222 results
Research agenda for transmission prevention within the Veterans Health Administration, 2024–2028
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 April 2024, pp. 1-10
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
59 Objectively-Measured Performance on Tests of Episodic Memory and Executive Function in Autopsy-Confirmed Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society / Volume 29 / Issue s1 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 December 2023, pp. 264-265
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Strengthening self-regulation and reducing poverty to prevent adolescent depression and anxiety: Rationale, approach and methods of the ALIVE interdisciplinary research collaboration in Colombia, Nepal and South Africa
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Epidemiology and Psychiatric Sciences / Volume 32 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 December 2023, e69
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Treatment effectiveness of antibiotic therapy in Veterans with multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter spp. bacteremia
-
- Journal:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship & Healthcare Epidemiology / Volume 3 / Issue 1 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 December 2023, e230
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Investigating the association between characteristics of local crisis care systems and service use in an English national survey – CORRIGENDUM
-
- Journal:
- BJPsych Open / Volume 10 / Issue 1 / January 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 December 2023, e6
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Investigating the association between characteristics of local crisis care systems and service use in an English national survey
-
- Journal:
- BJPsych Open / Volume 9 / Issue 6 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 November 2023, e209
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Lessons from leadership transition of an AMR telementoring program to sustain laboratory capacity building in Ethiopia
-
- Journal:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship & Healthcare Epidemiology / Volume 3 / Issue S2 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 September 2023, p. s123
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
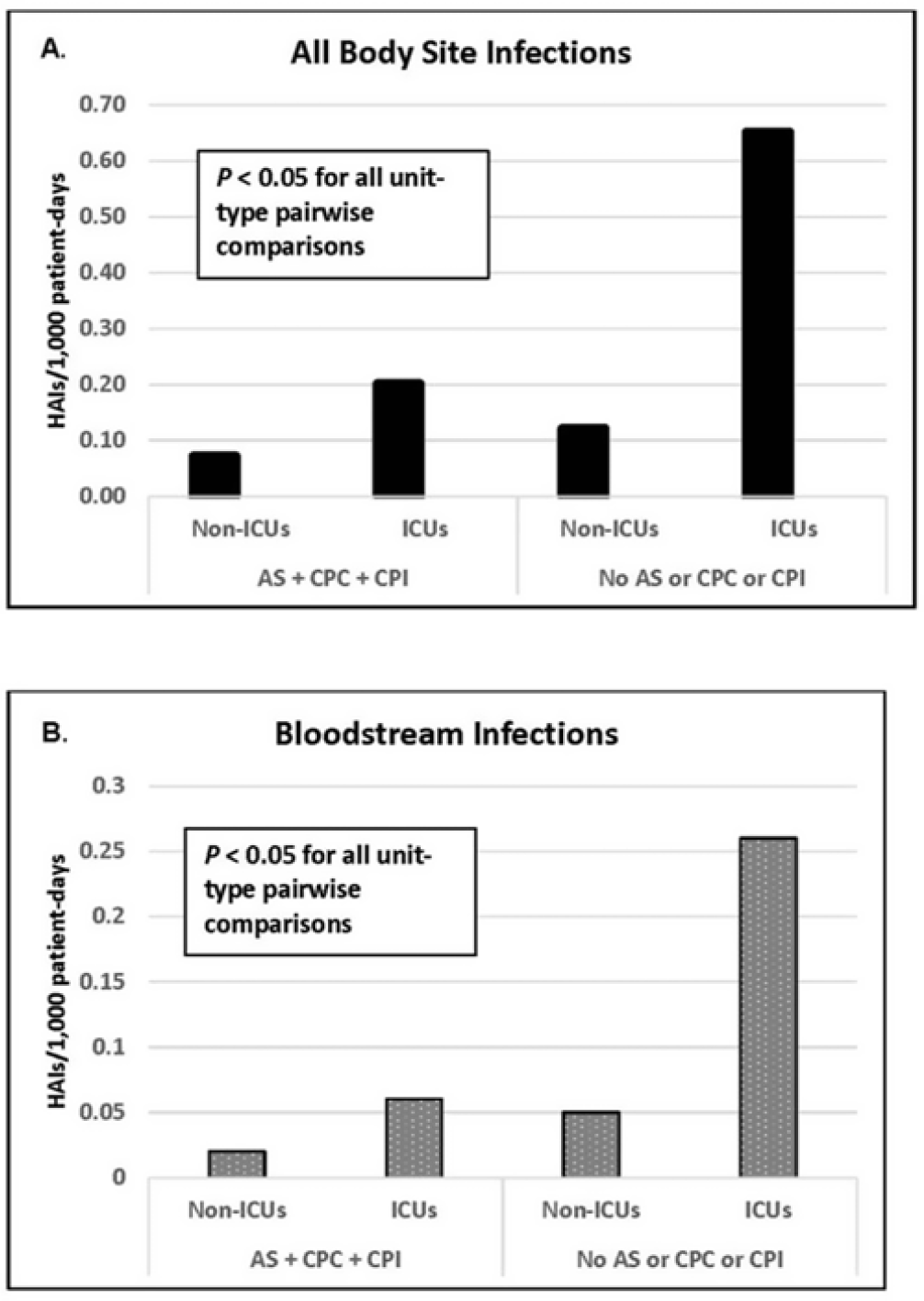
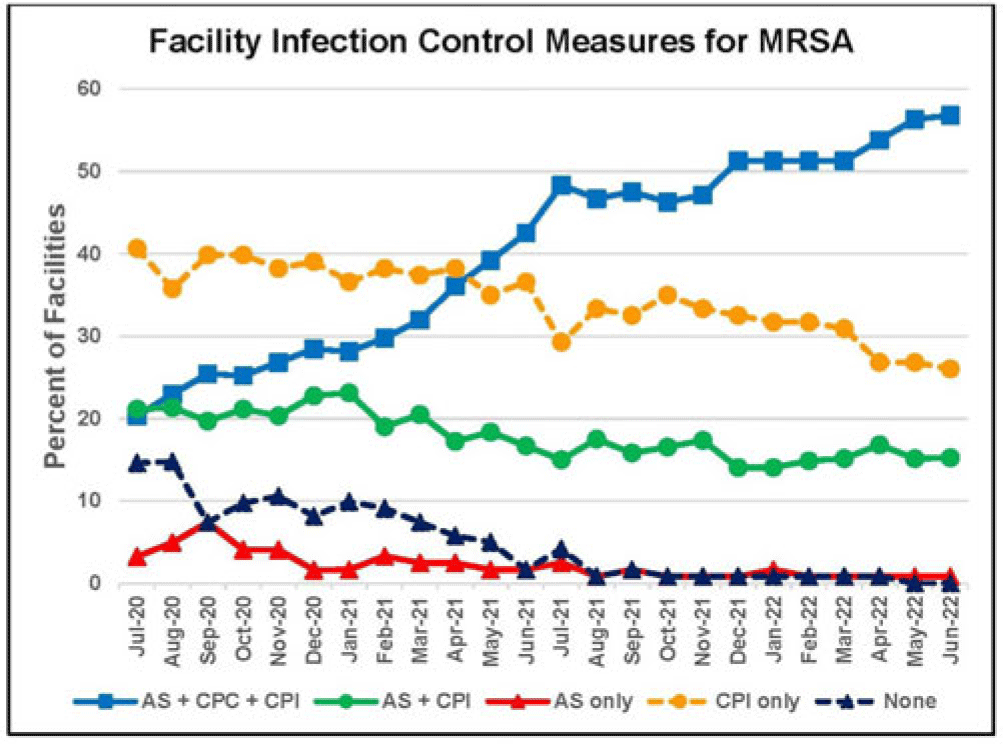
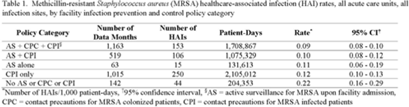
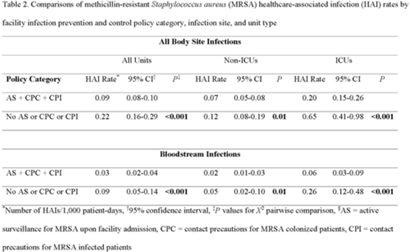
Active surveillance and contact precautions for preventing MRSA healthcare-associated infections during the COVID-19 pandemic
-
- Journal:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship & Healthcare Epidemiology / Volume 3 / Issue S2 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 September 2023, pp. s117-s118
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Increasing Registration for a VA Multidrug-Resistant Organism Alert Tool
-
- Journal:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship & Healthcare Epidemiology / Volume 3 / Issue S2 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 September 2023, pp. s124-s125
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Lessons from an evaluation of an antimicrobial resistance laboratory capacity telementoring program in Ethiopia and Kenya
-
- Journal:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship & Healthcare Epidemiology / Volume 3 / Issue S2 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 September 2023, p. s123
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
The development and validation of the Discrimination and Stigma Scale Ultra Short for People Living with Dementia (DISCUS-Dementia)
-
- Journal:
- BJPsych Open / Volume 9 / Issue 5 / September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 31 August 2023, e164
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Birds in Europe 4: the fourth assessment of Species of European Conservation Concern
-
- Journal:
- Bird Conservation International / Volume 33 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 June 2023, e66
-
- Article
- Export citation
The role of journals in supporting the socially responsible use of conservation technology
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Chapter 5 - Financing Health Care
- from Section 1 - Analyzing Health Systems: Concepts, Components, Performance
-
-
- Book:
- Making Health Systems Work in Low and Middle Income Countries
- Published online:
- 08 December 2022
- Print publication:
- 29 December 2022, pp 67-82
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Lack of correlation between standardized antimicrobial administration ratios (SAARs) and healthcare-facility–onset Clostridioides difficile infection rates in Veterans Affairs medical facilities
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 44 / Issue 6 / June 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 December 2022, pp. 945-947
- Print publication:
- June 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
The Evolutionary Map of the Universe Pilot Survey – ADDENDUM
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 39 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 November 2022, e055
-
- Article
- Export citation
Diseconomies of Scale in Quantitative and Fundamental Investment Styles
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Financial and Quantitative Analysis / Volume 58 / Issue 6 / September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 July 2022, pp. 2417-2445
- Print publication:
- September 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Increased carbapenemase testing following implementation of national VA guidelines for carbapenem-resistant Enterobacterales (CRE)
-
- Journal:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship & Healthcare Epidemiology / Volume 2 / Issue 1 / 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 June 2022, e88
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Winter Storms and Unplanned School Closure Announcements on Twitter: Comparison Between the States of Massachusetts and Georgia, 2017–2018
-
- Journal:
- Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness / Volume 17 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 April 2022, e132
-
- Article
- Export citation
Healthcare-associated infections in Veterans Affairs acute-care and long-term healthcare facilities during the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology / Volume 44 / Issue 3 / March 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 April 2022, pp. 420-426
- Print publication:
- March 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation