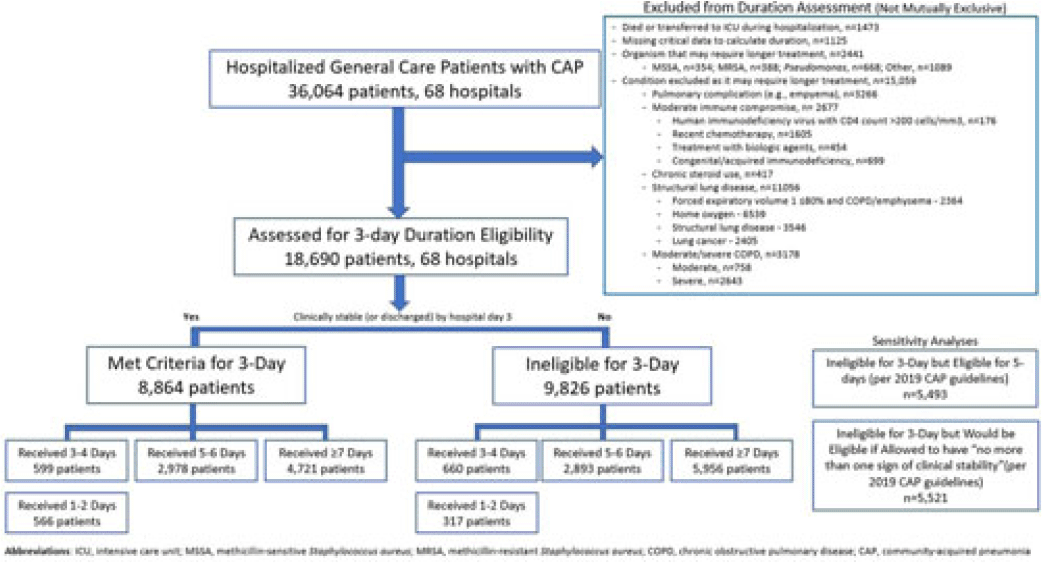
Three-day antibiotic duration in patients with pneumonia: A sixty-eight–hospital cohort
-
- Journal:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship & Healthcare Epidemiology / Volume 3 / Issue S2 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 September 2023, p. s22
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
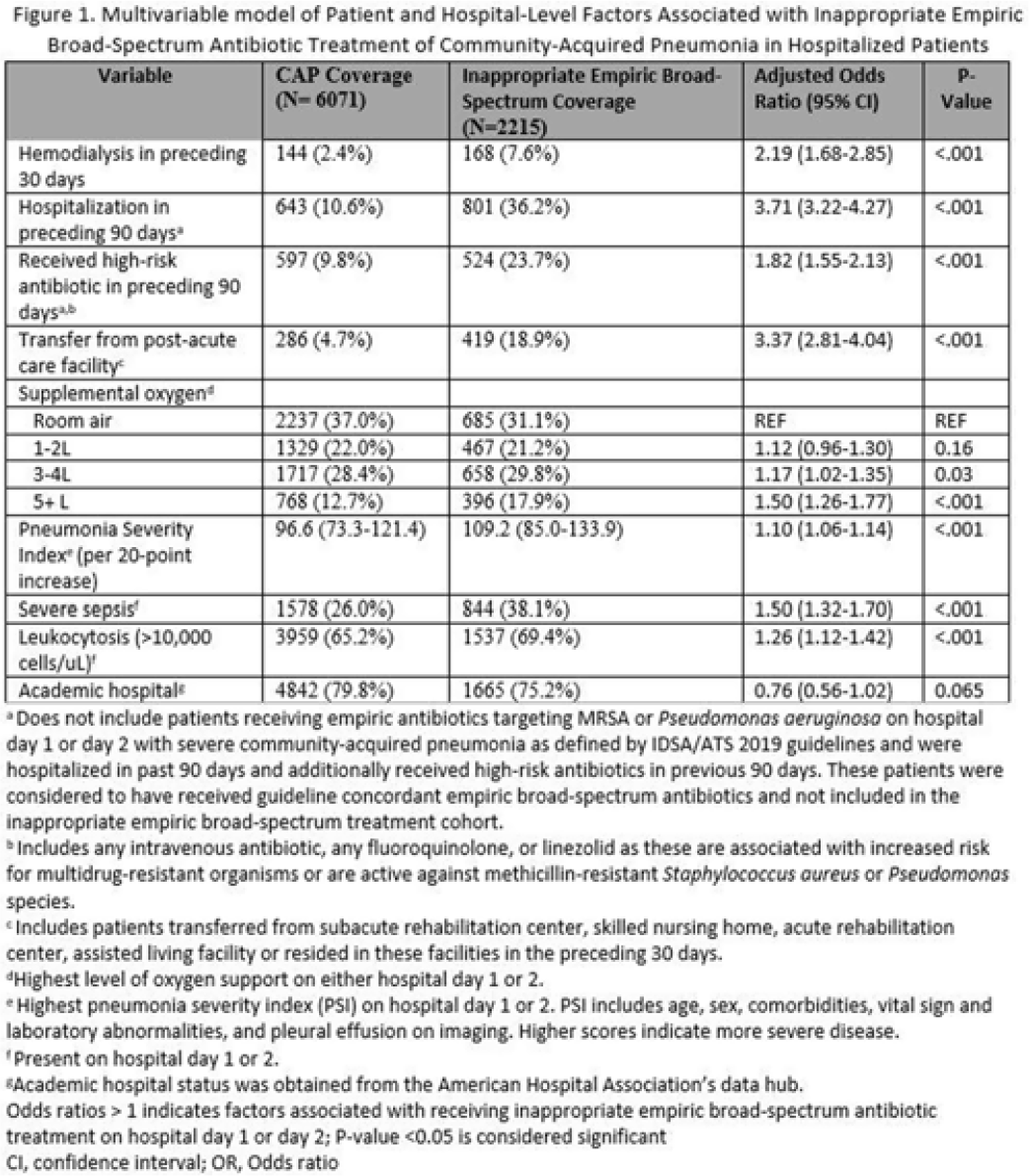
Risk Factors and outcomes associated with inappropriate empiric broad-spectrum antibiotic use in hospitalized patients with community-acquired pneumonia
-
- Journal:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship & Healthcare Epidemiology / Volume 3 / Issue S2 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 September 2023, pp. s31-s32
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation