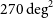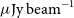342 results
Patterns of infracommunity species richness in eels, Anguilla anguilla
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Helminthology / Volume 78 / Issue 2 / June 2004
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 April 2024, pp. 141-146
-
- Article
- Export citation
Healthcare personnel with laboratory-confirmed mpox in California during the 2022 outbreak
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 March 2024, pp. 1-3
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Advocacy at the Eighth World Congress of Pediatric Cardiology and Cardiac Surgery
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 33 / Issue 8 / August 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 August 2023, pp. 1277-1287
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Examining the ontogeny of the Pennsylvanian cladid crinoid Erisocrinus typus Meek and Worthen, 1865
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Paleontology / Volume 97 / Issue 4 / July 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 July 2023, pp. 906-913
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Disparities in central line-associated bloodstream infection and catheter-associated urinary tract infection rates: An exploratory analysis
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 44 / Issue 11 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 April 2023, pp. 1857-1860
- Print publication:
- November 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Association of cumulative prenatal adversity with infant subcortical structure volumes and child problem behavior and its moderation by a coexpression polygenic risk score of the serotonin system
-
- Journal:
- Development and Psychopathology , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 April 2023, pp. 1-16
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Eskers associated with buried glaciers in Mars' mid latitudes: recent advances and future directions
-
- Journal:
- Annals of Glaciology / Volume 63 / Issue 87-89 / September 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 March 2023, pp. 33-38
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Evaluating automated electronic case report form data entry from electronic health records
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Clinical and Translational Science / Volume 7 / Issue 1 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 December 2022, e29
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
WALLABY pilot survey: Public release of H i data for almost 600 galaxies from phase 1 of ASKAP pilot observations
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 39 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 November 2022, e058
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The Evolutionary Map of the Universe Pilot Survey – ADDENDUM
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 39 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 November 2022, e055
-
- Article
- Export citation
Colon surgical-site infections and the impact of “present at the time of surgery (PATOS)” in a large network of community hospitals
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 44 / Issue 8 / August 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 September 2022, pp. 1255-1260
- Print publication:
- August 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Comparing the activity of novel antibiotic agents against carbapenem-resistant Enterobacterales clinical isolates
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 44 / Issue 5 / May 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 July 2022, pp. 762-767
- Print publication:
- May 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Timing of pulmonary valve replacement: can we use the same volumetric thresholds in repaired tetralogy of Fallot and pulmonary stenosis?
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 33 / Issue 1 / January 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 March 2022, pp. 90-95
-
- Article
- Export citation
GASKAP-HI pilot survey science I: ASKAP zoom observations of Hi emission in the Small Magellanic Cloud
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 39 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 February 2022, e005
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The ASKAP Variables and Slow Transients (VAST) Pilot Survey
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 38 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 October 2021, e054
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
The Evolutionary Map of the Universe pilot survey
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 38 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 September 2021, e046
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
A comparison of mdma-assisted psychotherapy to non-assisted psychotherapy in treatment-resistant PTSD: A systematic review and meta-analysis
-
- Journal:
- European Psychiatry / Volume 64 / Issue S1 / April 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 August 2021, pp. S141-S142
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Nomenclature for Pediatric and Congenital Cardiac Care: Unification of Clinical and Administrative Nomenclature – The 2021 International Paediatric and Congenital Cardiac Code (IPCCC) and the Eleventh Revision of the International Classification of Diseases (ICD-11)
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 31 / Issue 7 / July 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 July 2021, pp. 1057-1188
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Comparison of metrics used to track central-line–associated bloodstream infections (CLABSIs) and catheter-associated urinary tract infections (CAUTIs) across a regional network
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 43 / Issue 11 / November 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 July 2021, pp. 1712-1714
- Print publication:
- November 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
Role of age, gender and marital status in prognosis for adults with depression: An individual patient data meta-analysis
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology and Psychiatric Sciences / Volume 30 / 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 June 2021, e42
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation