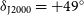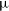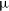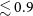531 results
Ethnic density and first episode psychosis in the British Pakistani population: findings from the East Lancashire Early Intervention Service
-
- Journal:
- The British Journal of Psychiatry , FirstView
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 April 2024, pp. 1-6
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Vitamin D status of pregnant women with obesity in the United Kingdom and its association with pregnancy outcomes: a secondary analysis of the UPBEAT study
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Accepted manuscript
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 April 2024, pp. 1-28
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Analysis and Implications of the Edge Structure of Dioctahedral Phyllosilicates
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 36 / Issue 2 / April 1988
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 April 2024, pp. 141-146
-
- Article
- Export citation
Thin-Film Analysis of Clay Particles Using Energy Dispersive X-Ray Analysis
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 30 / Issue 5 / October 1982
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 April 2024, pp. 375-382
-
- Article
- Export citation
Genesis and Morphology of Iron Sulfides in Gray Kaolins
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 39 / Issue 1 / February 1991
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 April 2024, pp. 70-76
-
- Article
- Export citation
Evaluating the Current State of Epilepsy Care in the Province of Ontario
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 March 2024, pp. 1-3
-
- Article
- Export citation
Sedimentary Structure in Gray Kaolins of Georgia
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 40 / Issue 5 / October 1992
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 February 2024, pp. 555-560
-
- Article
- Export citation
Identifying core global mental health professional competencies: A multi-sectoral perspective
-
- Journal:
- Cambridge Prisms: Global Mental Health / Volume 11 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 February 2024, e24
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Survey and monitoring of ASKAP’s RFI environment and trends I: Flagging statistics
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 41 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 January 2024, e012
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
L-Shell X-Ray Conversion Yields for Laser-Irradiated Tin and Silver Foils
-
- Journal:
- Laser and Particle Beams / Volume 2022 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, e17
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Smectite Clay Sequestration of Aflatoxin B1: Particle Size and Morphology
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 56 / Issue 5 / October 2008
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 558-570
-
- Article
- Export citation
Reductive Degradation of p,p′-DDT cy Fe(II) in Nontronite NAu-2
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 58 / Issue 6 / December 2010
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 821-836
-
- Article
- Export citation
Intercalation and Surface Modification of Smectite by Two Non-Ionic Surfactants
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 51 / Issue 2 / April 2003
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 150-161
-
- Article
- Export citation
Medicare Drug Pricing Negotiations: Assessing Constitutional Structural Limits
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Law, Medicine & Ethics / Volume 51 / Issue 4 / Winter 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 March 2024, pp. 956-960
- Print publication:
- Winter 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Variation in the clinical management of self-harm by area-level socio-economic deprivation: findings from the multicenter study of self-harm in England
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 54 / Issue 5 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 October 2023, pp. 1004-1015
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Perspectives of African American Church Leaders in Response to COVID-19 Emergency Preparedness and Risk Communication Efforts Within a Community Engaged Research Partnership: COVID-19 emergency risk communication
-
- Journal:
- Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness / Volume 17 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 October 2023, e532
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Supreme Court Impacts in Public Health Law: 2022-2023
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Law, Medicine & Ethics / Volume 51 / Issue 3 / Fall 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 December 2023, pp. 684-688
- Print publication:
- Fall 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
The Rapid ASKAP Continuum Survey IV: continuum imaging at 1367.5 MHz and the first data release of RACS-mid
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 40 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 August 2023, e034
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Hydra II: Characterisation of Aegean, Caesar, ProFound, PyBDSF, and Selavy source finders
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 40 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 June 2023, e027
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Hydra I: An extensible multi-source-finder comparison and cataloguing tool
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 40 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 June 2023, e028
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation