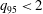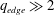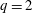45 results
COMPREHENSIVE UPDATE OF MARINE RESERVOIR VALUES FOR NEW ZEALAND COASTAL WATERS TO INFORM COASTAL HAZARD RESEARCH
-
- Journal:
- Radiocarbon / Volume 65 / Issue 6 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 January 2024, pp. 1253-1279
- Print publication:
- December 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Law and Religion in the Commonwealth: The Evolution of Case Law Renae Barker, Paul T Babie and Neil Foster Hart Publishing, Oxford, 2022, 352 pp (hardback £85), ISBN: 9781509950140
-
- Journal:
- Ecclesiastical Law Journal / Volume 25 / Issue 3 / September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 September 2023, pp. 390-393
- Print publication:
- September 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
P.017 Convergent and contrasting modulation of saccade and pupil responses by several neurodegenerative diseases during free viewing of video clips
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 50 / Issue s2 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 June 2023, p. S62
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Church, State, and Family: Reconciling Traditional Teachings and Modern Liberties John Witte Jr Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 2019, xxii + 434 pp (paperback £28), ISBN: 978-1-316-63612-1
-
- Journal:
- Ecclesiastical Law Journal / Volume 24 / Issue 3 / September 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 September 2022, pp. 386-389
- Print publication:
- September 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
P.002 Saccade parameters reveal cognitive impairment and differentially associate with cognitive domains across neurodegenerative diseases
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 49 / Issue s1 / June 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 June 2022, p. S8
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
The Blessings of Liberty: Human Rights and Religious Freedom in the Western Legal Tradition John Witte Jr Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 2022, 316 pp (hardback £85), ISBN: 978-1-108-65284-1
-
- Journal:
- Ecclesiastical Law Journal / Volume 24 / Issue 2 / May 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 April 2022, pp. 258-260
- Print publication:
- May 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
Pretreatment of Terrestrial Macrofossils
-
- Journal:
- Radiocarbon / Volume 62 / Issue 2 / April 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 February 2020, pp. 349-360
- Print publication:
- April 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation
Evaluation of the relative contribution of meteorological and oceanic forces to the drift of ice islands offshore Newfoundland
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Glaciology / Volume 66 / Issue 256 / April 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 January 2020, pp. 203-218
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Genetic Variation in the Ontario Neurodegenerative Disease Research Initiative
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences / Volume 46 / Issue 5 / September 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 August 2019, pp. 491-498
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Effects of obesity and weight loss on mitochondrial structure and function and implications for colorectal cancer risk
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Nutrition Society / Volume 78 / Issue 3 / August 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 March 2019, pp. 426-437
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Effect of weight loss on mitochondrial defects in the ageing human colon
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Nutrition Society / Volume 77 / Issue OCE4 / 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 October 2018, E172
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
An Investigation of the Energy Levels within a Common Perovskite Solar Cell Device and a Comparison of DC/AC Surface Photovoltage Spectroscopy Kelvin Probe Measurements of Different MAPBI3 Perovskite Solar Cell Device Structures
-
- Journal:
- MRS Advances / Volume 2 / Issue 21-22 / 2017
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 January 2017, pp. 1195-1201
- Print publication:
- 2017
-
- Article
- Export citation
The external kink mode in diverted tokamaks
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Plasma Physics / Volume 82 / Issue 3 / June 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 June 2016, 515820301
-
- Article
- Export citation
Is UK emergency food nutritionally adequate? A critical evaluation of the nutritional content of UK food bank parcels
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Nutrition Society / Volume 75 / Issue OCE1 / 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 January 2016, E8
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Panic disorder and incident coronary heart disease: a systematic review and meta-regression in 1 131 612 persons and 58 111 cardiac events
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 45 / Issue 14 / October 2015
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 June 2015, pp. 2909-2920
-
- Article
- Export citation
Can Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry (MALDI-TOF) Enhance Antimicrobial Stewardship Efforts in the Acute Care Setting?
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 34 / Issue 9 / September 2013
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 January 2015, pp. 990-995
- Print publication:
- September 2013
-
- Article
- Export citation
Revision of the Nearctic Species of Thanatus C. L. Koch (Araneae: Thomisidae)
-
- Journal:
- The Canadian Entomologist / Volume 96 / Issue 4 / April 1964
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 May 2012, pp. 636-656
-
- Article
- Export citation
AN IMPROVED BERLESE–TULLGREN FUNNEL AND A FLOTATION SEPARATOR FOR EXTRACTING GRASSLAND ARTHROPODS
-
- Journal:
- The Canadian Entomologist / Volume 103 / Issue 11 / November 1971
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 May 2012, pp. 1549-1552
-
- Article
- Export citation
The Spider Genus Xysticus C. L. Koch (Araneae: Thomisidae) in Canada
-
- Journal:
- The Canadian Entomologist / Volume 97 / Issue 12 / December 1965
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 May 2012, pp. 1233-1280
-
- Article
- Export citation
Contributors
-
-
- Book:
- Neurogenetics
- Published online:
- 05 May 2012
- Print publication:
- 12 April 2012, pp vi-viii
-
- Chapter
- Export citation